Abstract
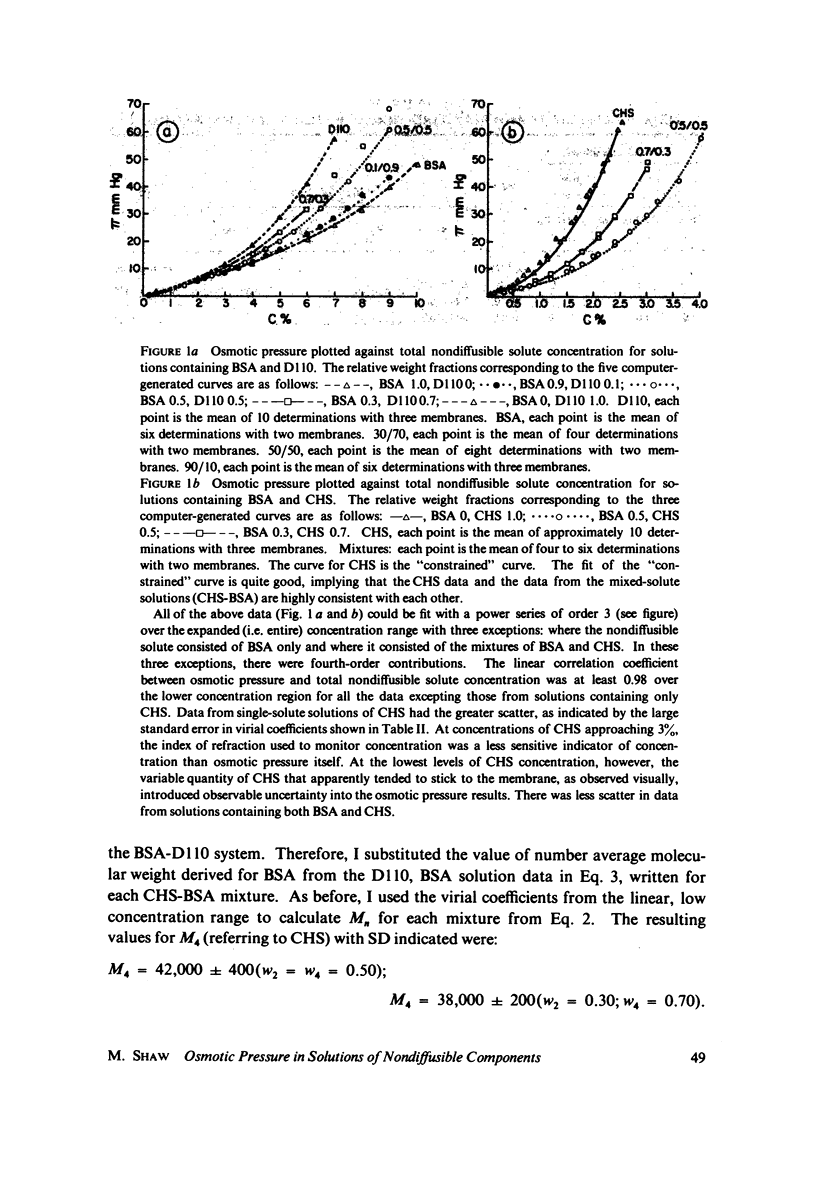
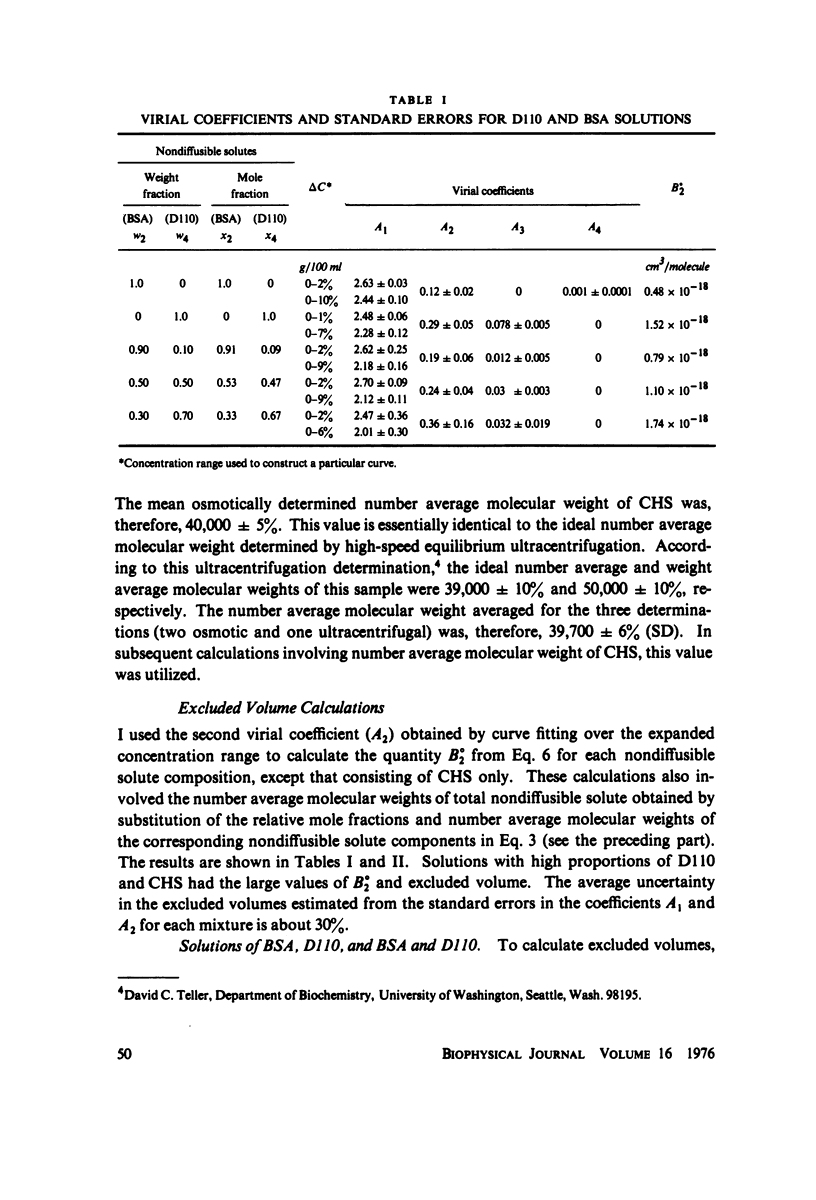
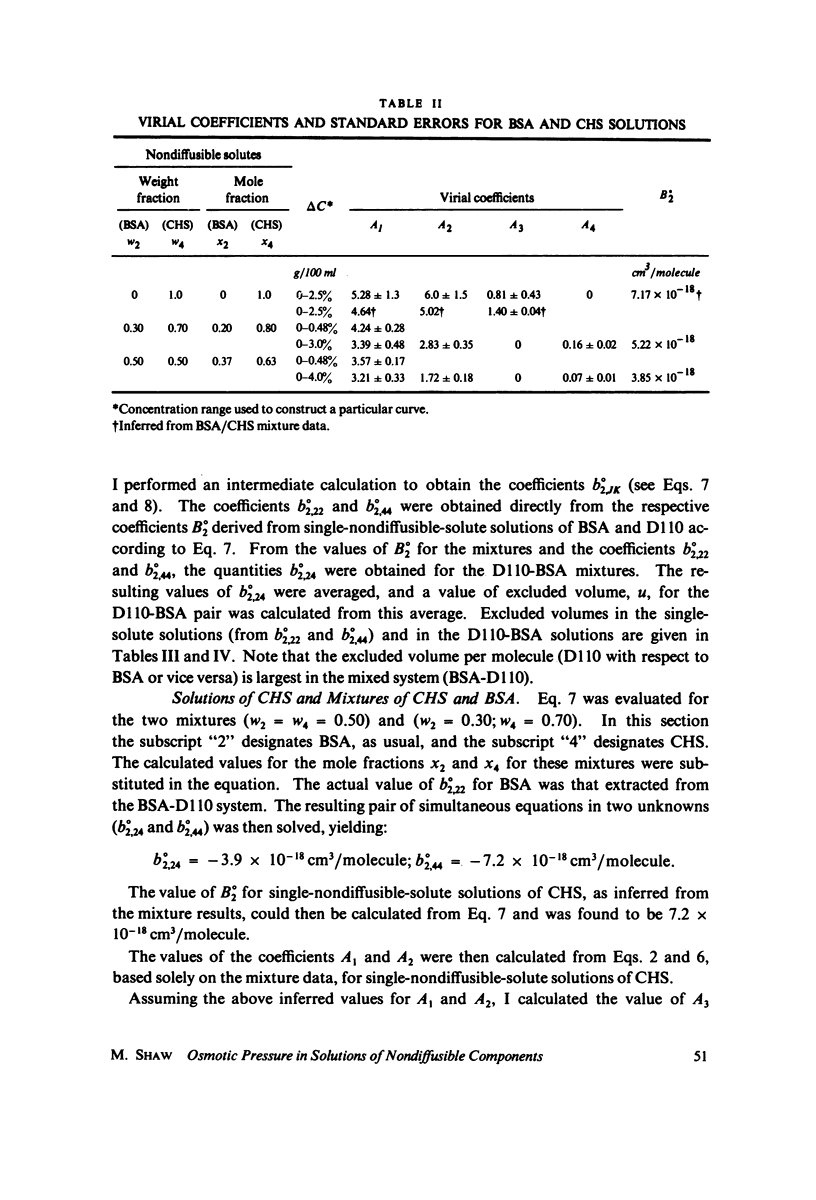
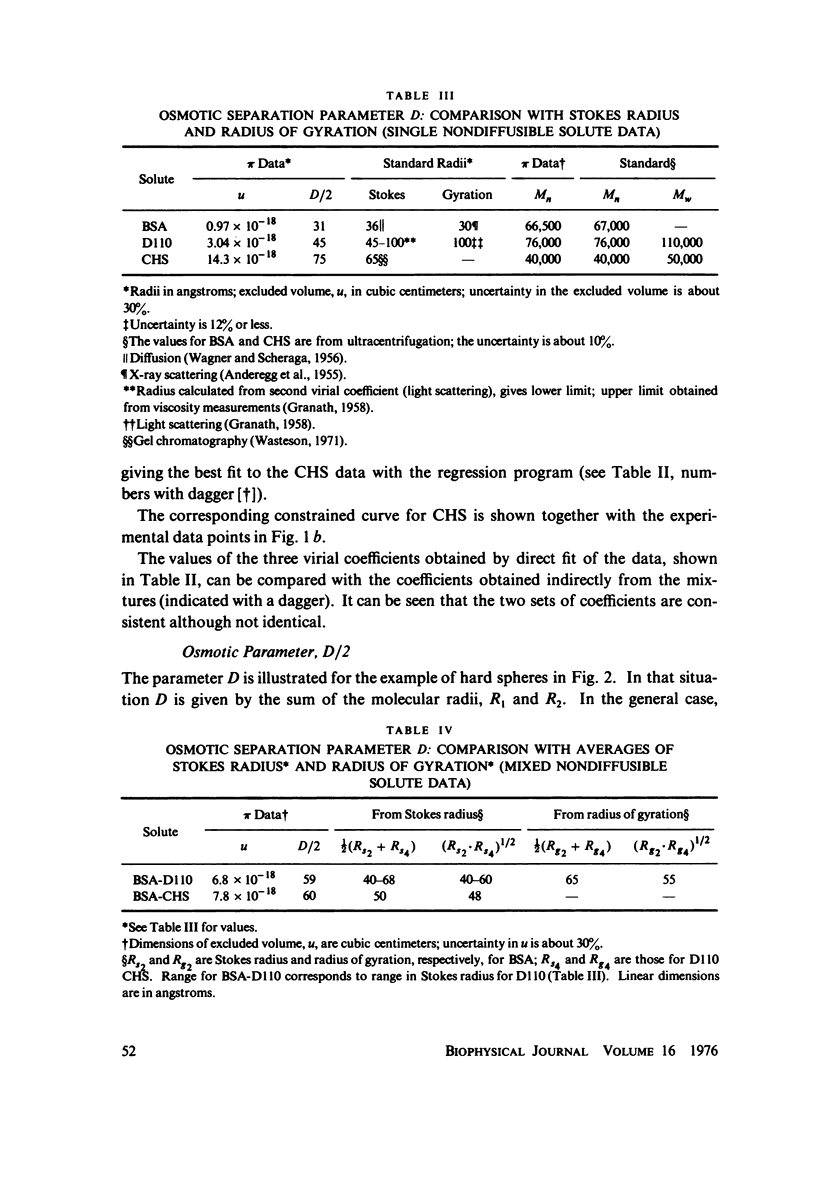
Osmotic pressure data from aqueous solutions of nondiffusible serum albumin (BSA), chondroitin sulfate (CHS), and dextran T110 (D110), taken singly and in binary combinations, were interpreted in terms of excluded volume. The principal solvent was phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.2, at 23 degrees C. Osmotic pressures were measured with a membrane osmometer fitted with Amicon PM-10 membranes. Data from each solution were fit by stepwise regression with a three- or four-term polynomial in integral powers of total nondiffusible solute concentration in accordance with the general solution theory of McMillan and Mayer (1945, J. Chem. Phys. 13:276) as extended by Yamakawa (1971, Modern Theory of Polymer Solutions, Harper & Row, New York). The date display a high internal consistency, and the results correlate well with published molecular weights and exclusion data where available. Number average molecular weights calculated from the "first virial coefficients" are: BSA, 67,000 +/- 11%; D110, 76,000 +/- 11%, CHS, 39,000 +/- 6%. Excluded volumes (in cubic centimeters per molecule) calculated from the "second virial coefficients" are: BSA, 0.97 X 10(-18); D110, 3.04 X 10(-18); CHS, 14.3 X 10(-18); BSA-D110, 6.8 X 10(-18); BSA-CHS, 7.8 X 10(-18). Uncertainty is about 30%. An empirical model for interpretation of calculated excluded volumes is proposed. It appears that CHS has the "largest" exclusion effect of the three molecules.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CASASSA E. F., EISENBERG H. THERMODYNAMIC ANALYSIS OF MULTICOMPONENT SOLUTIONS. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:287–395. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A. Properties of fractionated chondroitin sulphate from ox nasal septa. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):477–485. doi: 10.1042/bj1220477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


