Abstract
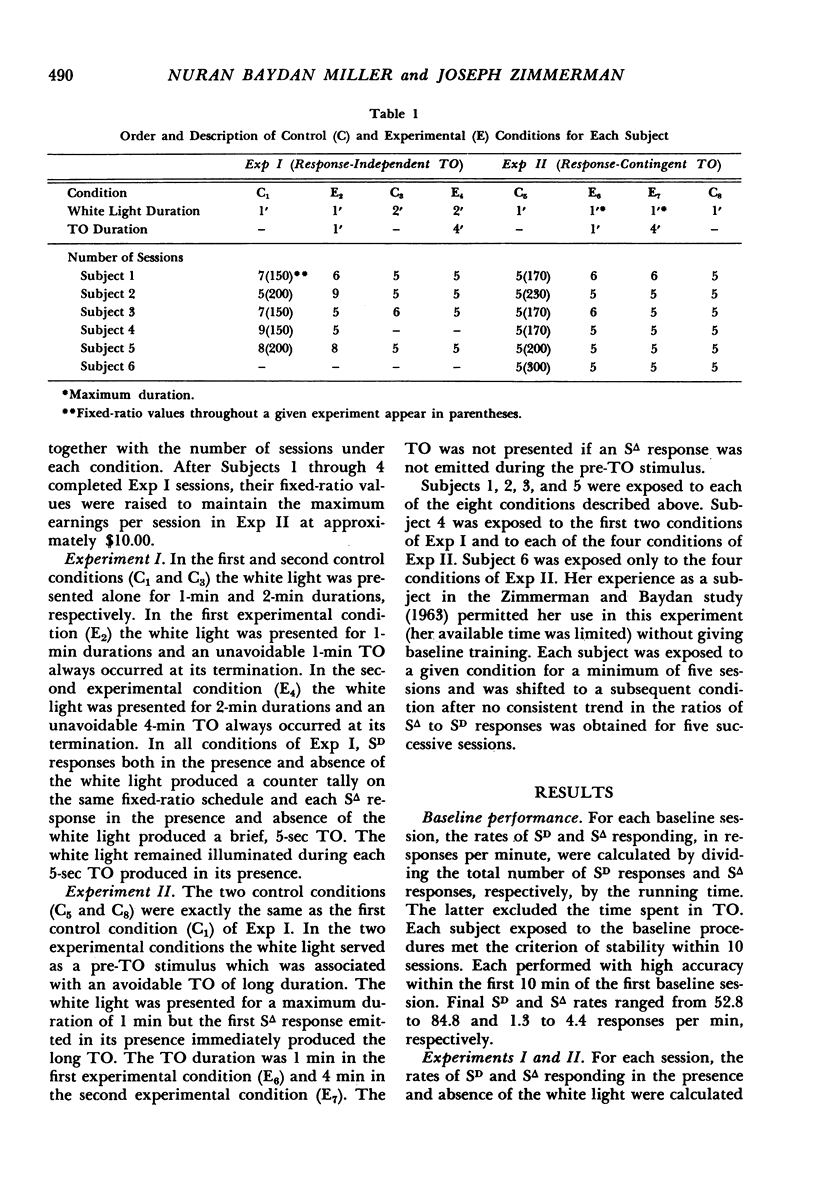
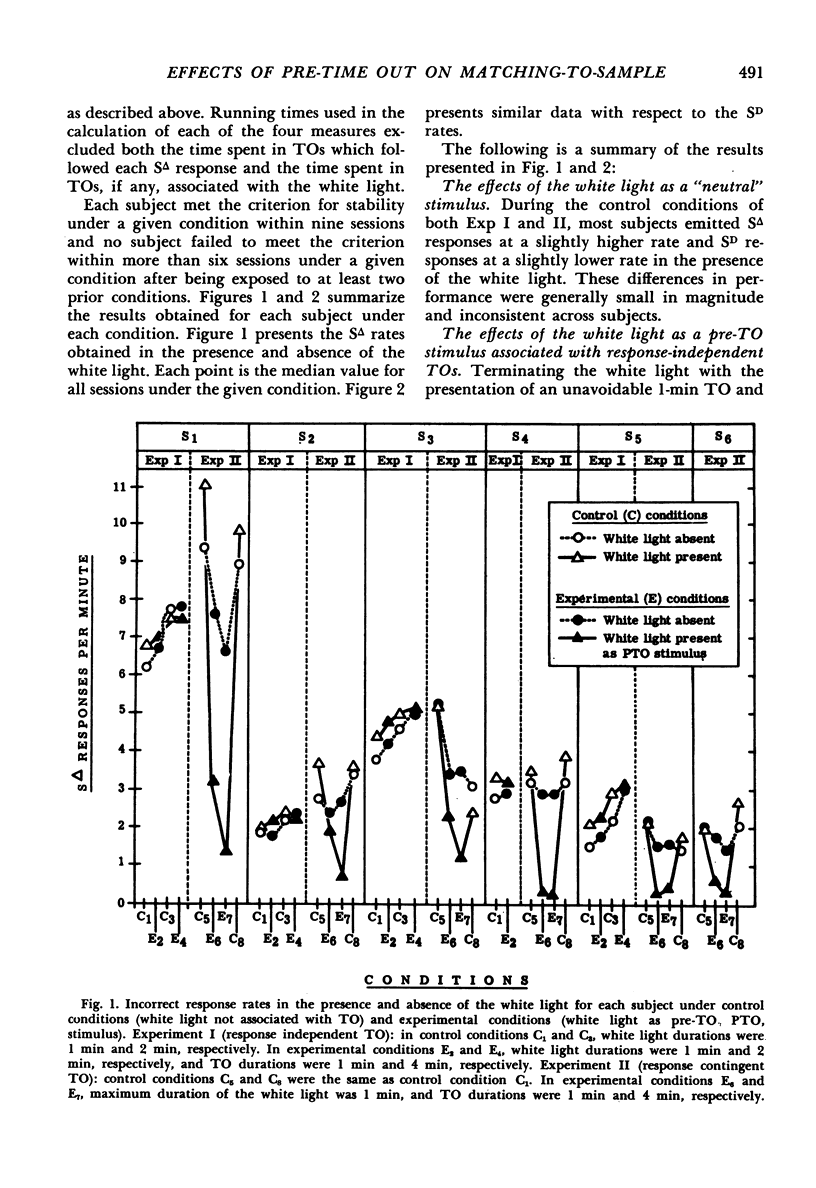
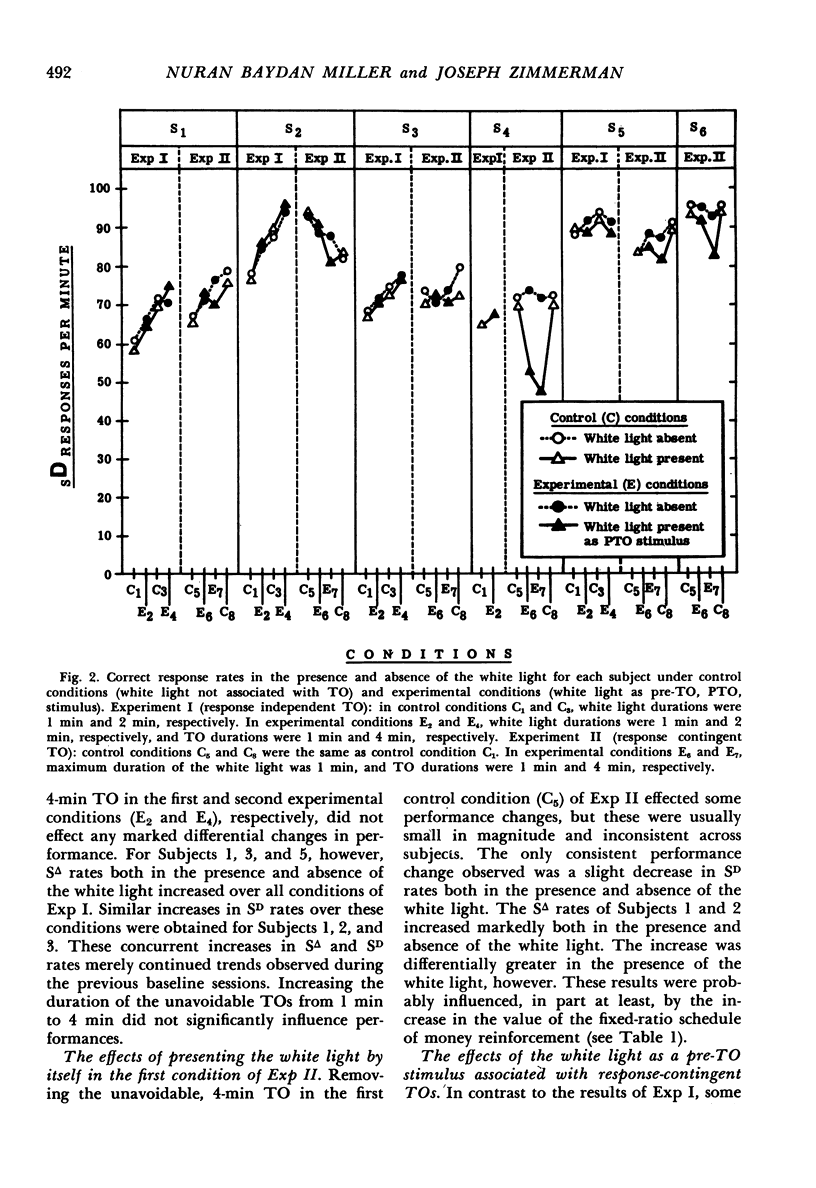
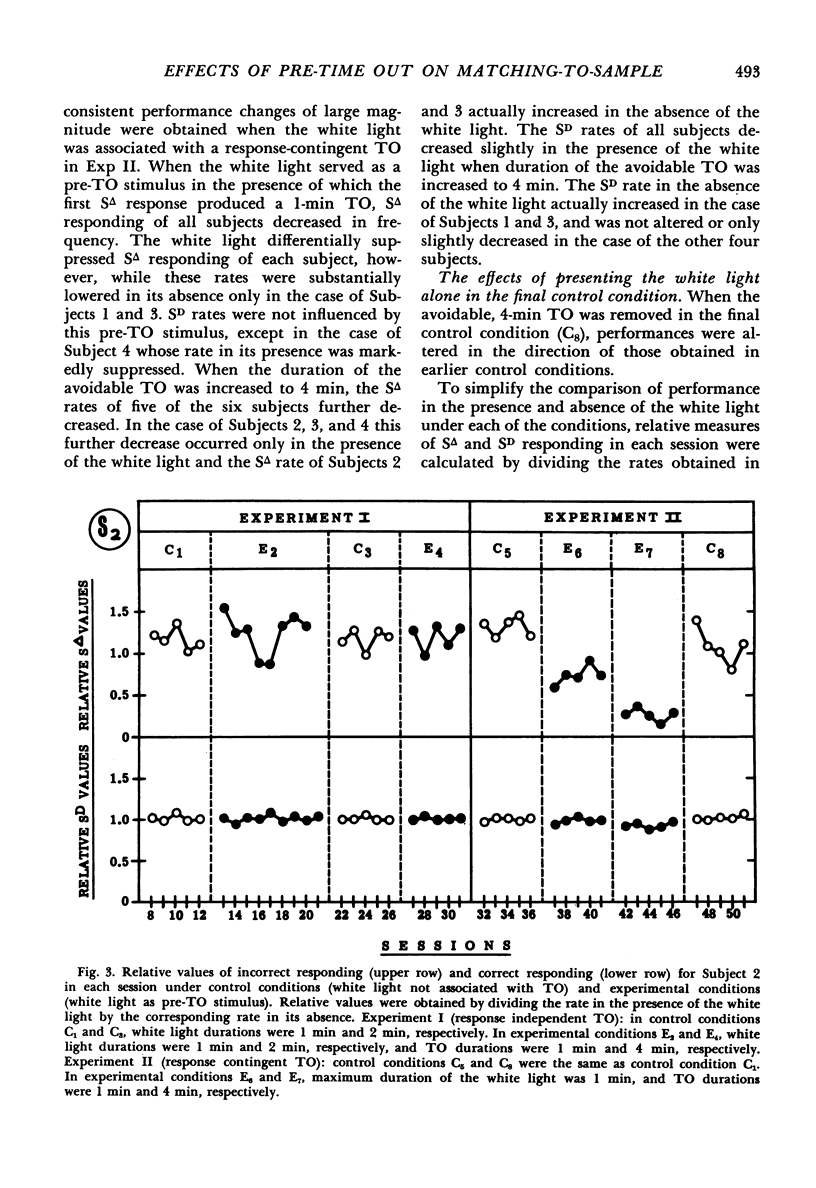
In each of two experiments human subjects were intermittently reinforced with money on a fixed-ratio schedule for emitting correct matching responses. A pre-time-out stimulus which signaled removal of positive reinforcement was periodically superimposed. In the first experiment the superimposed pre-time-out stimulus was paired with a 1-min or 4-min response-independent time out. In the second experiment the pre-time-out stimulus was paired with a 1-min or 4-min time out contingent on the incorrect responses. The pre-time-out stimulus did not markedly influence performance when the time out was response independent. In contrast, the pre-time-out stimulus markedly suppressed incorrect responding when the time out was contingent on the incorrect responses. When duration of this time-out was increased from 1-min to 4-min, suppression of incorrect responding increased and correct responding was suppressed. Therefore, behavioral suppression by a pre-time-out stimulus was obtained only when the signaled aversive event—time out—was response produced. In this case, suppression was influenced by time-out duration.
