Abstract
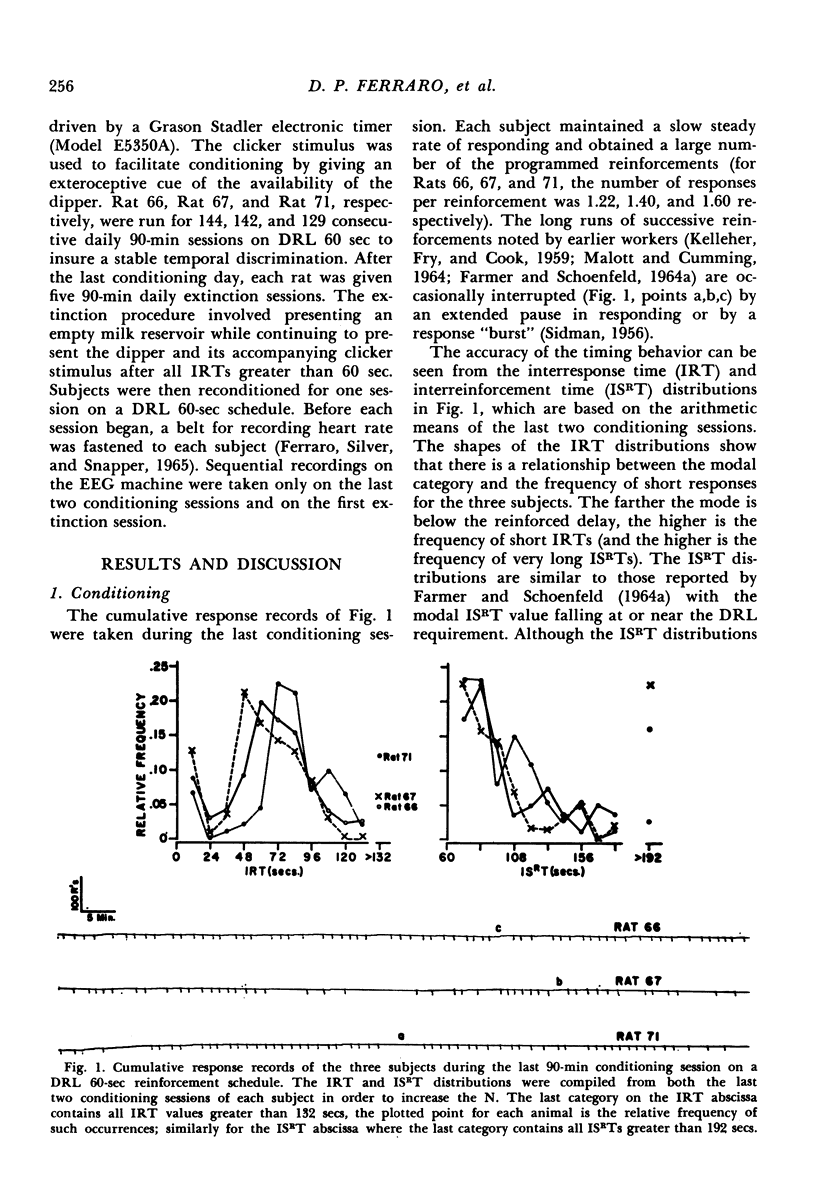
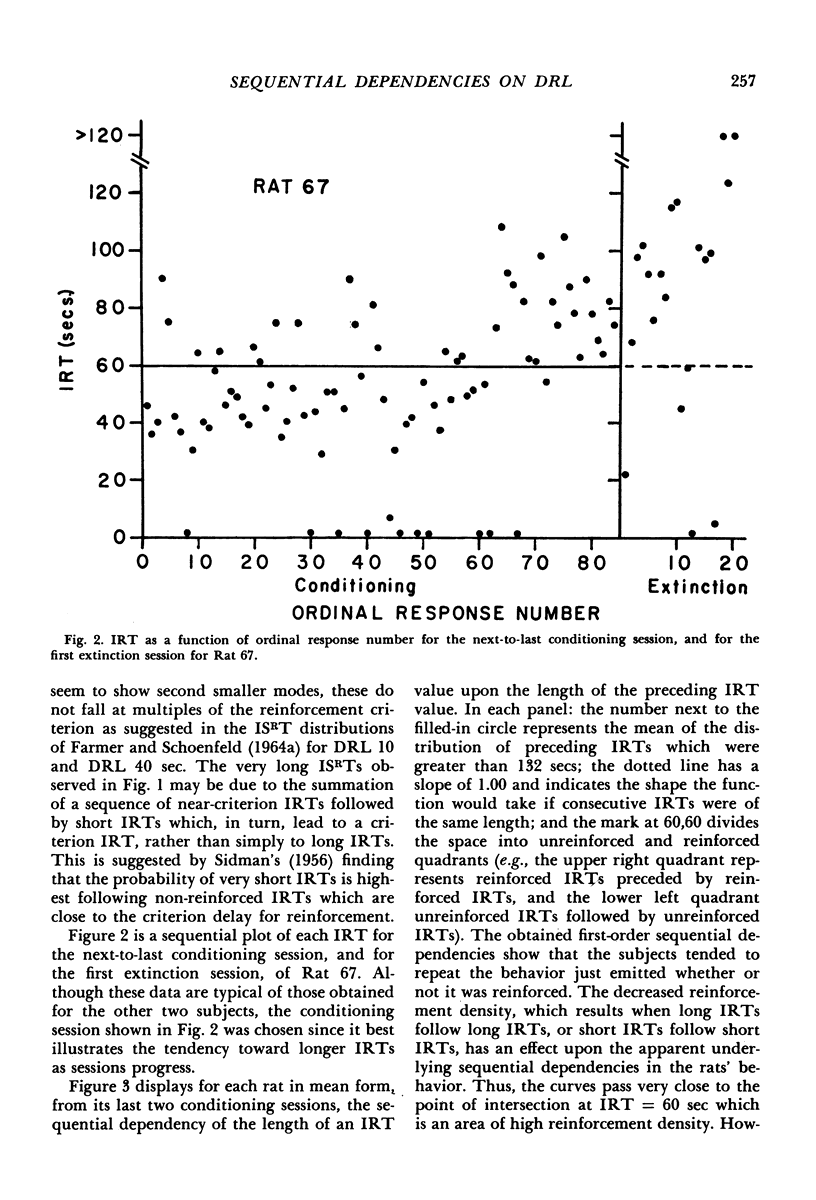
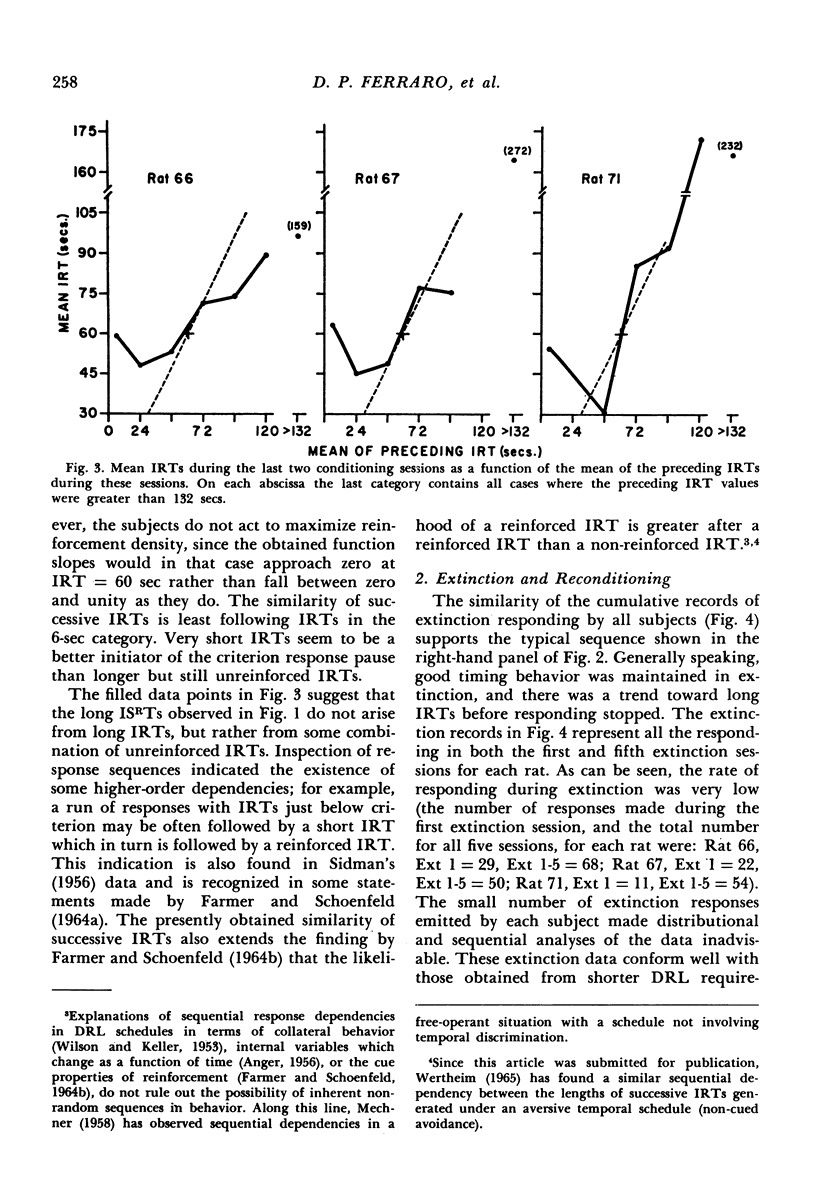
Sequential IRT data were obtained for three rats on a DRL 60-sec reinforcement schedule. It was found that first-order sequential dependencies exist under this schedule, including the partial dependence of the length of any given IRT on the length of the preceding IRT. The sequential analysis also served to extend the finding in the literature, based on frequency distributions, that the likelihood of a reinforced IRT is greater after a reinforced IRT than a non-reinforced IRT. Rapid extinction and reconditioning were obtained.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITTERMAN M. E., FEDDERSEN W. E., TYLER D. W. Secondary reinforcement and the discrimination hypothesis. Am J Psychol. 1953 Jul;66(3):456–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J., SCHOENFELD W. N. EFFECTS OF A DRL CONTINGENCY ADDED TO A FIXED-INTERVAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Nov;7:391–399. