Abstract
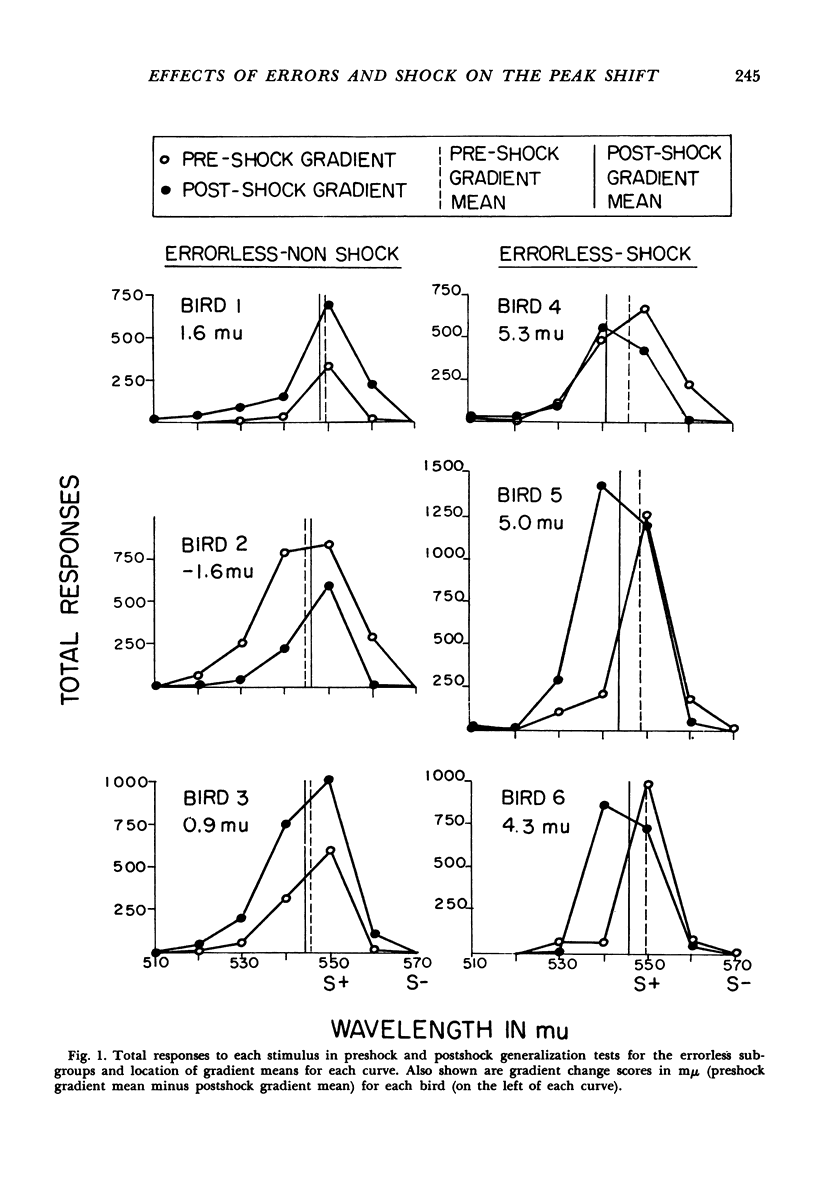
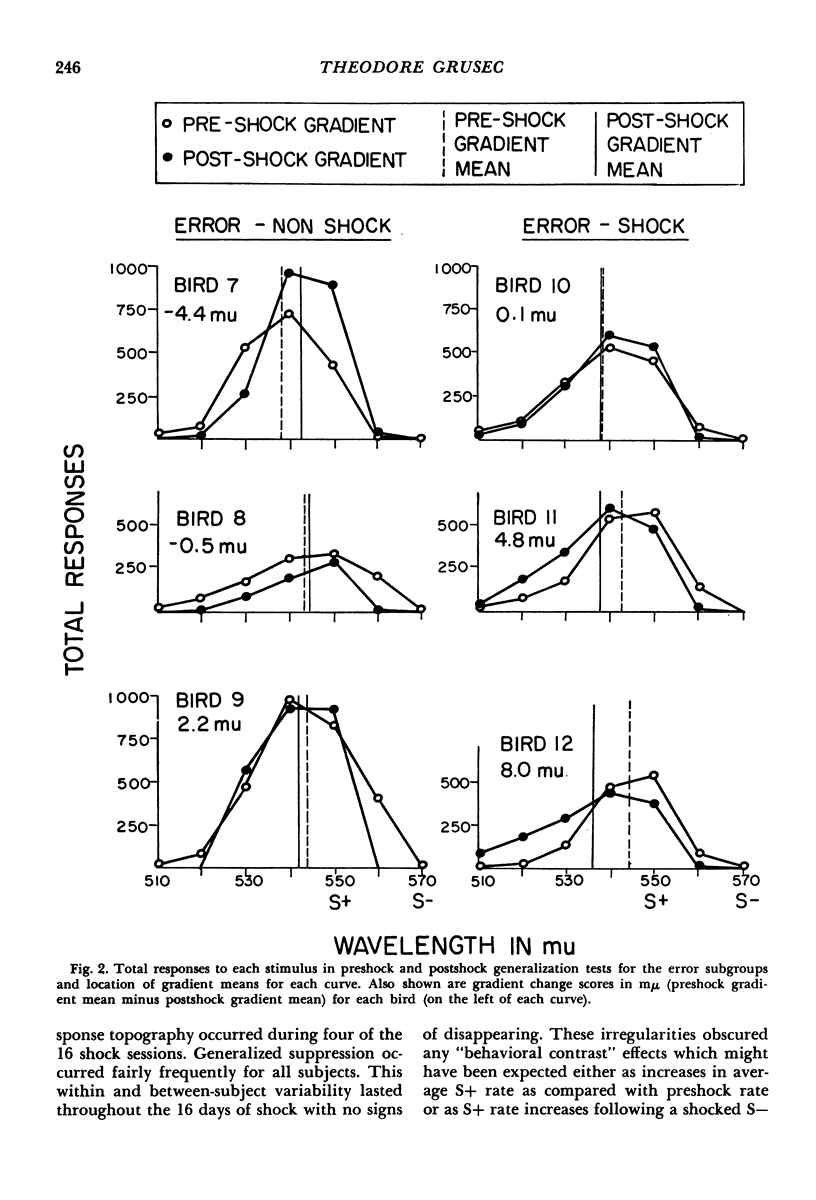
Terrace suggested that the peak shift in stimulus generalization occurs because the training stimulus not correlated with reinforcement has become aversive. This hypothesis is plausible in the light of instances where the peak shift is obtained compared with those where it fails to appear. The present experiment attempted to test implications of this hypothesis. Two groups of pigeons learned the same two-stimulus discrimination between colors by different training methods in a free-operant situation. When the discrimination was trained with many errors, a large peak shift was obtained in a subsequent generalization test of wavelength; after discrimination training with few errors, a negligible shift was observed. Half of each group then received noncontingent aversive shock during presentations of the stimulus not correlated with reinforcement in continued discrimination training. After this treatment, the errorless-shock subgroup showed a large peak shift and the error-shock subgroup tended to show a larger shift than before. Nonshocked control groups showed little change in the peak shift. It was concluded that pairing aversive shock with a stimulus not correlated with reinforcement is sufficient to produce or enhance a peak shift. In their effect on the peak shift, aversive shock and large amounts of nonreinforced responding appear to be equivalent.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOUGH D. S. Spectral sensitivity in the pigeon. J Opt Soc Am. 1957 Sep;47(9):827–833. doi: 10.1364/josa.47.000827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMAN N. Generalization gradients around stimuli associated with different reinforcement schedules. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Nov;58:335–340. doi: 10.1037/h0045679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON H. M. Effects of discrimination training on stimulus generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Nov;58:321–334. doi: 10.1037/h0042606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN H. S., FLESHLER M. Aversive control with the pigeon. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Jul;2:213–218. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HONIG W. K. Prediction of preference, transposition, and transposition-reversal from the generalization gradient. J Exp Psychol. 1962 Sep;64:239–248. doi: 10.1037/h0048290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless discrimination learning inthe pigeon: effects of chlorpromazine and impiramine. Science. 1963 Apr 19;140(3564):318–319. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3564.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless transfer of a discrimination across two continua. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:223–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. WAVELENGTH GENERALIZATION AFTER DISCRIMINATION LEARNING WITH AND WITHOUT ERRORS. Science. 1964 Apr 3;144(3614):78–80. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3614.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning and inhibition. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1677–1680. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



