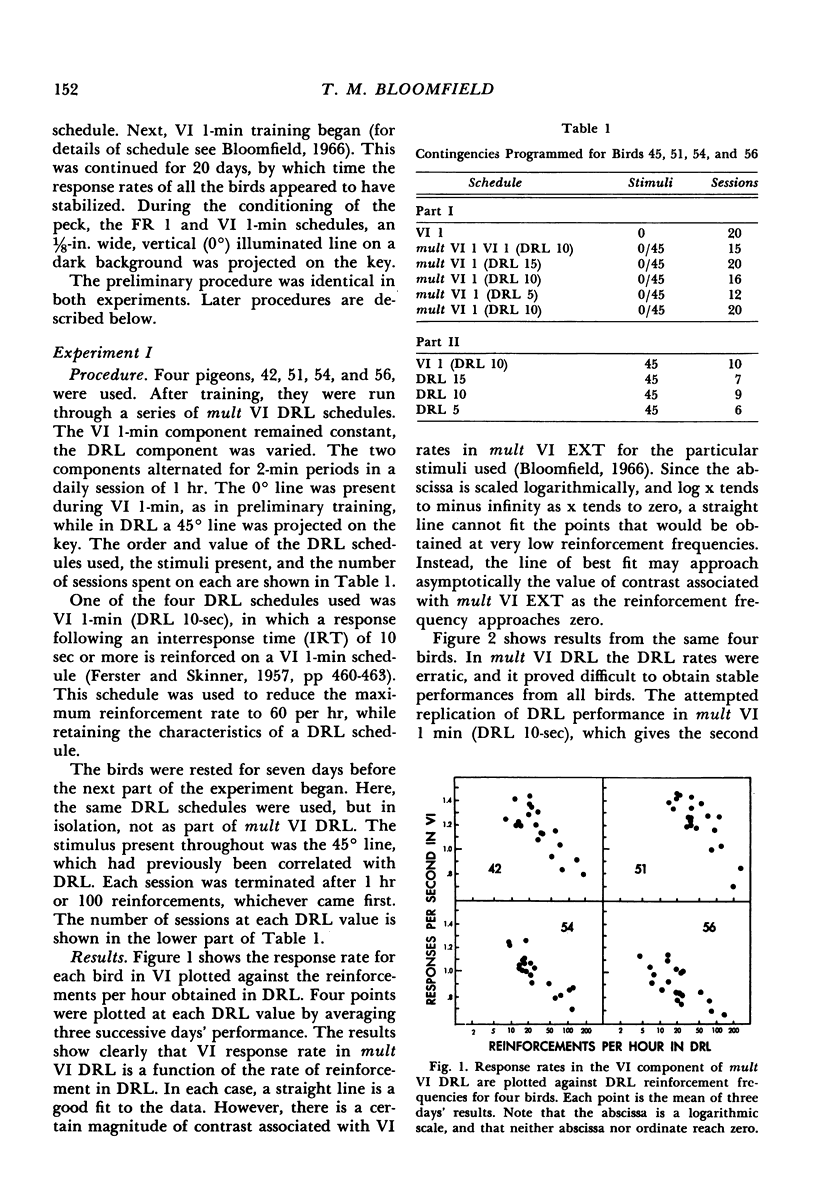
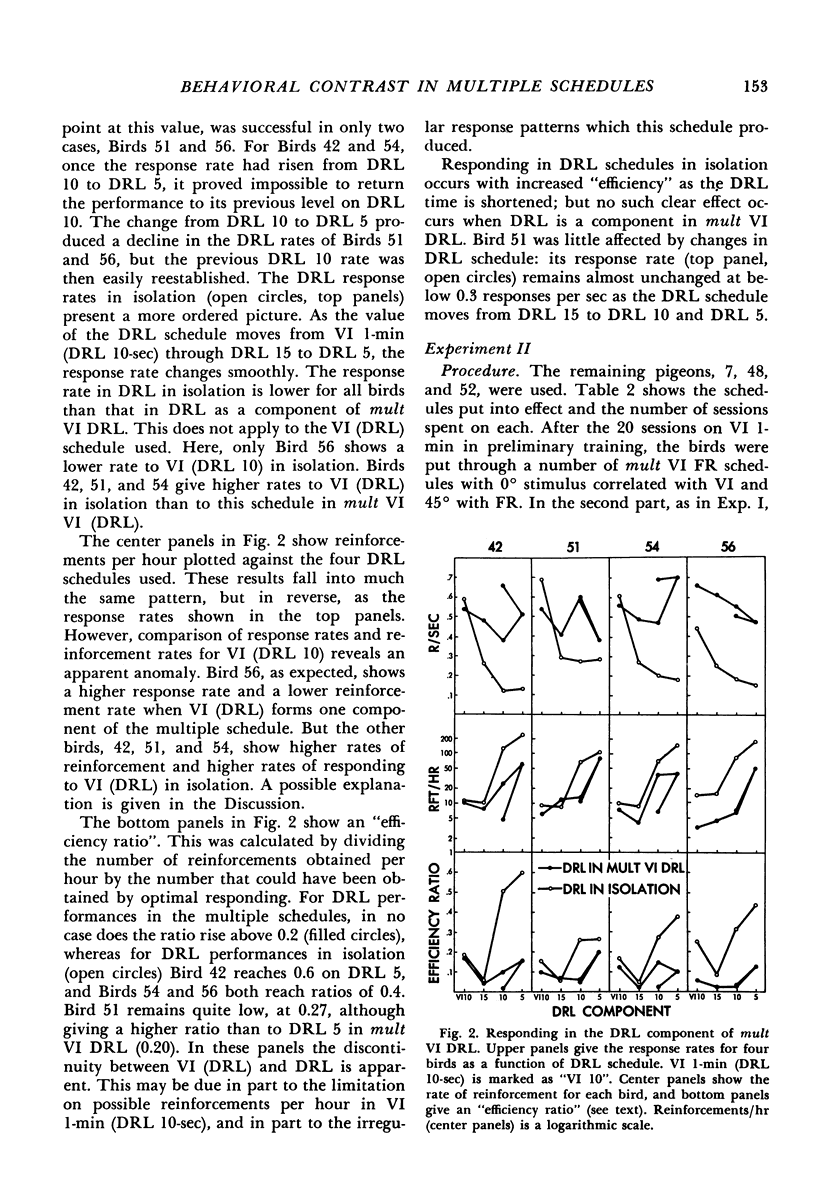
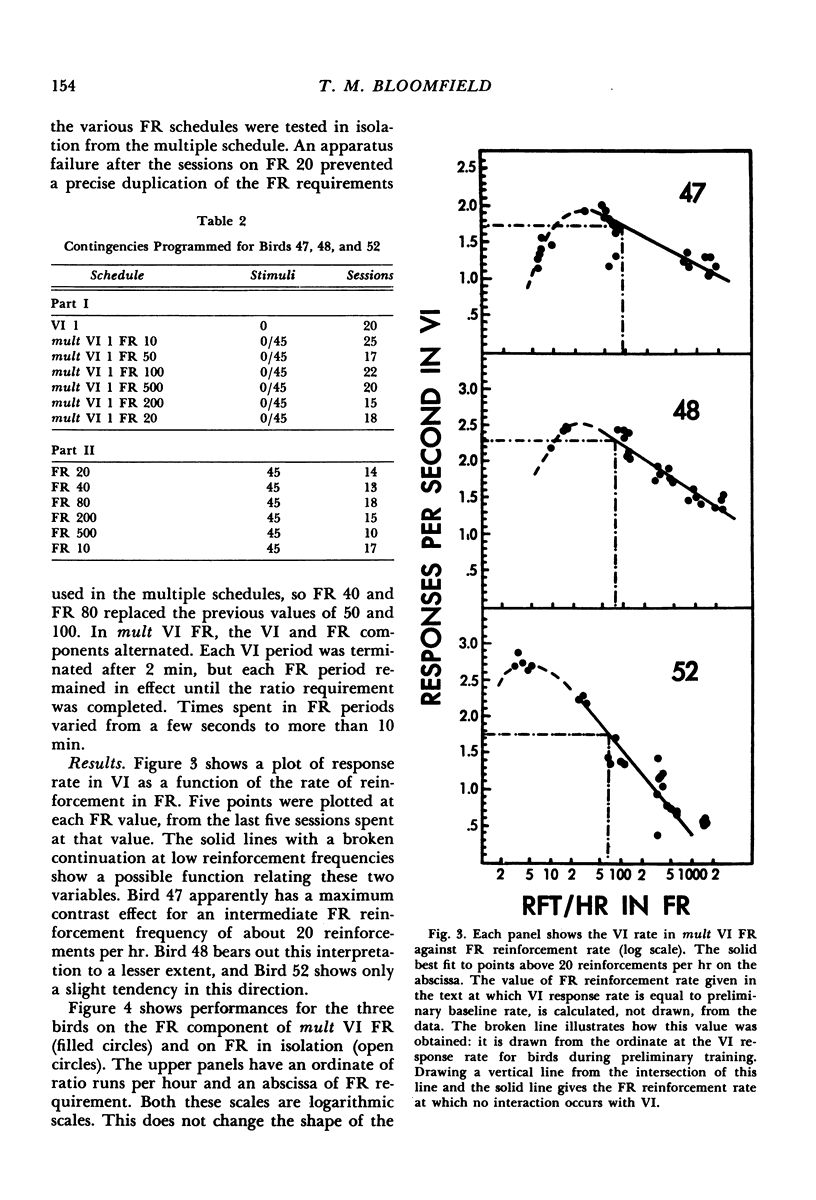
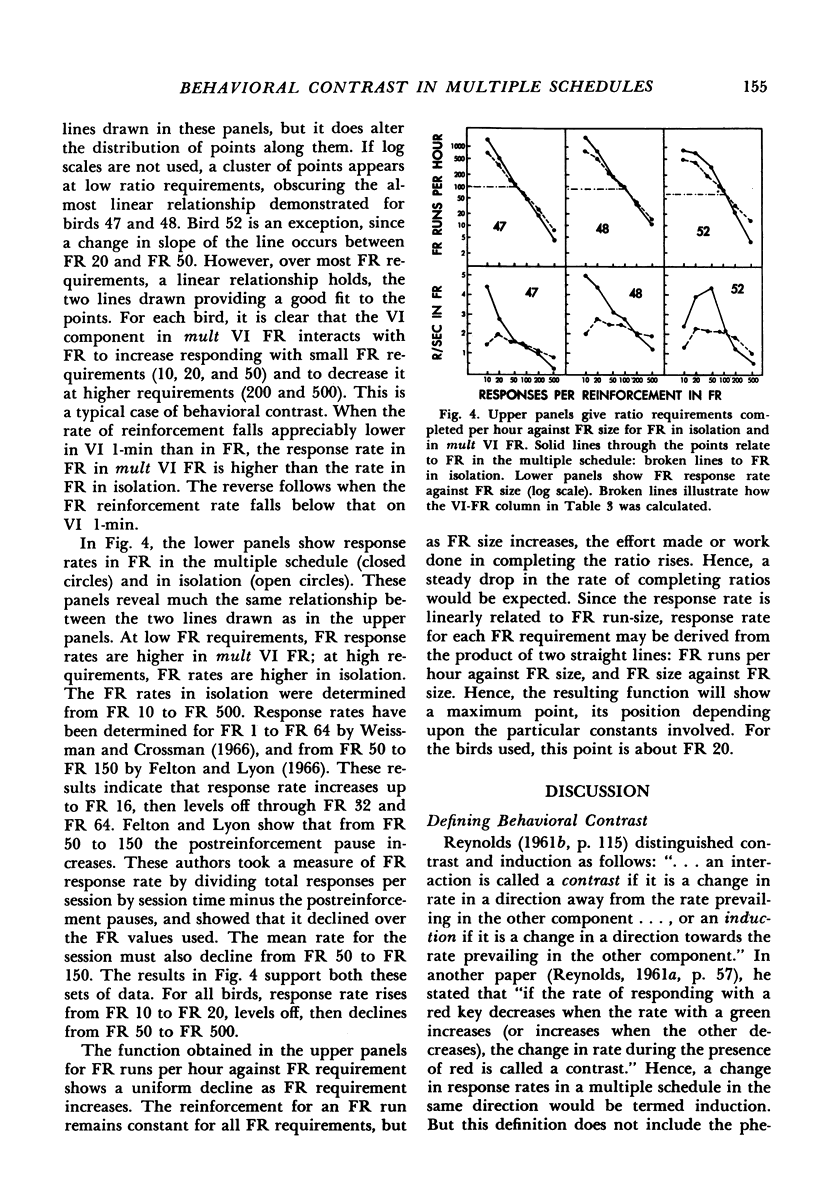
Abstract
After preliminary variable-interval training, one group of pigeons was trained on a series of multiple variable-interval low-rate reinforcement schedules, while another group was trained on a series of multiple variable-interval fixed-ratio reinforcement schedules. Contrast effects were observed as variable-interval baseline rate changed in a direction away from the change in reinforcement frequency in the other component. The effects of the variable-interval component on performance in the low-rate and fixed-ratio reinforcement components in the multiple schedules were assessed by comparing the birds' performances on each of these schedules alone. Fixed-ratio reinforcement schedules showed a susceptibility to contrast effects, low-rate reinforcement schedules did not. The rate of reinforcement in fixed-ratio schedules at which no interaction occurred in the multiple schedules was higher than that in variable-interval 1-min schedules, suggesting that pigeons may prefer time-based, rather than response-based, reinforcement.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APPEL J. B. Aversive aspects of a schedule of positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:423–428. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Time-out from positive reinforcement. Science. 1961 Feb 10;133(3450):382–383. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3450.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield T. M. Two types of behavioral contrast in discrimination learning. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):155–161. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felton M., Lyon D. O. The post-reinforcement pause. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):131–134. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S., CATANIA A. C. Behavioral contrast with fixed interval and low-rate reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:387–391. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Relativity of response rate and reinforcement frequency in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:179–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. An analysis of interactions in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4(2):107–117. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON D. M. ESCAPE FROM SD ASSOCIATED WITH FIXED-RATIO REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:1–8. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON D. M. PUNISHMENT BY SD ASSOCIATED WITH FIXED-RATIO REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 May;8:189–194. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. P., KELLER F. S. On the selective reinforcement of spaced responses. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1953 Jun;46(3):190–193. doi: 10.1037/h0057705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman N. W., Crossman E. K. A comparison of two types of extinction following fixed-ratio training. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):41–46. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