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J., SCHOENFELD W. N. INTER-REINFORCEMENT TIMES FOR THE BAR-PRESSING RESPONSE OF WHITE RATS ON TWO DRL SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:119–122. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERRARO D. P., SILVER M. P., SNAPPER A. G. A METHOD FOR CARDIAC RECORDING FROM SURFACE ELECTRODES IN THE RAT DURING FREE-OPERANT PROCEDURES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jan;8:17–18. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., FRY W., COOK L. Inter-response time distribution as a function of differential reinforcement of temporally spaced responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Apr;2:91–106. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS D. J., DUNCAN C. P. Expectation and resistance to extinction of a leverpulling response as a function of percentage of reinforcement and number of acquisition trials. J Exp Psychol. 1958 Feb;55(2):121–128. doi: 10.1037/h0046622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechner F. Sequential dependencies of the lengths of consecutive response runs. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Aug;1(3):229–233. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. ACCURATE AND RAPID RECONDITIONING OF SPACED RESPONDING. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 May;7:273–275. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Time discrimination and behavioral interaction in a free operant situation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Oct;49(5):469–473. doi: 10.1037/h0041892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERTHEIM G. A. SOME SEQUENTIAL ASPECTS OF IRTS EMITTED DURING SIDMAN-AVOIDANCE BEHAVIOR IN THE WHITE RAT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jan;8:9–15. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. P., KELLER F. S. On the selective reinforcement of spaced responses. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1953 Jun;46(3):190–193. doi: 10.1037/h0057705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. P. Periodic reinforcement interval and number of periodic reinforcements as parameters of response strength. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1954 Feb;47(1):51–56. doi: 10.1037/h0057224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



