Abstract
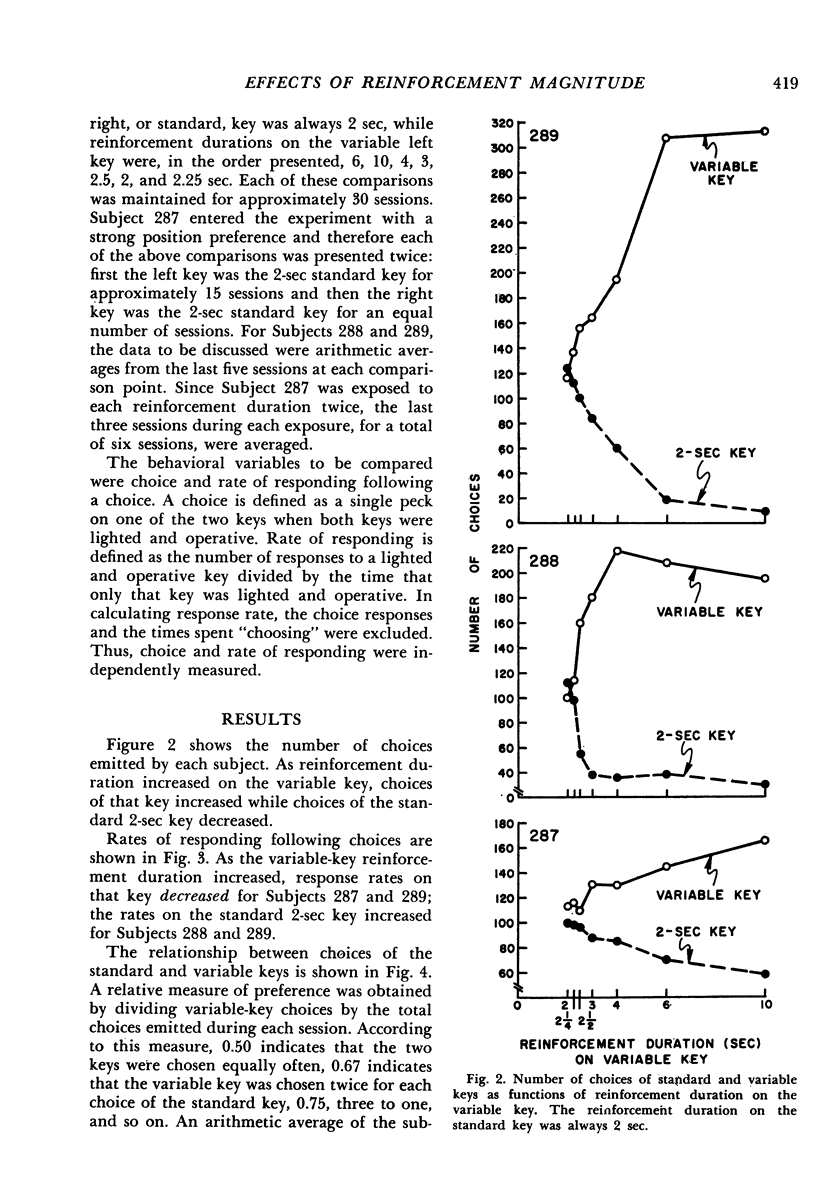
Behavior is sometimes insensitive, and sometimes extremely sensitive, to changes in reinforcement magnitude. The present work attempted to analyze this disparity by comparing, in a single experimental situation, a pigeon's choices with its response rates. Whereas choices varied directly with reinforcement duration, rates of responding were comparatively insensitive to duration changes. These results suggest that the effect of reinforcement magnitude on responding partly depends upon the extent to which responding influences the amount of reinforcement.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON K. N. T-MAZE CHOICE LEARNING AS A JOINT FUNCTION OF THE REWARD MAGNITUDES FOR THE ALTERNATIVES. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1964 Dec;58:333–338. doi: 10.1037/h0040817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. H., Herrnstein R. J. Choice and delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):67–74. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DENNY M. R., KING G. F. Differential response learning on the basis of differential size of reward. J Genet Psychol. 1955 Dec;87(2):317–320. doi: 10.1080/00221325.1955.10532944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURCHTGOTT E., RUBIN R. D. The effect of magnitude of reward on maze learning in the white rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1953 Feb;46(1):9–12. doi: 10.1037/h0055050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRY D. P. The effect of correlated amount of reward on performance on a fixed-interval schedule of reinforcement. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1962 Jun;55:387–391. doi: 10.1037/h0046507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDRY D. P., VAN-TOLLER C. PERFORMANCE ON A FIXED-RATIO SCHEDULE WITH CORRELATED AMOUNT OF REWARD. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:207–209. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEESEY R. E., KLING J. W. Amount of reinforcement and free-operant responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:125–132. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLING J. W. Speed of running as a function of goal-box behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Oct;49(5):474–476. doi: 10.1037/h0046928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCKELVEY R. K. The relationship between training methods and reward variables in brightness discrimination learning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Oct;49(5):485–491. doi: 10.1037/h0044397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEREBOOM A. C. An analysis and revision of Hull's theorem 30. J Exp Psychol. 1957 Apr;53(4):234–238. doi: 10.1037/h0042856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H. The effect of shock intensity on concurrent and single-key responding in concurrent-chain schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):87–93. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHRIER A. M. Comparison of two methods of investigating the effect of amount of reward on performance. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Dec;51(6):725–731. doi: 10.1037/h0038761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHETTLEWORTH S., NEVIN J. A. RELATIVE RATE OF RESPONSE AND RELATIVE MAGNITUDE OF REINFORCEMENT IN MULTIPLE SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jul;8:199–202. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


