Abstract
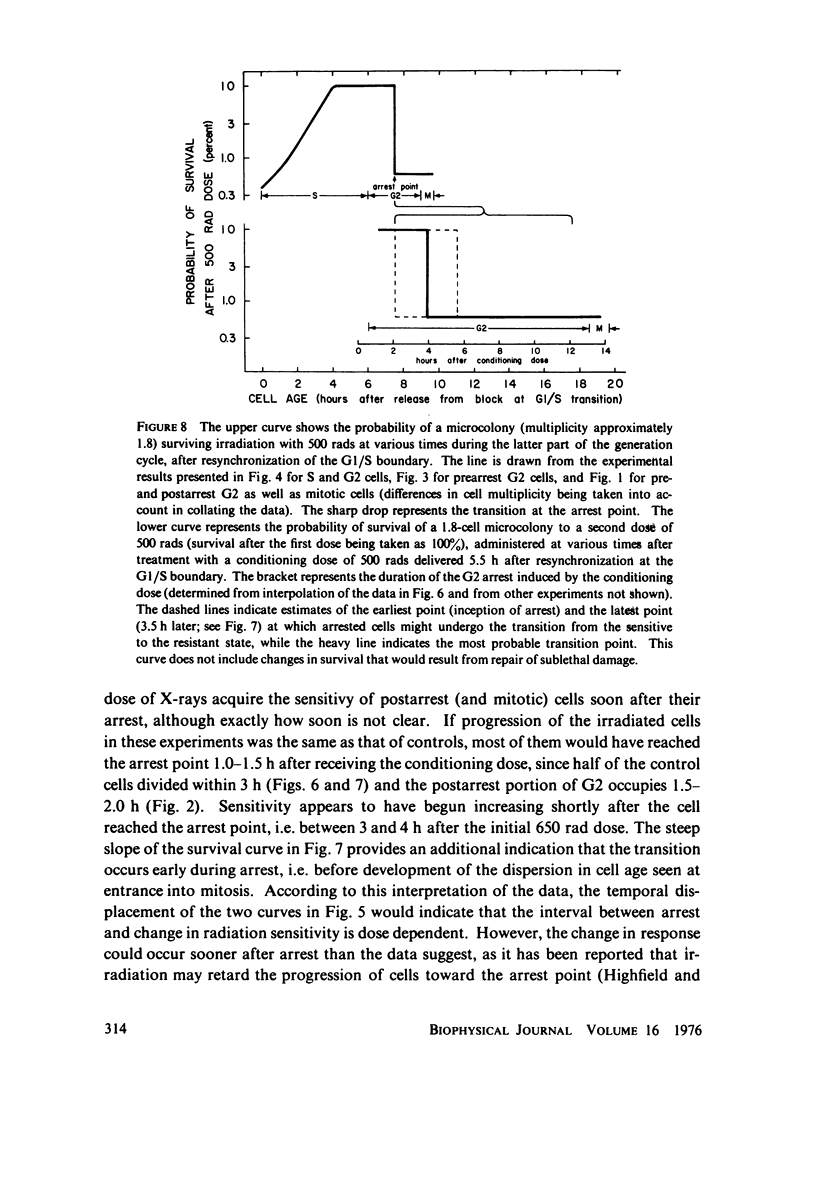
The age-response for the killing of HeLa S3 cells by X-rays during the latter part of the generation cycle has been examined in detail. As synchronous cells move from the G1/S boundary through S phase, the relatively high sensitivity of late G1 cells gradually decreases; minimum sensitivity is reached in mid-S and maintained during the remainder of that phase. The response of cells as they progress from S to the point in G2 at which they are temporarily arrested by radiation (or by inhibitors of protein synthesis) was measured in populations free of both S phase cells and late G2 cells that had passed the arrest point: cells retain their high resistance from early G2 up to the arrest point. The response of G2 cells that have passed the arrest point before being irradiated was examined by exposing randomly growing cultures to X-rays and collecting cells periodically thereafter, as they entered mitosis. Survival values very close to those of sensitive mitotic cells were found in the 2 h period after irradiation during which unarrested cells continued to reach mitosis. Values typical of lateS/early G2 were found only after cells that had been arrested began arriving at mitosis. Thus, HeLa S3 cell undergo an abrupt increase in sensitivity at or near the arrest point. The sensitivity to a second irradiation of cells arrested in G2 by a conditioning X-ray dose increases rapidly in the early part of the arrest period.
