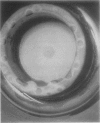
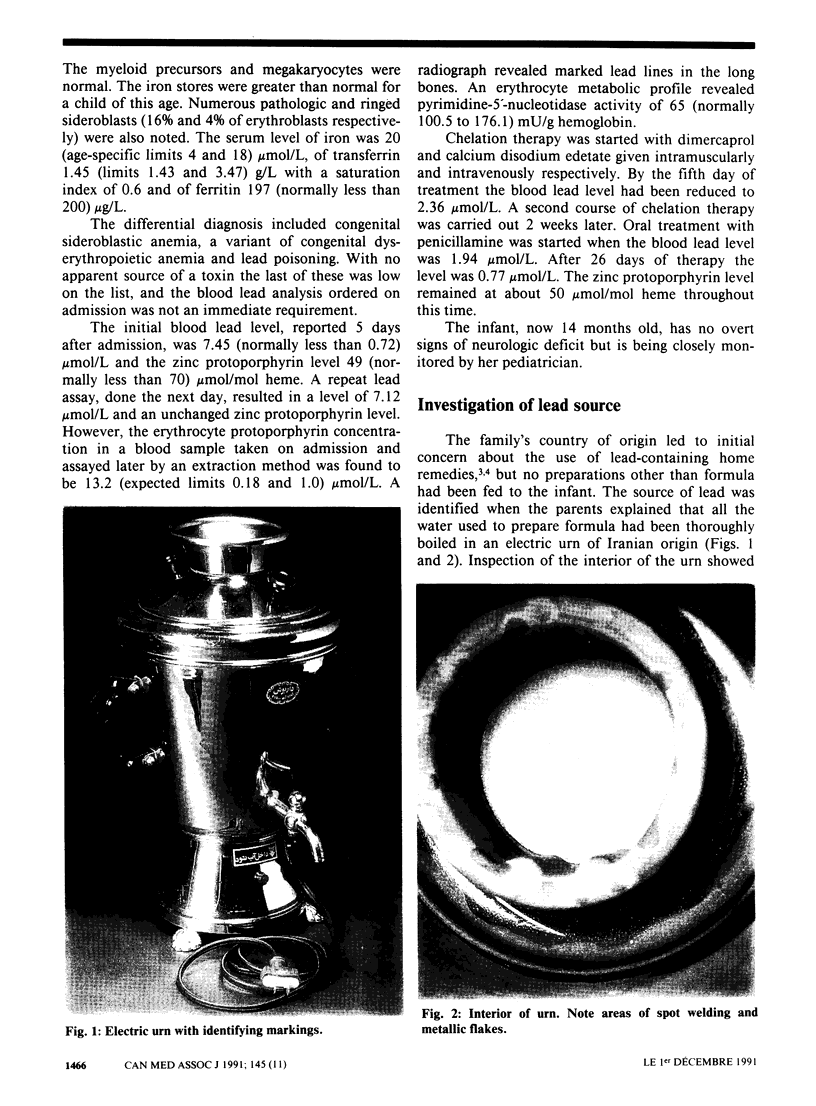
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdullah M. A. Lead poisoning among children in Saudi Arabia. J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Apr;87(2):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali A. R., Smales O. R., Aslam M. Surma and lead poisoning. Br Med J. 1978 Sep 30;2(6142):915–916. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6142.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg W. E., Eisinger J., Lamola A. A., Zuckerman D. M. Zinc protoporphyrin level in blood determined by a portable hematofluorometer: a screening device for lead poisoning. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Apr;89(4):712–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg A., Avni A., Grauer F., Weissenberg E., Acker C., Hamdallah M., Shahin S., Moreb J., Hershko C. Identification of community flour mills as the source of lead poisoning in West Bank Arabs. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Oct;145(10):1848–1851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. A., Weinberger H. L. Six children with lead poisoning. Am J Dis Child. 1990 Sep;144(9):1039–1044. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1990.02150330099031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada K., Miura H. Free erythrocyte protoporphyrin (FEP) and zinc protoporphyrin (ZnP) as biological parameters for lead poisoning. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1984;53(4):365–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00380676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. E., Lockitch G., Quigley G. Improved sample preparation for accurate determination of low concentrations of lead in whole blood by graphite furnace analysis. Clin Chem. 1991 Apr;37(4):515–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M., Namer R., Harpur E., Corbin R. Earthenware containers as a source of fatal lead poisoning. N Engl J Med. 1970 Sep 24;283(13):669–672. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009242831302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamola A. A., Yamane T. Zinc protoporphyrin in the erythrocytes of patients with lead intoxication and iron deficiency anemia. Science. 1974 Dec 6;186(4167):936–938. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4167.936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Martin D. J. Lead poisoning from lead-soldered electric kettles. Can Med Assoc J. 1977 Mar 5;116(5):508-9, 512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orfanos A. P., Guthrie R., Jinks D. C., Vollmer D. W. Simultaneous assay of zinc protoporphyrin and protoporphyrin IX in dried blood. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 May 15;181(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piomelli S. Free erythrocyte porphyrins in the detection of undue absorption of Pb and of Fe deficiency. Clin Chem. 1977 Feb;23(2 Pt 1):264–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh-Fitzpatrick M. B., Piomelli S., Young P., Hsu H., Harber L. C. Rapid quantitative assay for erythrocyte porphyrins. Arch Dermatol. 1974 Aug;110(2):225–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman H., Al Khayat A., Menon N. Lead poisoning in infancy--unusual causes in the U.A.E. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1986 Sep;6(3):213–217. doi: 10.1080/02724936.1986.11748442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton N. V., Gunter E. W., Parsons P. J., Field P. H. Empirically determined lead-poisoning screening cutoff for the Protofluor-Z hematofluorometer. Clin Chem. 1989 Oct;35(10):2104–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenenbein M. Does lead poisoning occur in Canadian children? CMAJ. 1990 Jan 1;142(1):40–41. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. P. An interlaboratory comparison programme for several toxic substances in blood and urine. Sci Total Environ. 1988 Apr;71(1):111–123. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(88)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]