Abstract
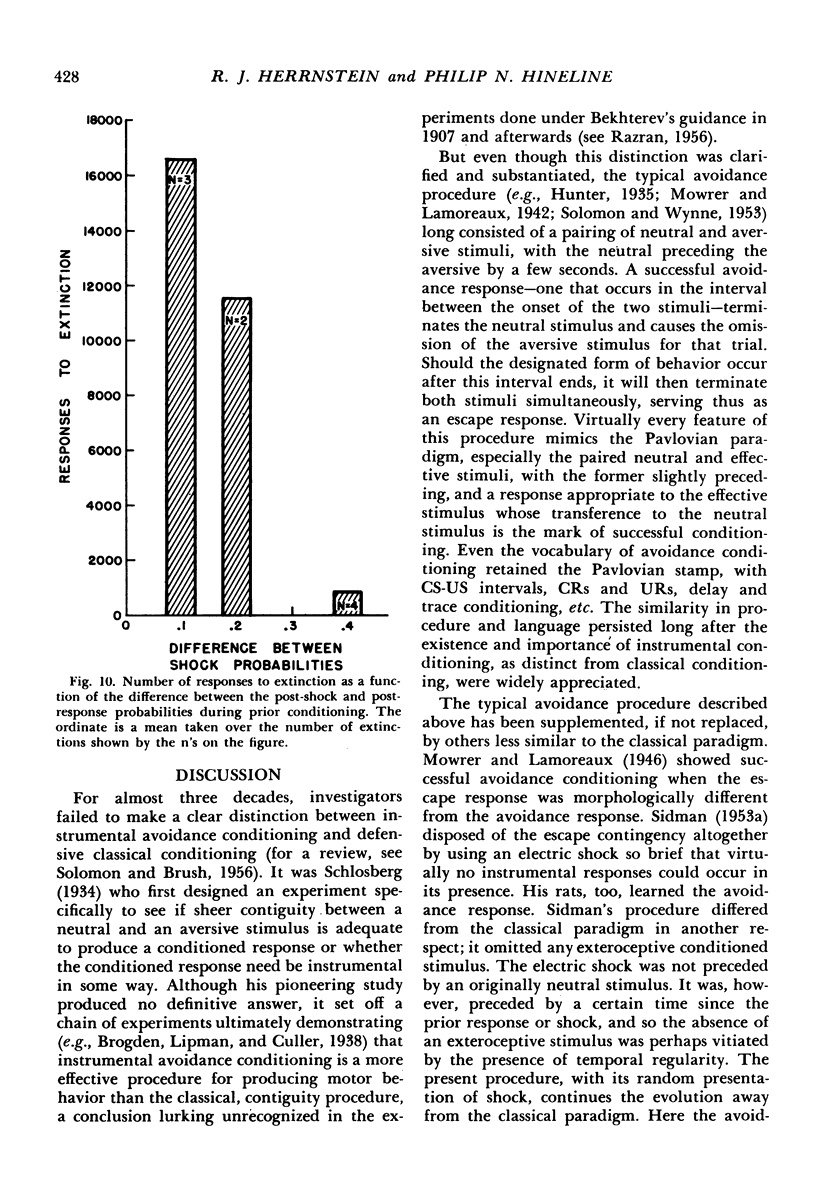
Is a conditioned aversive stimulus necessary in avoidance conditioning? Or is a reduction in the rate of aversive stimulation alone sufficient to generate and maintain an avoidance response? Rats were subjected to an avoidance procedure in which shocks occurred randomly in time, but a response could reduce the overall rate of shock. Fifteen acquisition curves, obtained from 16 animals, showed both immediate and delayed, rapid and gradual increases in response rate; there was no representative acquisition curve. Response rates were directly related to the amount by which the response reduced shock frequency. In extinction, when shock rates were not affected by responding, the response total was inversely related to the amount by which the response had reduced shock frequency during prior conditioning, with as many as 20,000 extinction responses when the shock frequency reduction had been relatively small. Responding on this procedure shows that avoidance conditioning can occur without benefit of either classical exteroceptive stimuli or covert stimuli inferred from the temporal constancies of a procedure. It also shows that reduction in shock rate is alone sufficient to maintain avoidance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANGER D. The role of temporal discriminations in the reinforcement of Sidman avoidance behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6(3):477–506. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-s477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLES R. C., POPP R. J., Jr PARAMETERS AFFECTING THE ACQUISITION OF SIDMAN AVOIDANCE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jul;7:315–321. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL B. A. The reinforcement difference limen (RDL) function for shock reduction. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Oct;52(4):258–262. doi: 10.1037/h0048706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. I. The avoidance hypothesis. Psychol Rev. 1954 Jan;61(1):34–46. doi: 10.1037/h0062725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMIN L. J. The effects of termination of the CS and avoidance of the US on avoidance learning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Aug;49(4):420–424. doi: 10.1037/h0088011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMIN L. J. The effects of termination of the CS and avoidance of the US on avoidance learning: an extension. Can J Psychol. 1957 Mar;11(1):48–56. doi: 10.1037/h0083690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZRAN G. Avoidant vs. unavoidant conditioning and partial reinforcement in Russian laboratories. Am J Psychol. 1956 Mar;69(1):127–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Avoidance conditioning with brief shock and no exteroceptive warning signal. Science. 1953 Aug 7;118(3058):157–158. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3058.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. On the persistence of avoidance behavior. J Abnorm Psychol. 1955 Mar;50(2):217–220. doi: 10.1037/h0039805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Reduction of shock frequency as reinforcement for avoidance behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:247–257. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Two temporal parameters of the maintenance of avoidance behavior by the white rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1953 Aug;46(4):253–261. doi: 10.1037/h0060730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON R. L., KAMIN L. J., WYNNE L. C. Traumatic avoidance learning: the outcomes of several extinction procedures with dogs. J Abnorm Psychol. 1953 Apr;48(2):291–302. doi: 10.1037/h0058943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