Full text
PDF


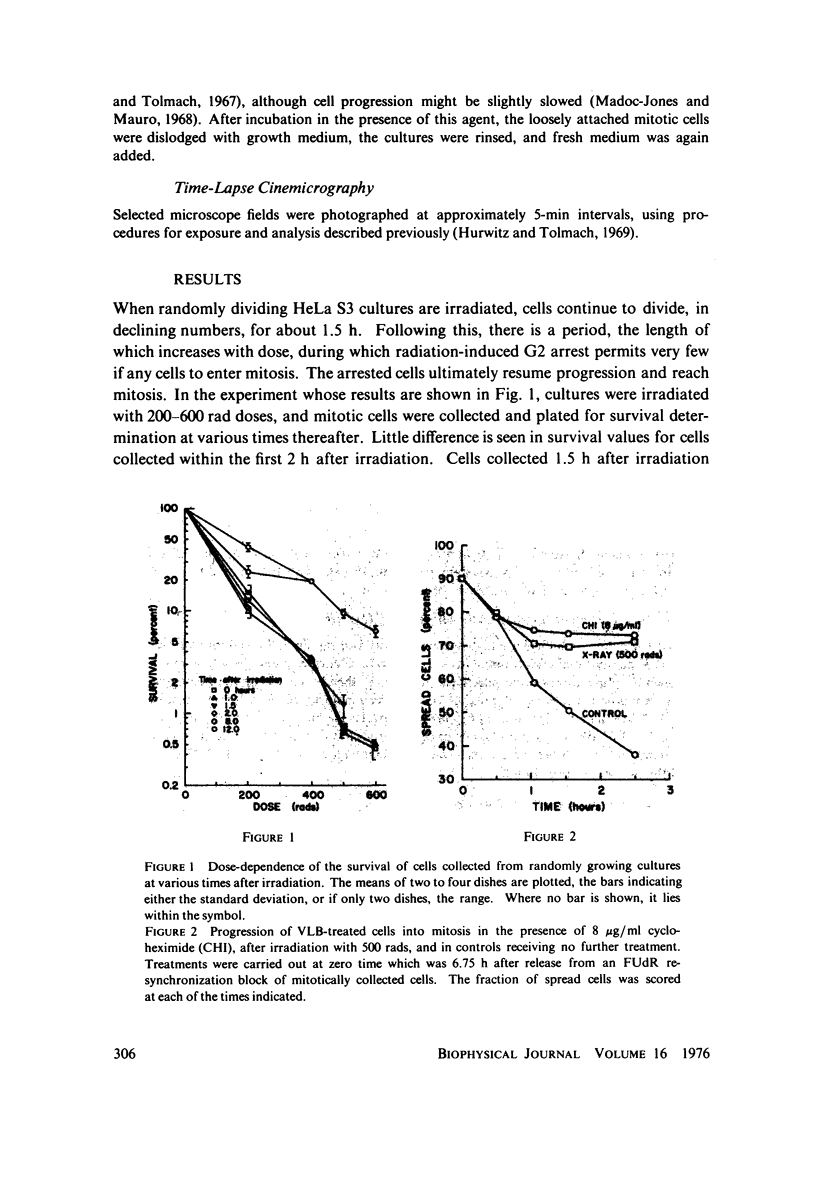


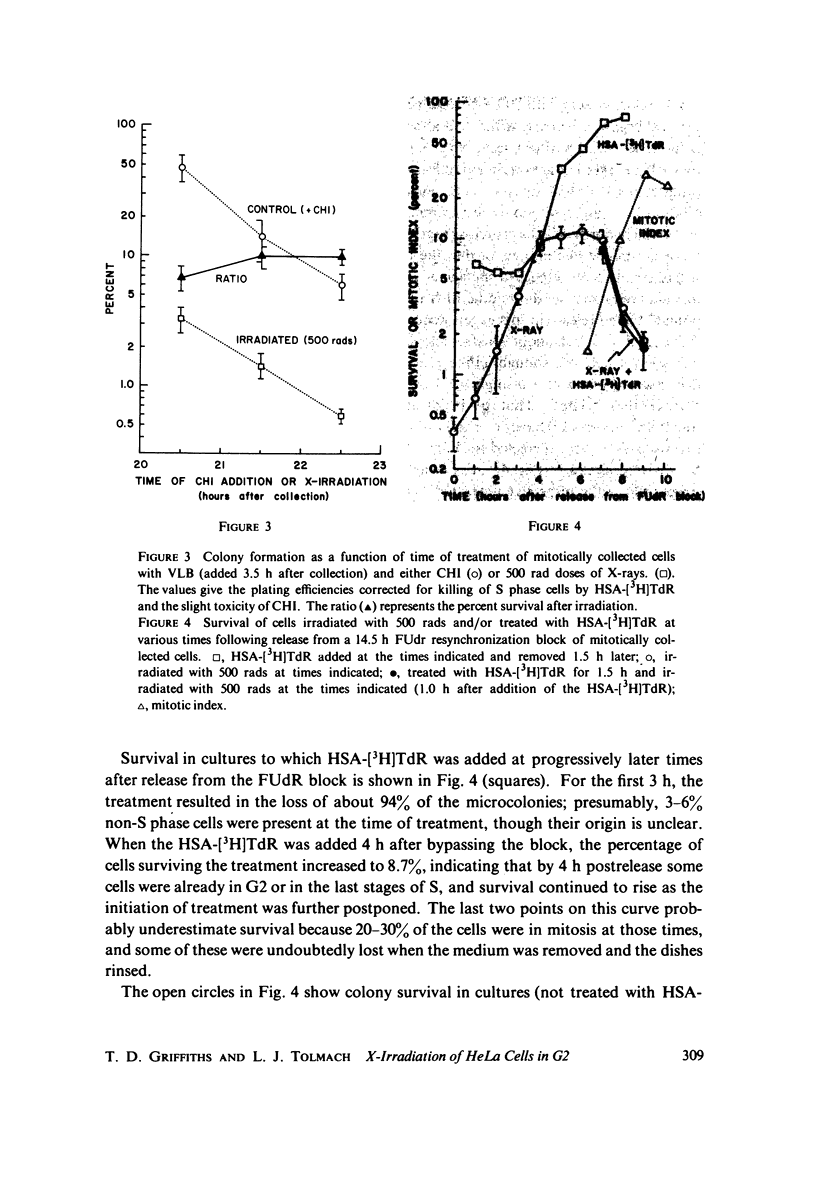

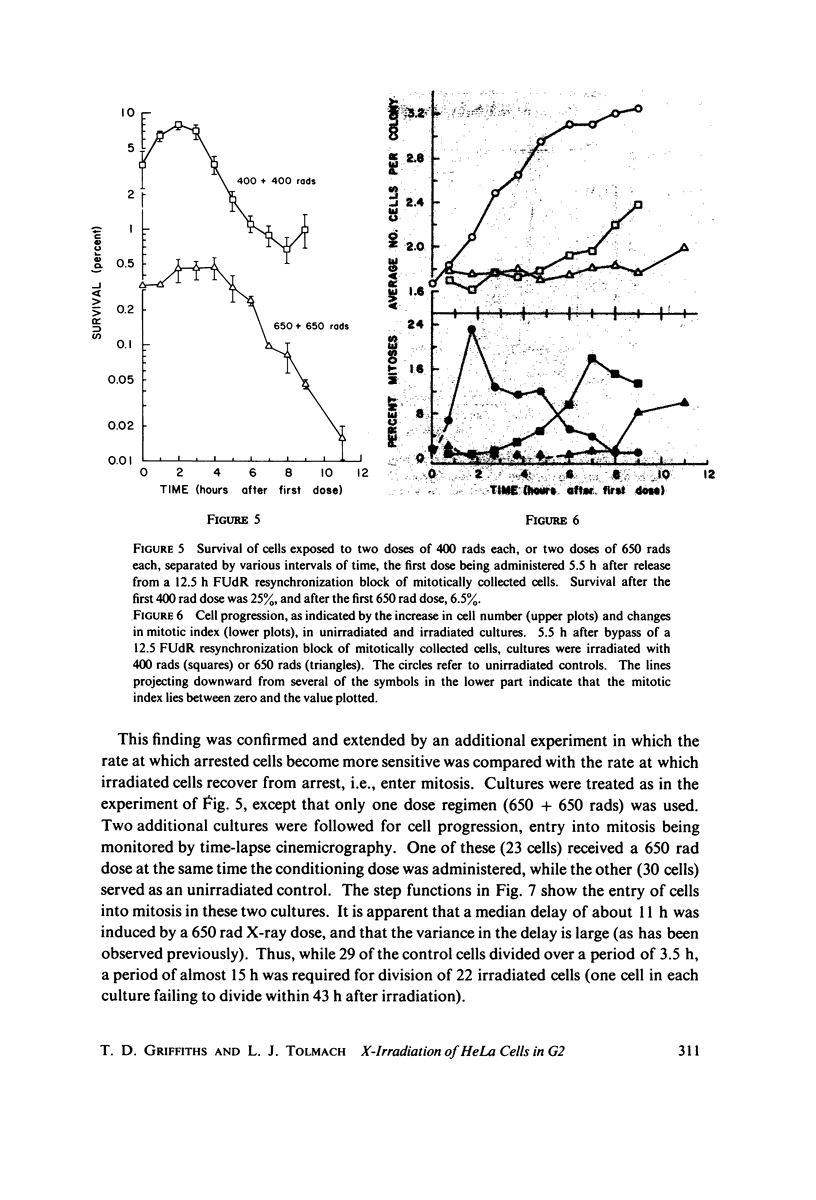
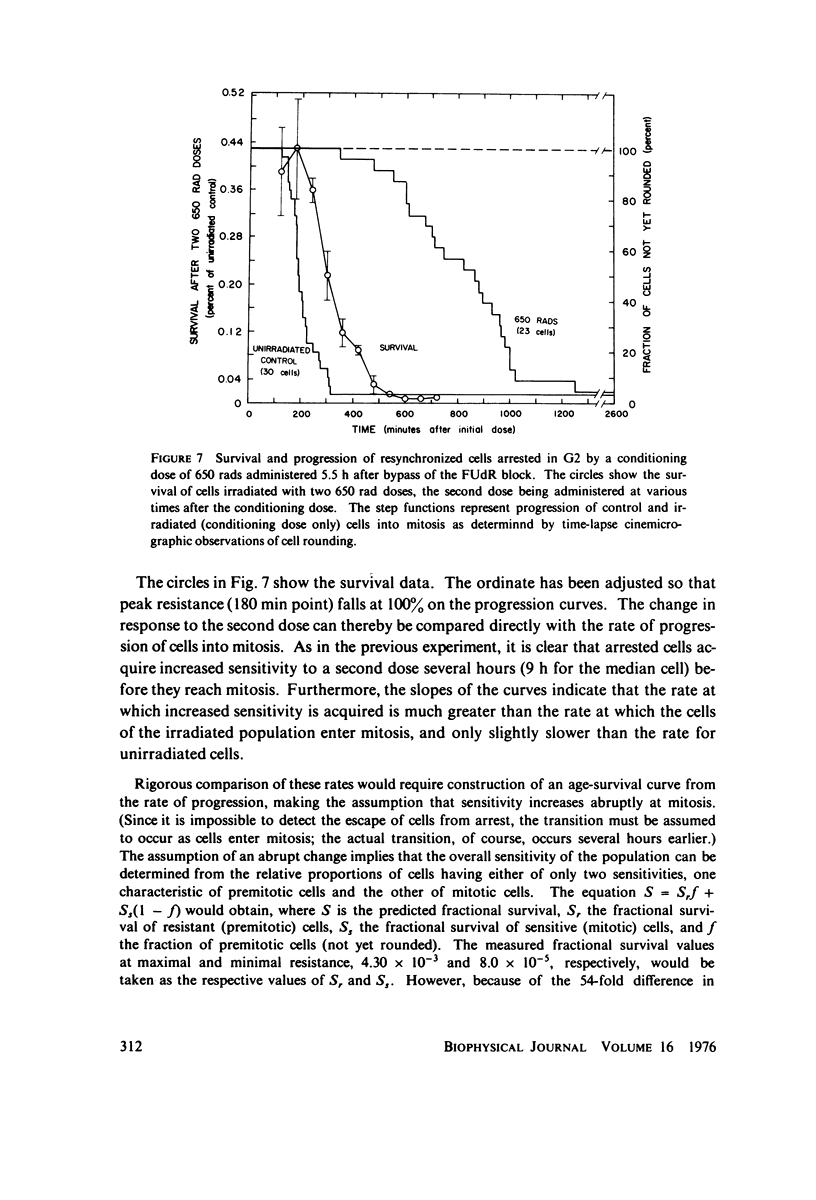





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Hur E., Elkind M. M., Bronk B. V. Thermally enhanced radioresponse of cultured Chinese hamster cells: inhibition of repair of sublethal damage and enhancement of lethal damage. Radiat Res. 1974 Apr;58(1):38–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CUTTS J. H. The effect of vincaleukoblastine on dividing cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 1961 Feb;21:168–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey W. C., Miller H. H., Leeper D. B. Chromosomal aberrations and mortality of x-irradiated mammalian cells: emphasis on repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):667–671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey W. C., Noel J. S., Dettor C. M. Changes in radiosensitivity and dispersion of chromatin during the cell cycle of synchronous Chinese hamster cells. Radiat Res. 1972 Nov;52(2):373–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic B., Tolmach L. J. X-ray sensitivity of HeLa S3 cells in the G2 phase comparison of two methods of synchronization. Biophys J. 2008 Dec 31;7(1):77–94. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86576-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELKIND M. M., SUTTON H. X-ray damage and recovery in mammalian cells in culture. Nature. 1959 Oct 24;184:1293–1295. doi: 10.1038/1841293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths T. D., Tolmach L. J. Age-dependence of the x-ray-induced deficiency in DNA synthesis in HeLa S3 cells during Generation 1. Radiat Res. 1975 Sep;63(3):501–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. An improved nutrient solution for diploid Chinese hamster and human cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Feb;29:515–526. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(63)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highfield D. P., Dewey W. C. Use of the mitotic selection procedure for cell cycle analysis: emphasis on radiation-induced mitotic delay. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):85–101. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. The oxygen requirement for recovery in split-dose experiments with Oedogonium. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1968 Nov 29;14(4):341–350. doi: 10.1080/09553006814551191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz C., Tolmach L. J. Time lapse cinemicrographic studies of x-irradiated HeLa S3 cells. I. Cell progression and cell disintegration. Biophys J. 1969 Apr;9(4):607–633. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86407-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIMBALL R. F. Postirradiation processes in the induction of recessive lethals by ionizing radiation. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1961 Dec;58(3):163–170. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030580416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl P. E., Sörenby L. A new method for the continuous selection of cells in mitosis. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Sep;43(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madoc-Jones H., Mauro F. Interphase action of vinblastine and vincristine: differences in their lethal action through the mitotic cycle of cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Dec;72(3):185–196. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER C. G., LIVENGOOD D., WARREN A. K., SIMPSON P. J., JOHNSON I. S. The action of the vincaleukolastine on mitosis in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1960 Jun;20:198–201. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(60)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., STEFFEN J. LIFE CYCLE ANALYSIS OF MAMMALIAN CELLS. I. A METHOD FOR LOCALIZING METABOLIC EVENTS WITHIN THE LIFE CYCLE, AND ITS APPLICATION TO THE ACTION OF COLCEMIDE AND SUBLETHAL DOSES OF X-IRRADIATION. Biophys J. 1963 Sep;3:379–397. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86828-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S. E., Tolmach L. J. Selecting synchronous populations of mammalian cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 14;213(5072):139–142. doi: 10.1038/213139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. A., Tolmach L. J. Repair of potentially lethal damage in x-irradiated HeLa cells. Radiat Res. 1966 Nov;29(3):413–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockwell S., Kallman R. F. Cyclic radiation-induced variations in cellular radiosensitivity in a mouse mammary tumor. Radiat Res. 1974 Jan;57(1):132–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sax K. The Time Factor in X-Ray Production of Chromosome Aberrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1939 May;25(5):225–233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.25.5.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair W. K. Cyclic x-ray responses in mammalian cells in vitro. Radiat Res. 1968 Mar;33(3):620–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair W. K., Morton R. A. X-ray sensitivity during the cell generation cycle of cultured Chinese hamster cells. Radiat Res. 1966 Nov;29(3):450–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward P. G., Hahn G. M. The application of age response functions to the optimization of treatment schedules. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1971 May;4(3):279–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1971.tb01539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Changes in x-ray sensitivity of HeLa cells during the division cycle. Nature. 1961 Jun 24;190:1210–1211. doi: 10.1038/1901210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Growth and nucleic acid synthesis in synchronously dividing populations of HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Apr;30:344–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. Variations in several responses of HeLa cells to x-irradiation during the division cycle. Biophys J. 1963 Jan;3:11–33. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(63)86801-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERASIMA T., TOLMACH L. J. X-ray sensitivity and DNA synthesis in synchronous populations of HeLa cells. Science. 1963 May 3;140(3566):490–492. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3566.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolmach L. J., Weiss B. G., Hopwood L. E. Ionizing radiations and the cell cycle. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1742–1751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters R. A., Burchill B. R., Petersen D. F. Radiosensitivity of mammalian cells. 3. Effect of suboptimal growth temperatures on recovery from radiation-induced division delay. Biophys J. 1969 Nov;9(11):1323–1328. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(69)86454-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters R. A., Petersen D. F. Radiosensivity of mammalian cells. I. Timing and dose-dependence of radiation-induced division delay. Biophys J. 1968 Dec;8(12):1475–1486. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(68)86567-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore G. F., Gulyas S. Synchronization of mammalian cells with tritiated thymidine. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):691–694. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


