Abstract
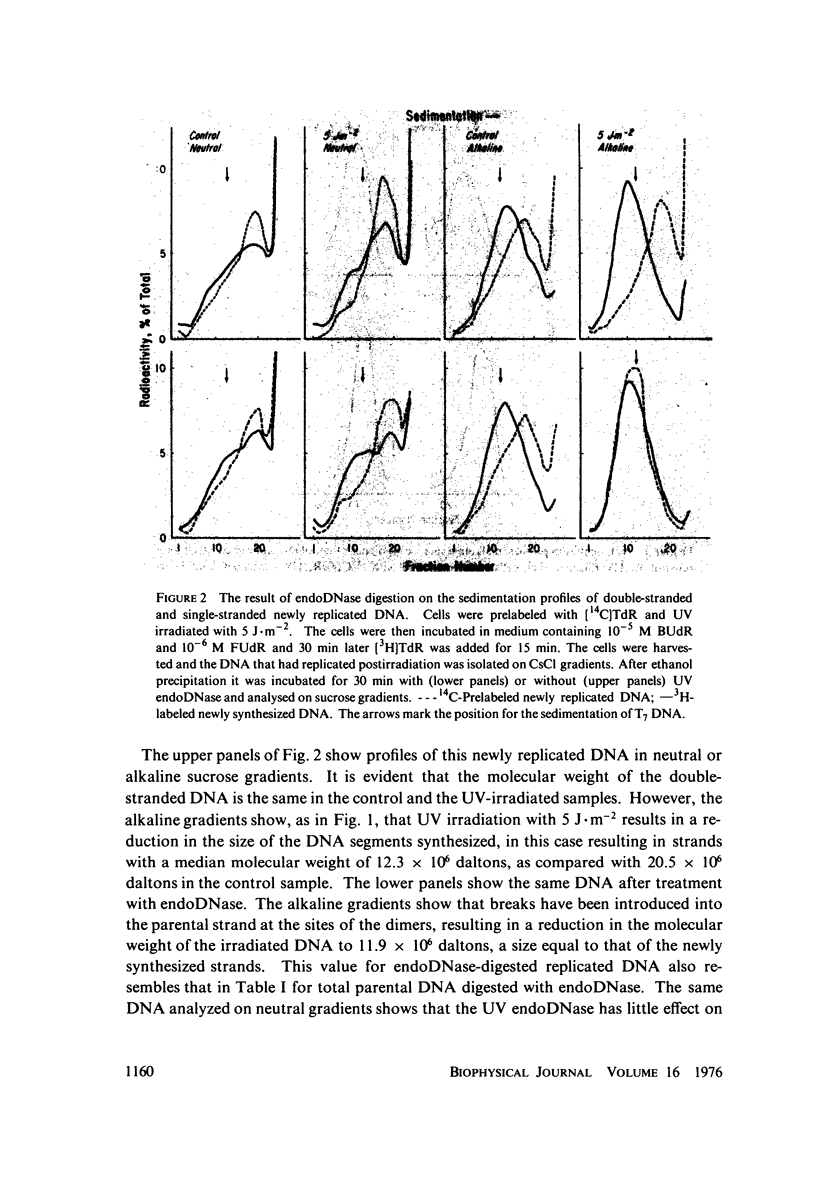
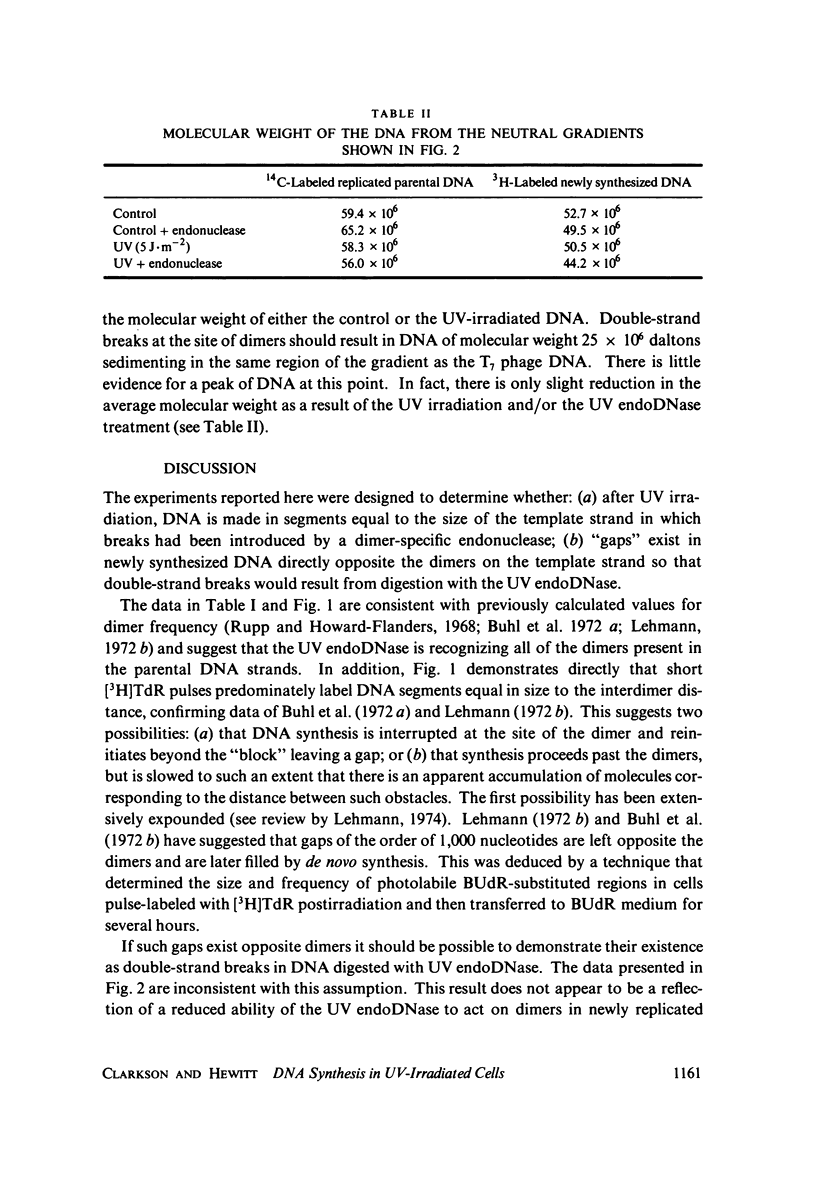
DNA synthesized after UV irradiation is smaller than that in unirradiated cells even when pulse-labeling times are increased to compensate for the overall reduction in the rate of DNA replication. By isolating newly replicated DNA, incubating it with dimer-specific endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus, and analyzing it on alkaline sucrose gradients, we have been able to demonstrate that this DNA is synthesized in segments corresponding in size to the interdimer distance on the parental strand. In addition, the same DNA analyzed on neutral gradients shows no reduction in molecular weight as a result of UV irradiation and/or endonuclease digestion. Our data are thus inconsistent with the presence of "gaps" in newly synthesized DNA opposite the dimers on the parental strand. We suggest that if such gaps are produced as a result of delayed synthesis around dimers, they are filled before the growing point reaches the next dimer.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buhl S. N., Regan J. D. Repair endonuclease-sensitive sites in daughter DNA of ultraviolet-irradiated human cells. Nature. 1973 Dec 21;246(5434):484–484. doi: 10.1038/246484a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. DNA repair in Potorous tridactylus. Biophys J. 1974 Oct;14(10):791–803. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85949-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. Steps in DNA chain elongation and joining after ultra-violet irradiation of human cells. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1972 Nov;22(5):417–424. doi: 10.1080/09553007214551301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhl S. N., Stillman R. M., Setlow R. B., Regan J. D. DNA chain elongation and joining in normal human and xeroderma pigmentosum cells after ultraviolet irradiation. Biophys J. 1972 Sep;12(9):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86154-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. F., Rauth A. M. Nascent DNA synthesis in ultraviolet light-irradiated mouse L cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 31;259(2):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90056-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Thomas G. H. Single strand interruptions in DNA and the effects of caffeine in Chinese hamster cells irradiated with ultraviolet light. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 23;36(2):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90315-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freifelder D. Molecular weights of coliphages and coliphage DNA. IV. Molecular weights of DNA from bacteriophages T4, T5 and T7 and the general problem of determination of M. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Kondo T. Caffeine-sensitive repair of ultraviolet light-damaged DNA of mouse L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 12;47(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90915-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan A. K. Persistence of pyrimidine dimers during post-replication repair in ultraviolet light-irradiated Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jul 25;87(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi J. R., Kern R. M., Painter R. B. Modification of replicon operation in HeLa cells by 2,4-dinitrophenol. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 5;80(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. C., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Enzymatic repair of DNA. 3. Properties of the UV-endonuclease and UV-exonuclease. Biochemistry. 