Abstract
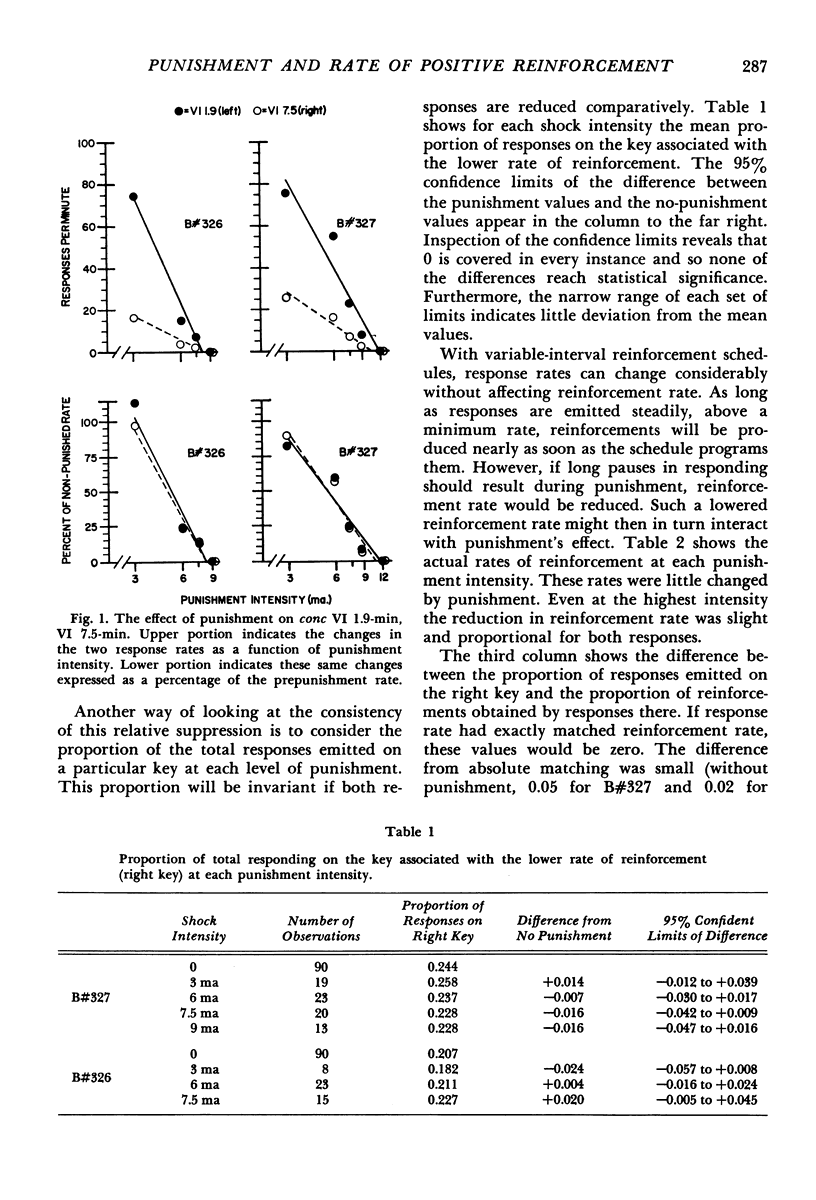
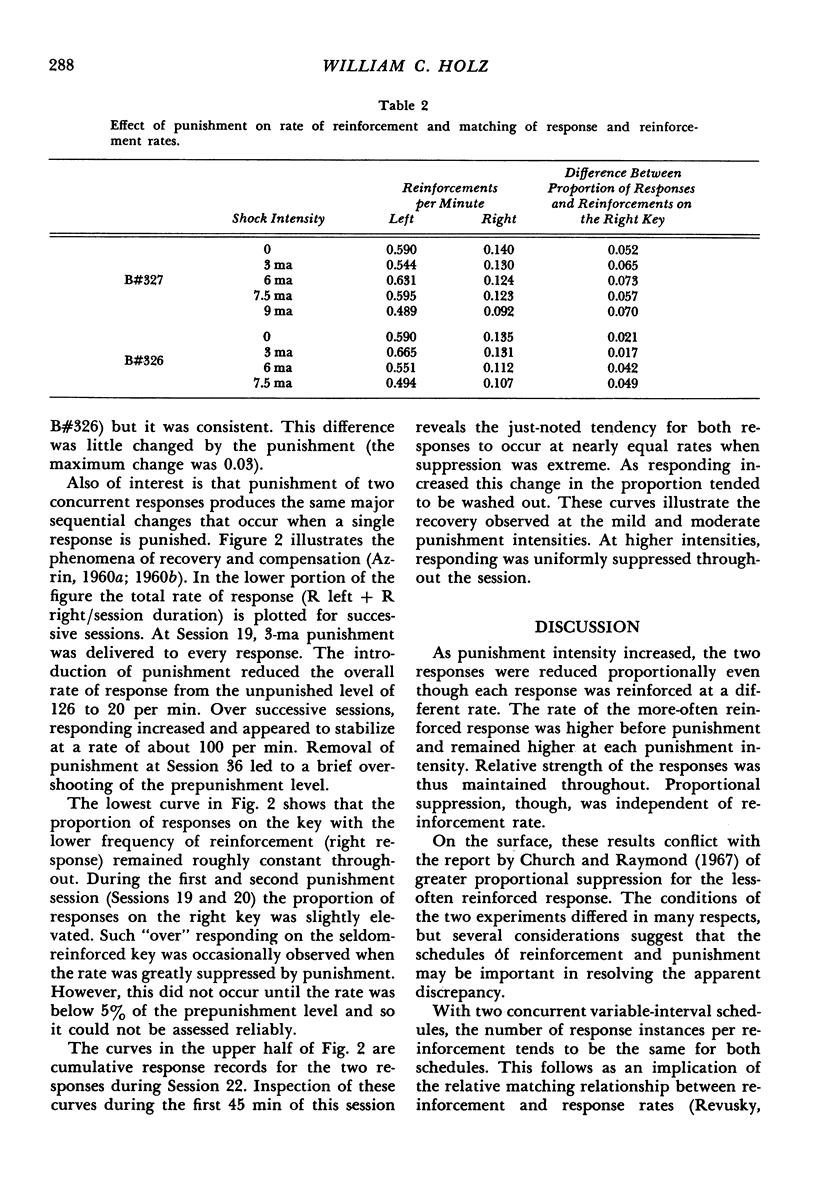
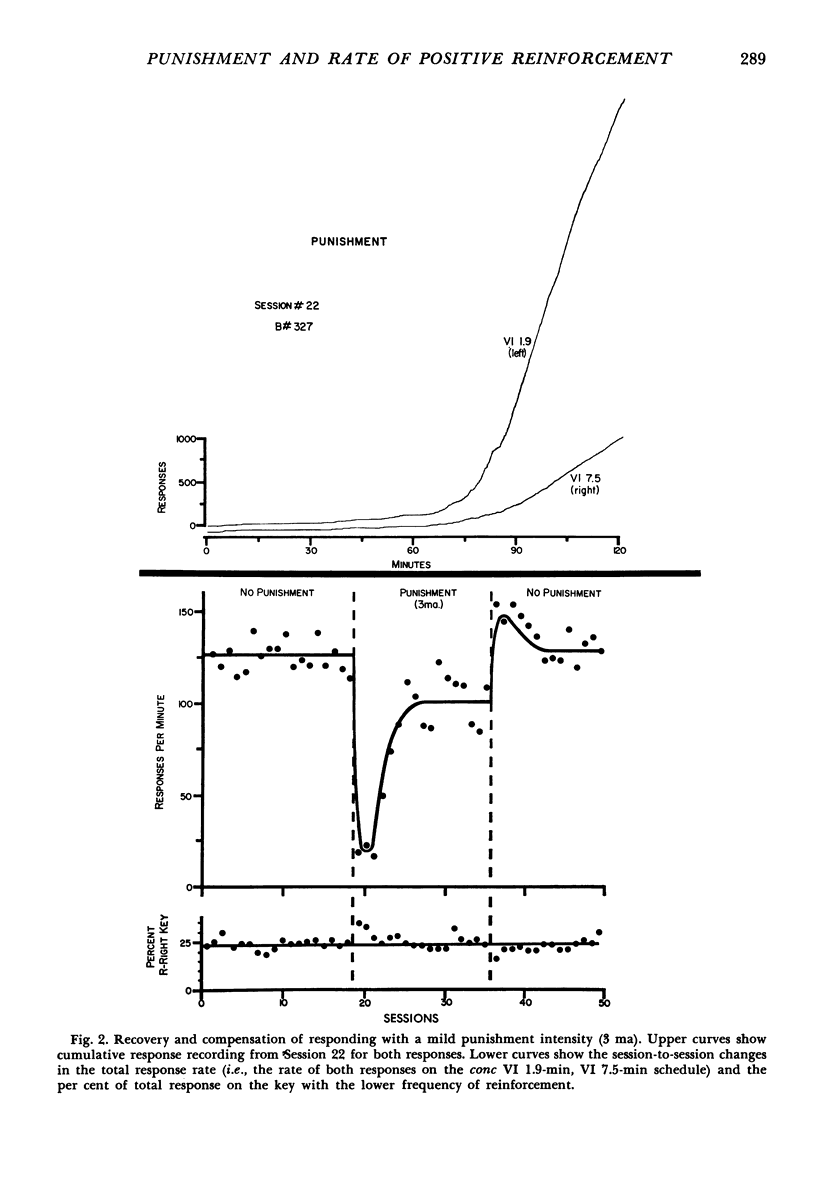
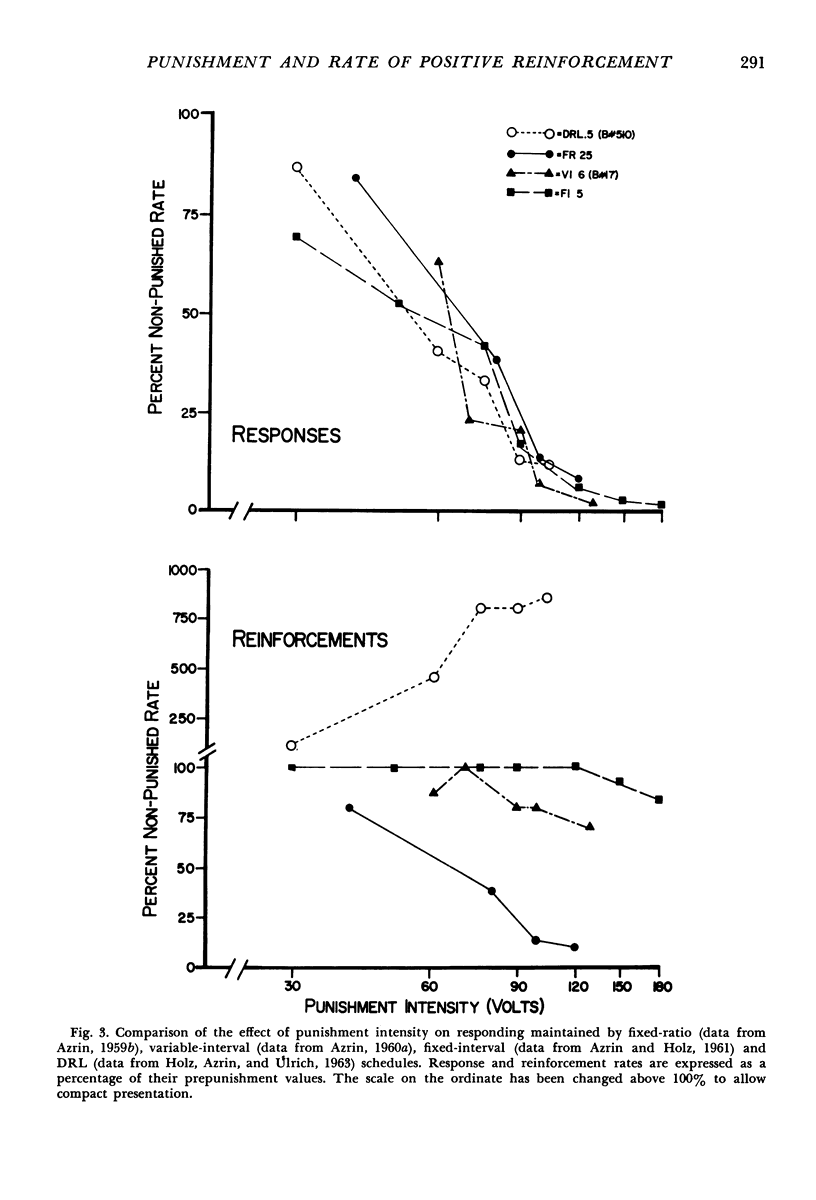
This experiment investigated the effect of several punishment intensities on two responses maintained by contrasting rates of reinforcement. The responses were concurrently reinforced according to two different variable-interval schedules. Because these schedules were independent of one another and programmed different rates of reinforcement, the two responses occurred at dissimilar rates. When responses were simultaneously suppressed by punishment, both rates were reduced proportionately until suppression was virtually complete. In other words, the per cent suppression resulting from punishment was independent of the rate at which the response was reinforced. Phenomena found in single-response studies were duplicated here. Responding tended to increase both within and between punishment sessions at mild and moderate punishment intensities. Cessation of punishment led to a “compensatory” overshooting beyond the prepunished response rate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C., HAKE D. F. Fixed-ratio punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:141–148. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C. Punishment during fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Oct;4:343–347. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Sequential effects of punishment. Science. 1960 Feb 26;131(3400):605–606. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3400.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHURCH R. M. THE VARIED EFFECTS OF PUNISHMENT ON BEHAVIOR. Psychol Rev. 1963 Sep;70:369–402. doi: 10.1037/h0046499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. M., Raymond G. A. Influence of the schedule of positive reinforcement on punished behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Apr;63(2):329–332. doi: 10.1037/h0024382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. A comparison of several procedures for eliminating behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:399–406. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H., ULRICH R. E. Punishment of temporally spaced responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:115–122. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Effects of reinforcement magnitude on choice and rate of responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):417–424. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVUSKY S. H. A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RESPONSES PER REINFORCEMENT AND PREFERENCE DURING CONCURRENT. VI. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:518–518. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