Full text
PDF


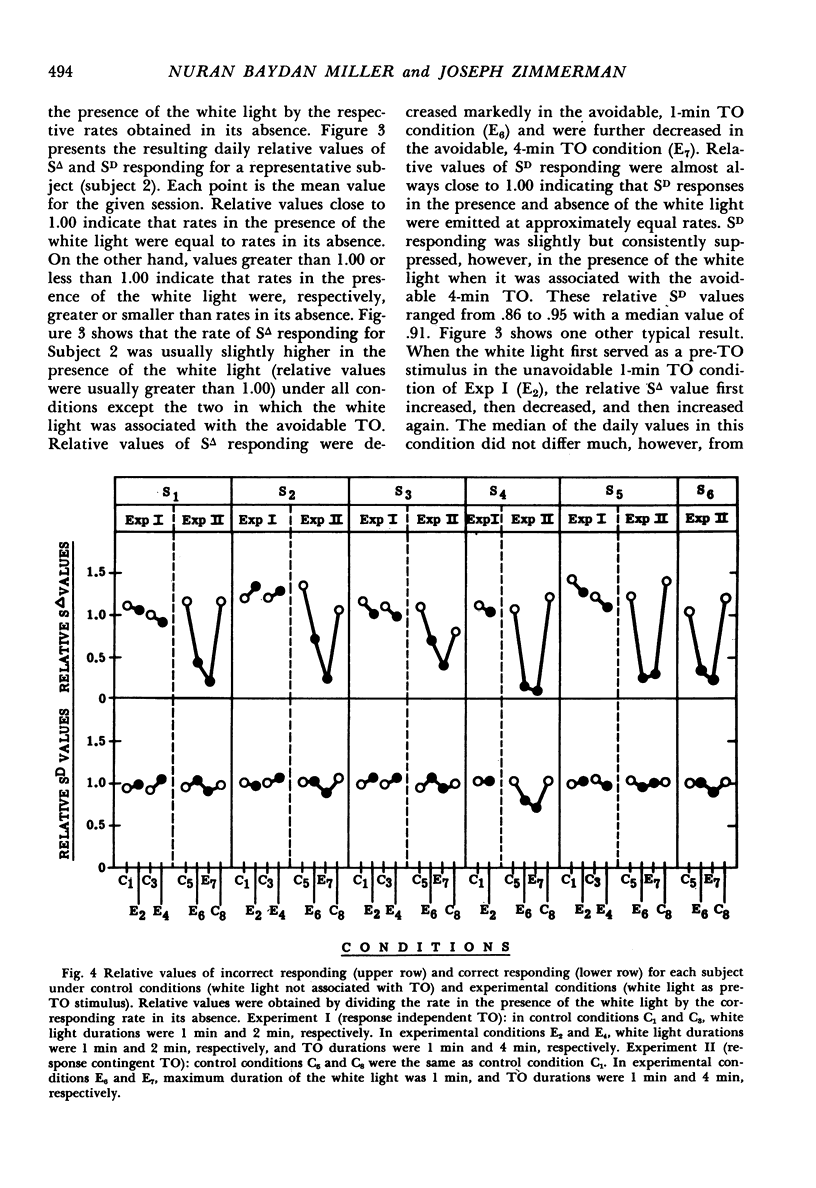




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H. Some Effects of Noise on Human Behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):183–200. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAER D. M. Escape and avoidance response of pre-school children to two schedules of reinforcement withdrawal. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:155–159. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAER D. M. Laboratory control of thumbsucking by withdrawal and re-presentation of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:525–528. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., APPEL J. B., HISS R. A. The effect of drugs on a fixed-ratio performance suppressed by a pre-time-out stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5:73–88. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., APPEL J. B. Punishment of S delta responding in matching to sample by time out from positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:45–56. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B. Suppression of a performance under differential reinforcement of low rates by a pre-time-out stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:143–153. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H., AYLLON T. Elimination of behavior of mental patients by response-produced extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:407–412. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Avoidance conditioning with brief shock and no exteroceptive warning signal. Science. 1953 Aug 7;118(3058):157–158. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3058.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER H. RESPONSE COST AND FIXED-RATIO PERFORMANCE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:79–81. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., BAYDAN N. T. PUNISHMENT OF S-DELTA RESPONDING OF HUMANS IN CONDITIONAL MATCHING TO SAMPLE BY TIME-OUT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:589–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