1971 Aug 31;10(18):3315–3324. doi: 10.1021/bi00794a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R. Post-replication repair of DNA in ultraviolet-irradiated mammalian cells. No gaps in DNA synthesized late after ultraviolet irradiation. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 18;31(3):438–445. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02550.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R. Postreplication repair of DNA in ultraviolet-irradiated mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R., Stevens S. Postreplication repair of DNA in chick cells: studies using photoreactivation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 21;402(2):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lett J. T., Klucis E. S., Sun C. On the size of the DNA in the mammalian chromosome. Structural subunits. Biophys J. 1970 Mar;10(3):277–292. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86300-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini R. Gaps in DNA synthesized by ultraviolet light-irradiated WI38 human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini R., Hanawalt P. T4-endonuclease V-sensitive sites in DNA from ultraviolet-irradiated human cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 2;425(4):428–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn R. E., Hewitt R. R., Thomas L. F., Humphrey R. M. Effects of ultraviolet irradiation on the rate and sequence of DNA replication in synchronized Chinese hamster cells. Biophys J. 1976 May;16(5):517–525. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85706-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn R. E., Humphrey R. M. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in ultraviolet-light-irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Biophys J. 1971 Mar;11(3):295–301. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(71)86215-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyn R. E., Vizard D. L., Hewitt R. R., Humphrey R. M. The fate of pyrimidine dimers in the DNA of ultraviolet-irradiated Chinese hamster cells. Photochem Photobiol. 1974 Sep;20(3):221–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1974.tb06570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll H. Characterization of macromolecules by constant velocity sedimentation. Nature. 1967 Jul 22;215(5099):360–363. doi: 10.1038/215360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Painter R. B. DNA damage and repair in eukaryotic cells. Genetics. 1974 Sep;78(1):139–148. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Lohman P. H., Sluyter M. L. Use of UV endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus to monitor the progress of DNA repair in UV-irradiated human cells. Mutat Res. 1973 Aug;19(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. D., Trosko J. E., Carrier W. L. Evidence for excision of ultraviolet-induced pyrimidine dimers from the DNA of human cells in vitro. Biophys J. 1968 Mar;8(3):319–325. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86490-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Reno D. L., Howard-Flanders P. Exchanges between DNA strands in ultraviolet-irradiated Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):25–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward D. L., Humphrey R. M. Induction of thymine dimers in synchronized populations of Chinese hamster cells. Nature. 1966 Oct 15;212(5059):298–300. doi: 10.1038/212298b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


