Abstract
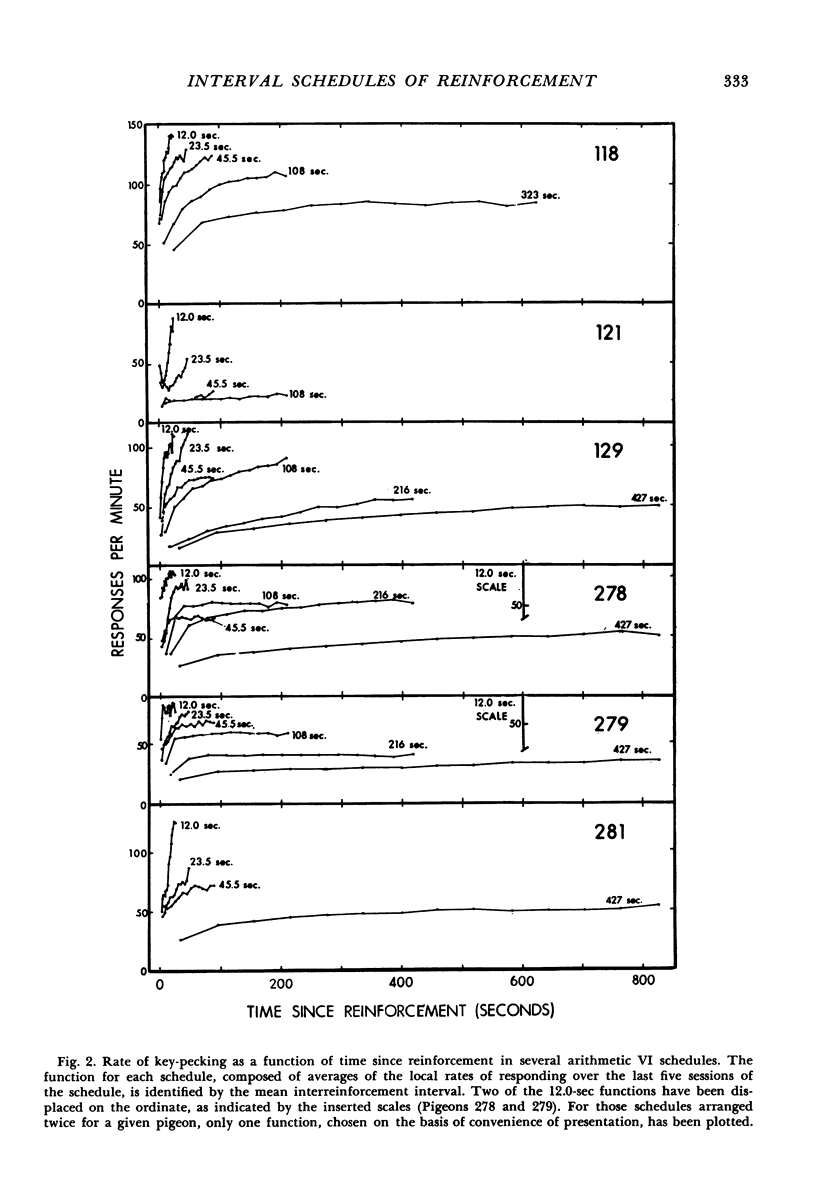
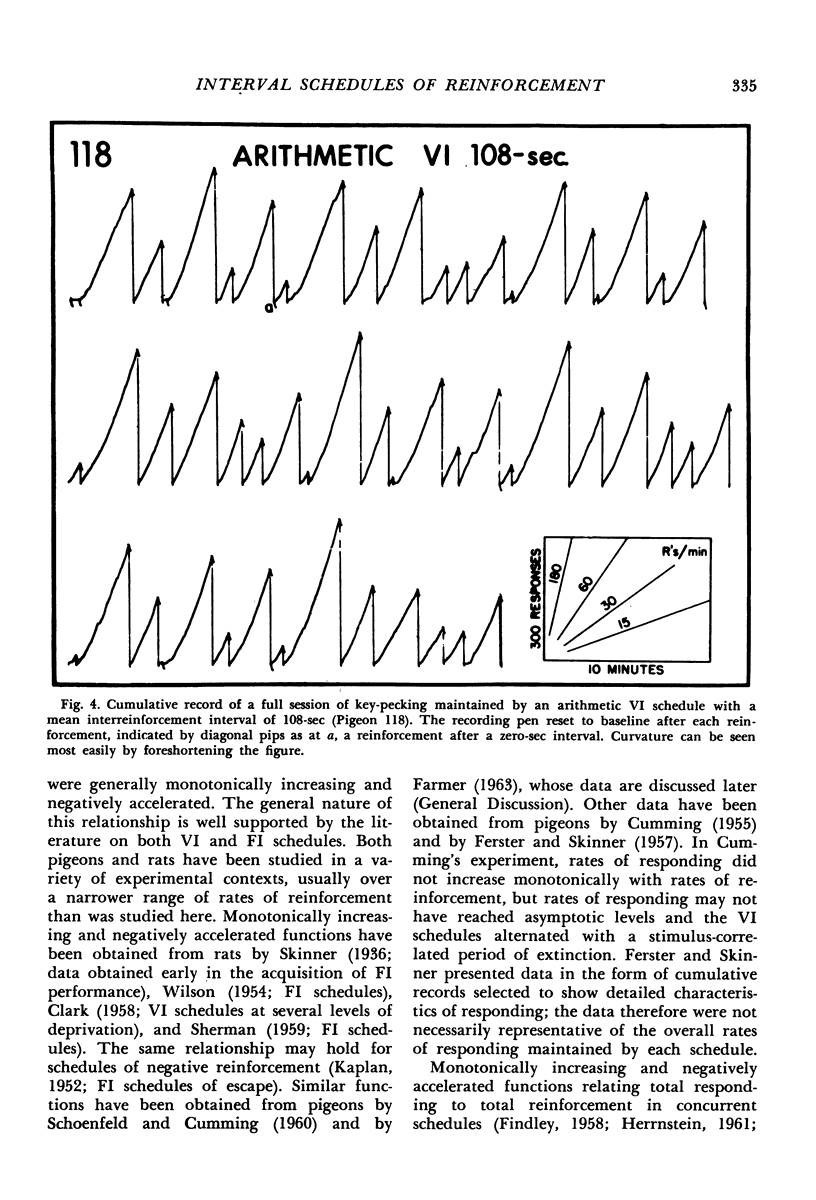
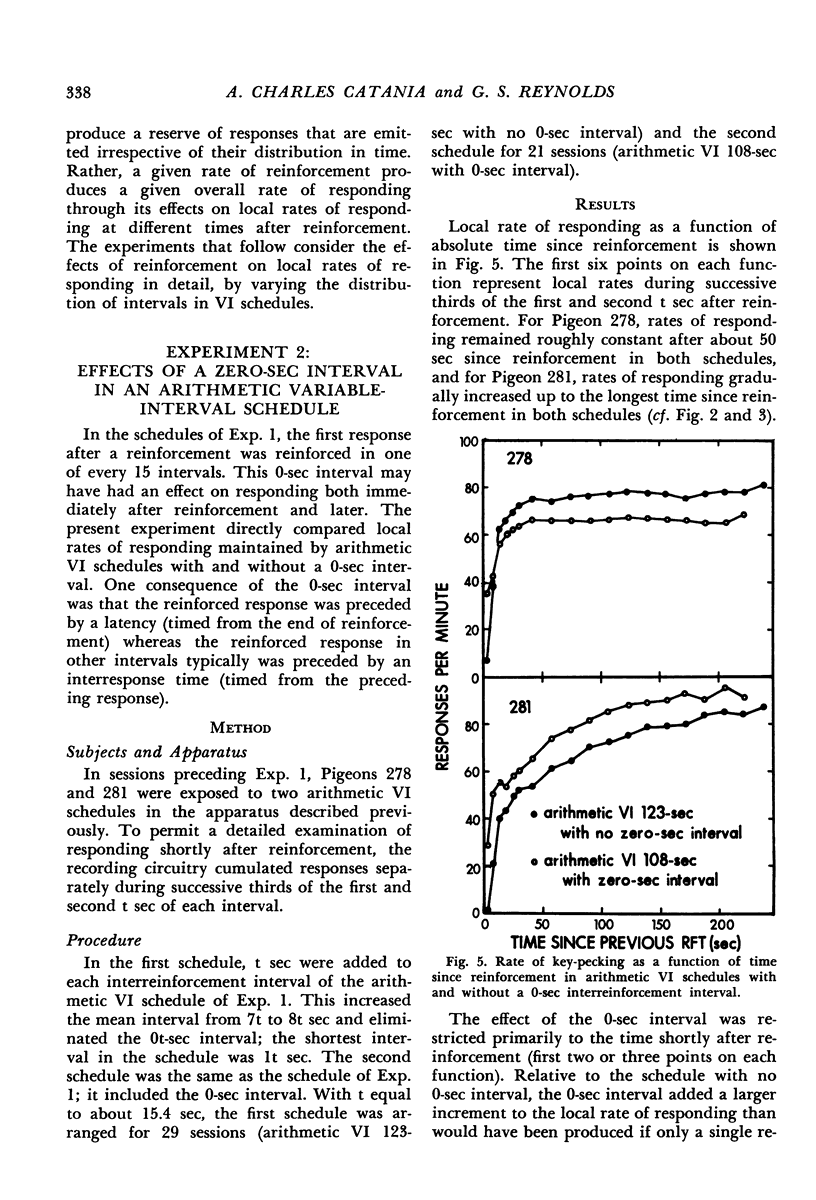
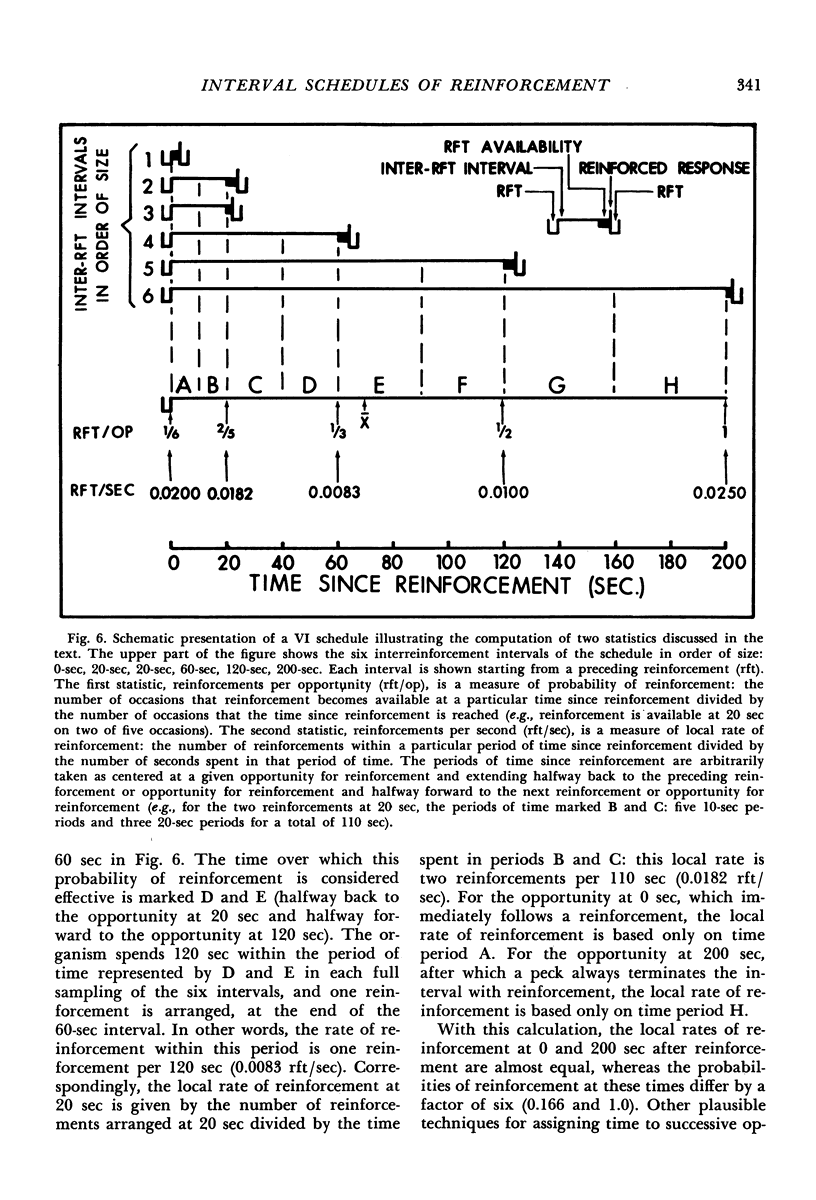
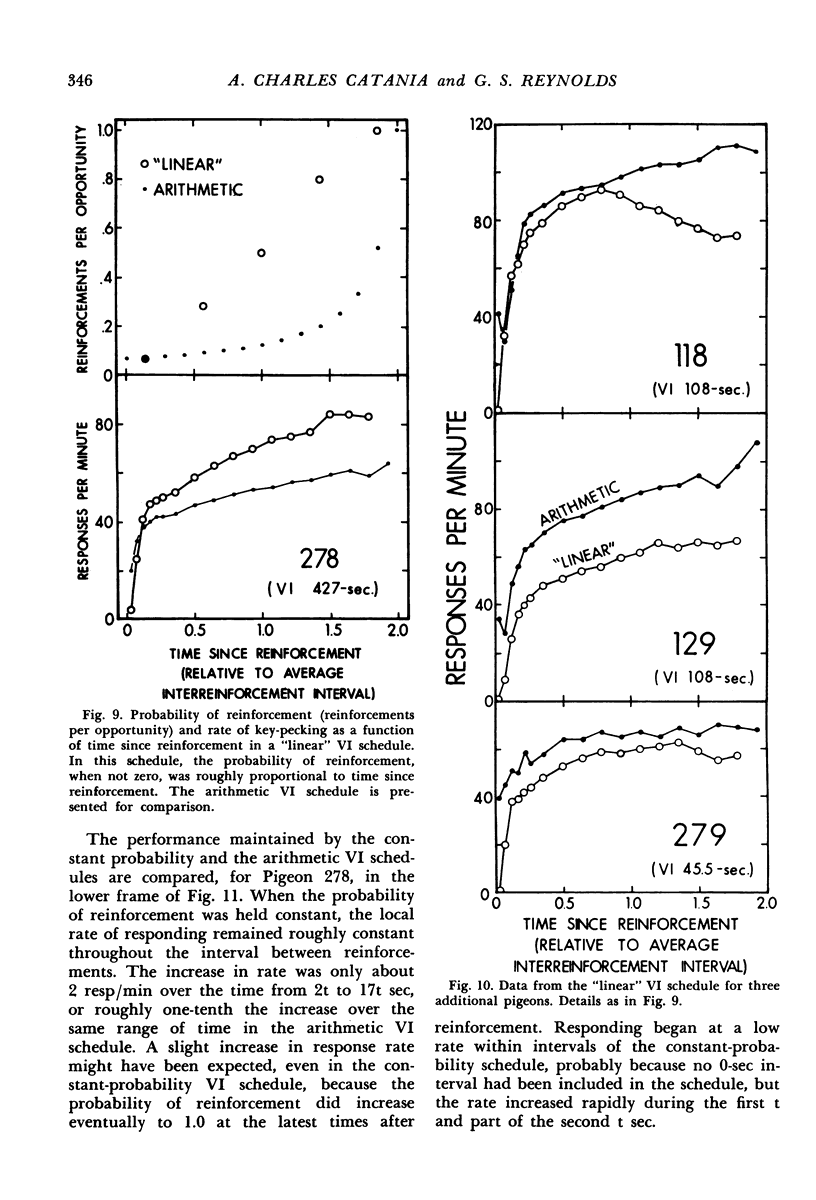
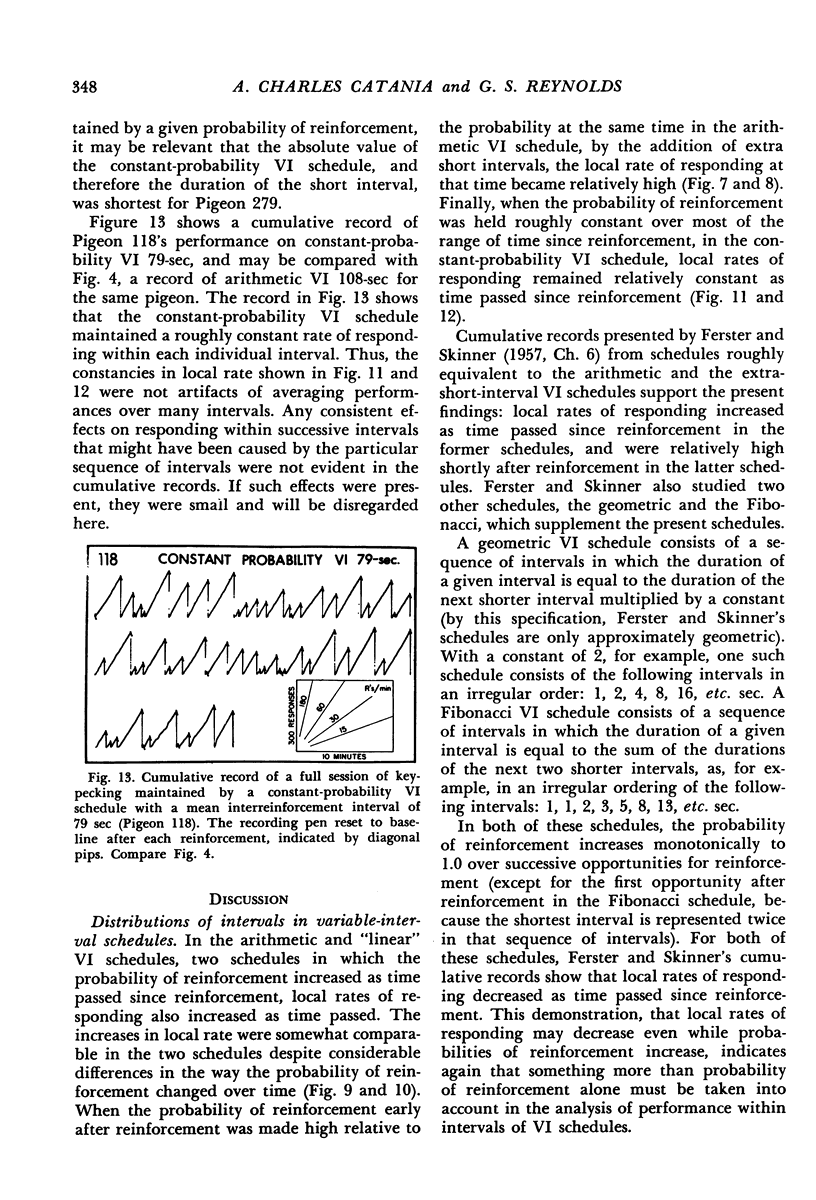
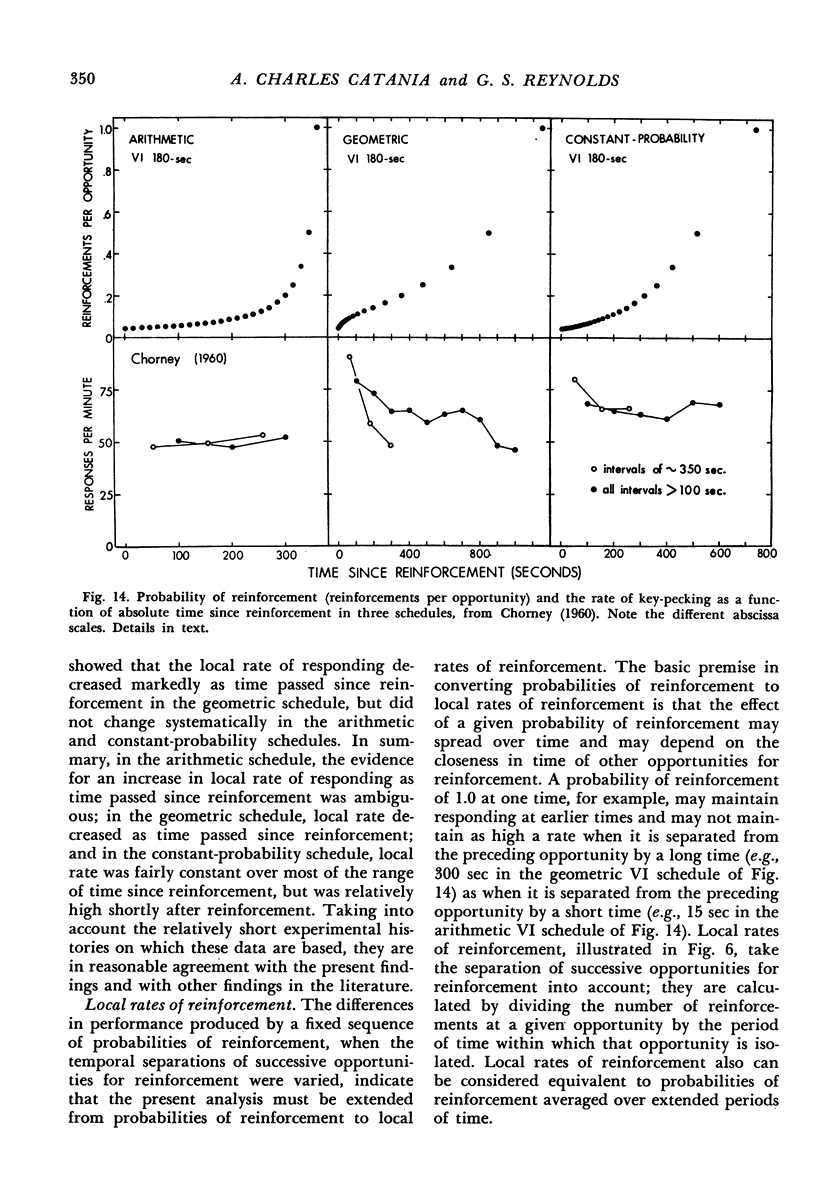
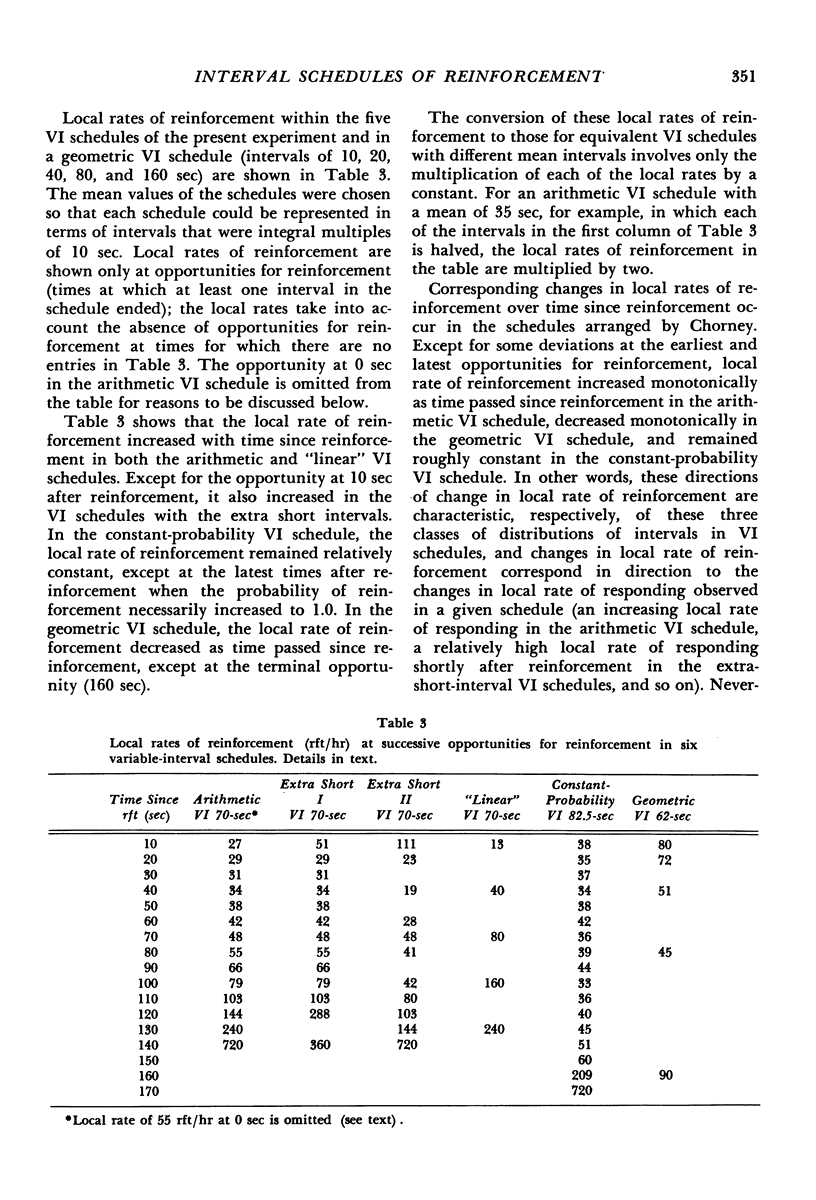
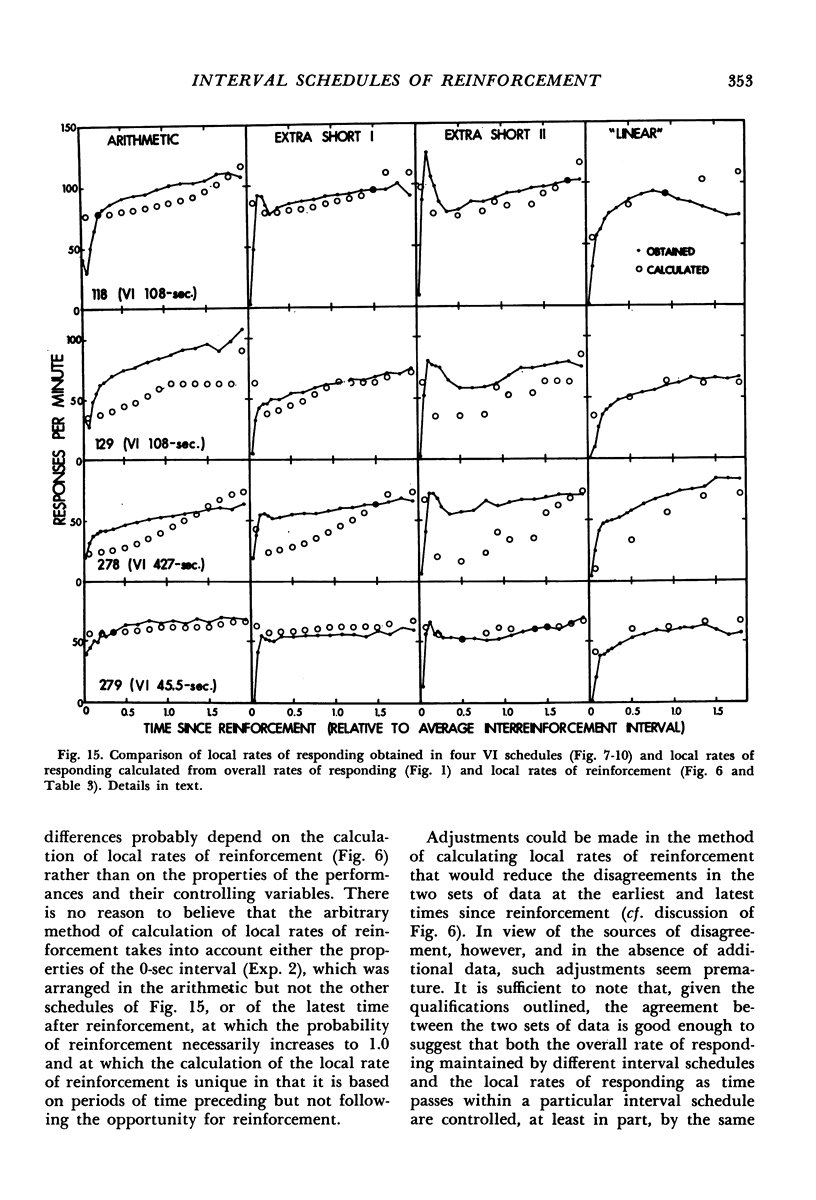
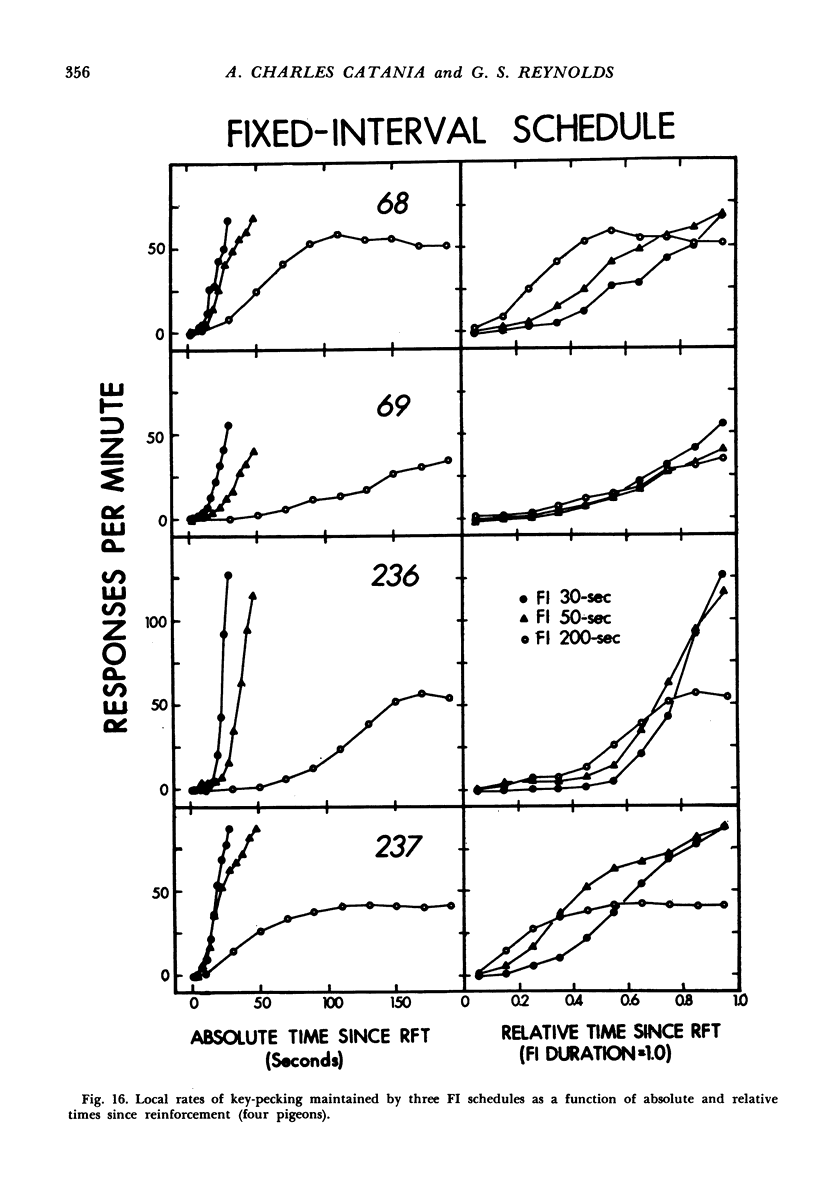
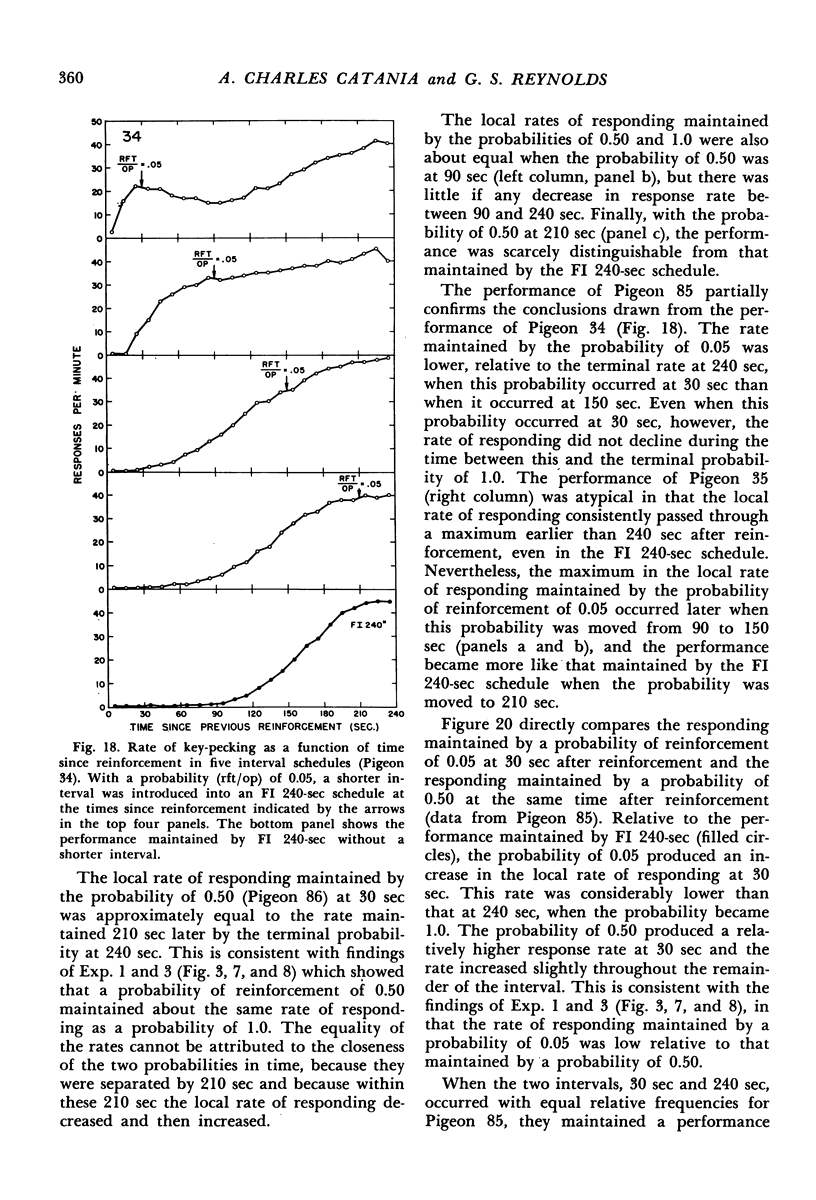
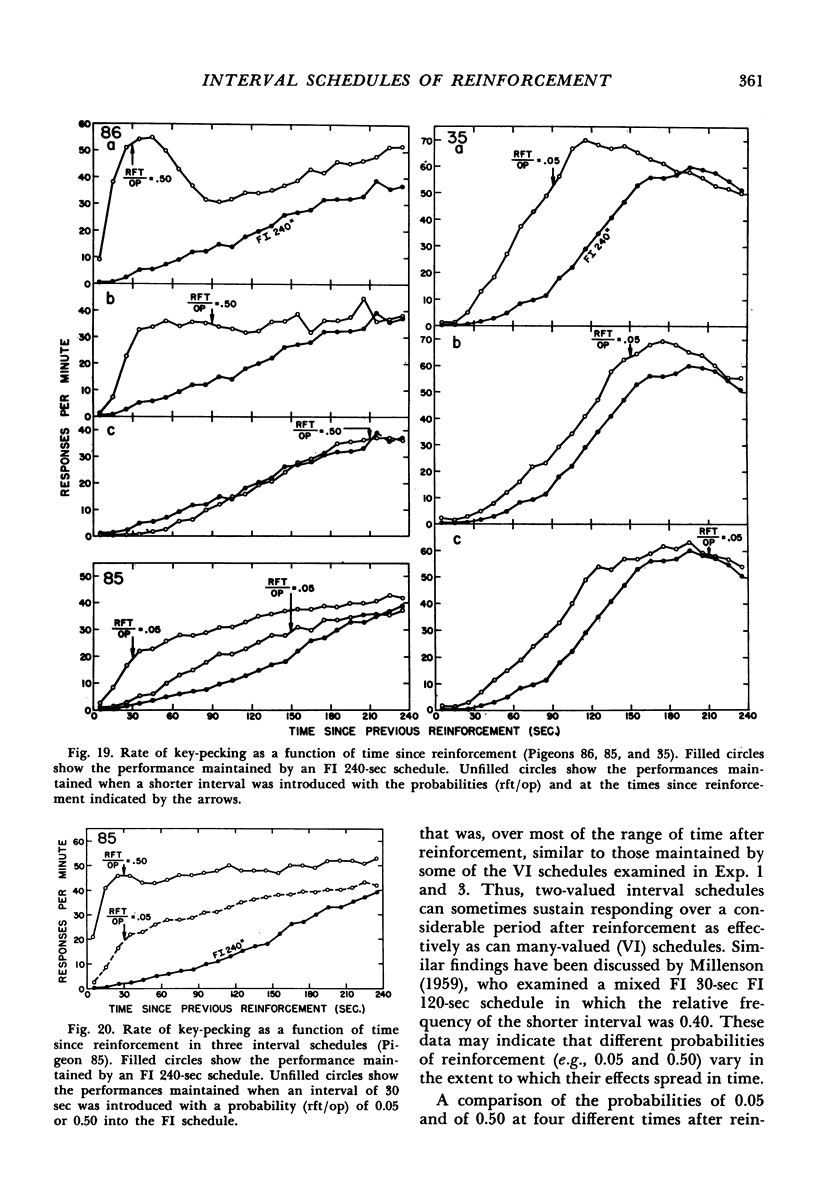
Interval schedules of reinforcement maintained pigeons' key-pecking in six experiments. Each schedule was specified in terms of mean interval, which determined the maximum rate of reinforcement possible, and distribution of intervals, which ranged from many-valued (variable-interval) to single-valued (fixed-interval). In Exp. 1, the relative durations of a sequence of intervals from an arithmetic progression were held constant while the mean interval was varied. Rate of responding was a monotonically increasing, negatively accelerated function of rate of reinforcement over a range from 8.4 to 300 reinforcements per hour. The rate of responding also increased as time passed within the individual intervals of a given schedule. In Exp. 2 and 3, several variable-interval schedules made up of different sequences of intervals were examined. In each schedule, the rate of responding at a particular time within an interval was shown to depend at least in part on the local rate of reinforcement at that time, derived from a measure of the probability of reinforcement at that time and the proximity of potential reinforcements at other times. The functional relationship between rate of responding and rate of reinforcement at different times within the intervals of a single schedule was similar to that obtained across different schedules in Exp. 1. Experiments 4, 5, and 6 examined fixed-interval and two-valued (mixed fixed-interval fixed-interval) schedules, and demonstrated that reinforcement at one time in an interval had substantial effects on responding maintained at other times. It was concluded that the rate of responding maintained by a given interval schedule depends not on the overall rate of reinforcement provided but rather on the summation of different local effects of reinforcement at different times within intervals.
Full text
PDF







































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. The reinforcement of least-frequent interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):581–591. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: a baseline for the study of reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:299–300. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. C. The effect of deprivation and frequency of reinforcement on variable-interval responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Aug;1(3):221–228. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. Some time-correlated reinforcement schedules and their effects on behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Jan;2(1):1–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming W. W., Schoenfeld W. N. Behavior under extended exposure to a high-value fixed interval reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Aug;1(3):245–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. Free-operant behavior under conditions of delayed reinforcement. I. CRF-type schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:221–234. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEWS P. B. The effect of multiple S delta periods on responding on a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jul;5:369–374. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J. PROPERTIES OF BEHAVIOR UNDER RANDOM INTERVAL REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:607–616. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLEY J. D. An experimental outline for building and exploring multi-operant behavior repertoires. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5(Suppl):113–166. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLLUB L. R. THE RELATIONS AMONG MEASURES OF PERFORMANCE ON FIXED-INTERVAL SCHEDULES. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Sep;7:337–343. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E. The behavioral effects of some temporally defined schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Jan;1:45–55. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. The effects of noxious stimulus intensity and duration during intermittent reinforcement of escape behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1952 Dec;45(6):538–549. doi: 10.1037/h0055989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLENSON J. R. Some behavioral effects of a two-valued, temporally defined reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1959 Jul;2:191–202. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1959.2-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malott R. W., Cumming W. W. Concurrent schedules of interresponse time reinforcement: probability of reinforcement and the lower bounds of the reinforced interresponse time intervals. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):317–325. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millenson J. R. Probability of response and probability of reinforcement in a response-defined analogue of an interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Mar;9(2):87–94. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millenson J. R. Random interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6(3):437–443. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVIN J. A. TWO PARAMETERS OF CONDITIONED REINFORCEMENT IN A CHAINING SITUATION. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1964 Dec;58:367–373. doi: 10.1037/h0046266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Chung S. H. Quasi-reinforcement: control of responding by a percentage-reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):45–54. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S., CATANIA A. C. Temporal discrimination in pigeons. Science. 1962 Jan 26;135(3500):314–315. doi: 10.1126/science.135.3500.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Relativity of response rate and reinforcement frequency in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Apr;4:179–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Some limitations on behavioral contrast and induction during successive discrimination. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:131–139. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. Discrimination and emission of temporal intervals by pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):65–68. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADDON J. E. SOME PROPERTIES OF SPACED RESPONDING IN PIGEONS. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Jan;8:19–27. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld W. N., Cumming W. W., Hearst E. ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Aug;42(8):563–570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.8.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenfeld W. N., Cumming W. W. STUDIES IN A TEMPORAL CLASSIFICATION OF REINFORCEMENT SCHEDULES: SUMMARY AND PROJECTION. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 May;46(5):753–758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.5.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P. The reinforcement of short interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):425–434. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Attention and temporal discrimination: factors controlling responding under a cyclic-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jul;10(4):349–359. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs A. The discrimination of stimulus duration by pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):223–238. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS B., LATIES V. G. DRUG EFFECTS ON THE TEMPORAL PATTERNING OF BEHAVIOR. Fed Proc. 1964 Jul-Aug;23:801–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS B., MOORE E. W. Drive level as a factor in distribution of responses in fixed-interval reinforcement. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Aug;52(2):82–84. doi: 10.1037/h0045007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON M. P. Periodic reinforcement interval and number of periodic reinforcements as parameters of response strength. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1954 Feb;47(1):51–56. doi: 10.1037/h0057224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


