Abstract
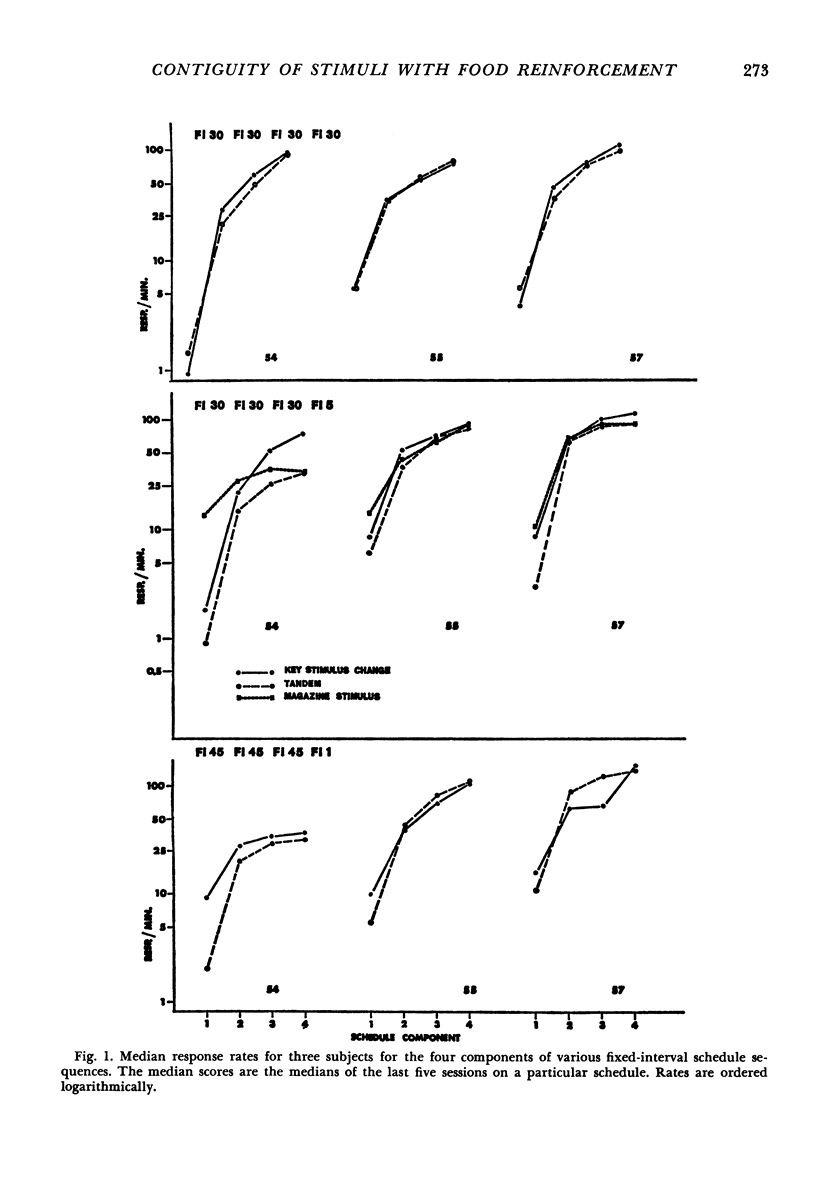
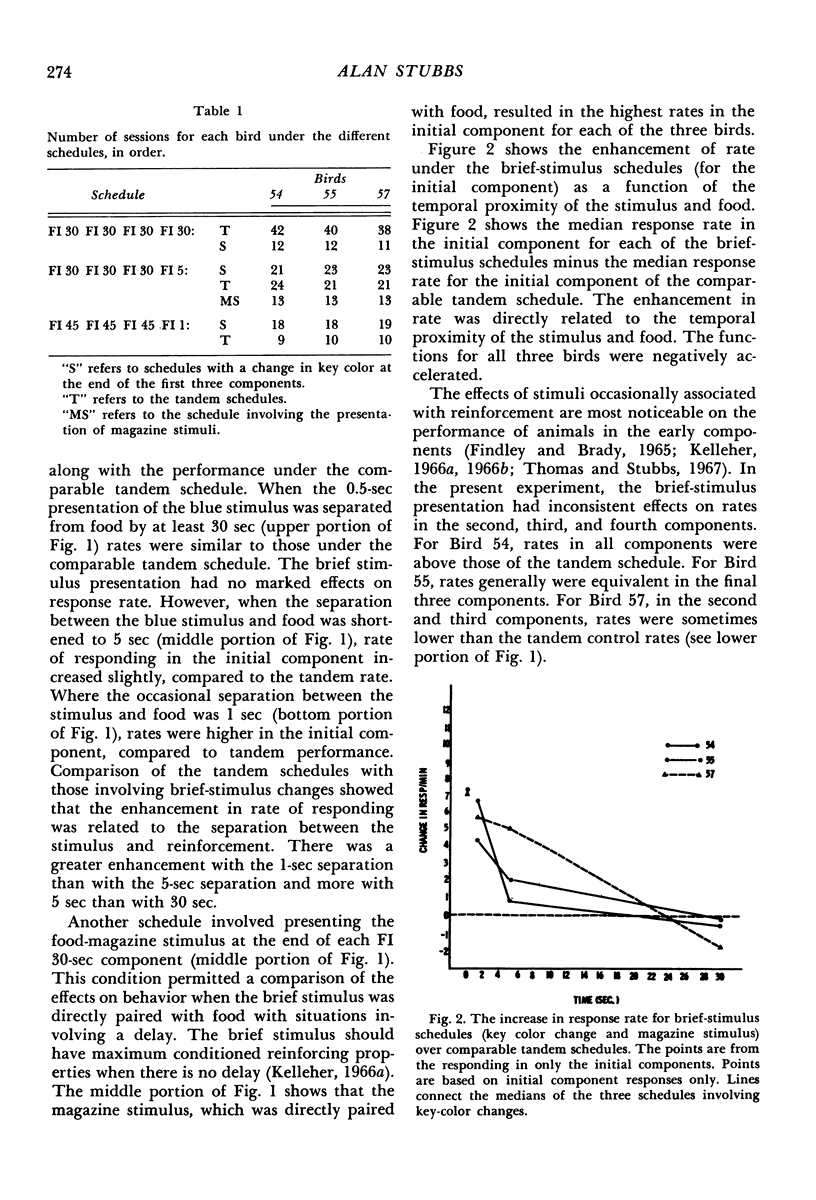
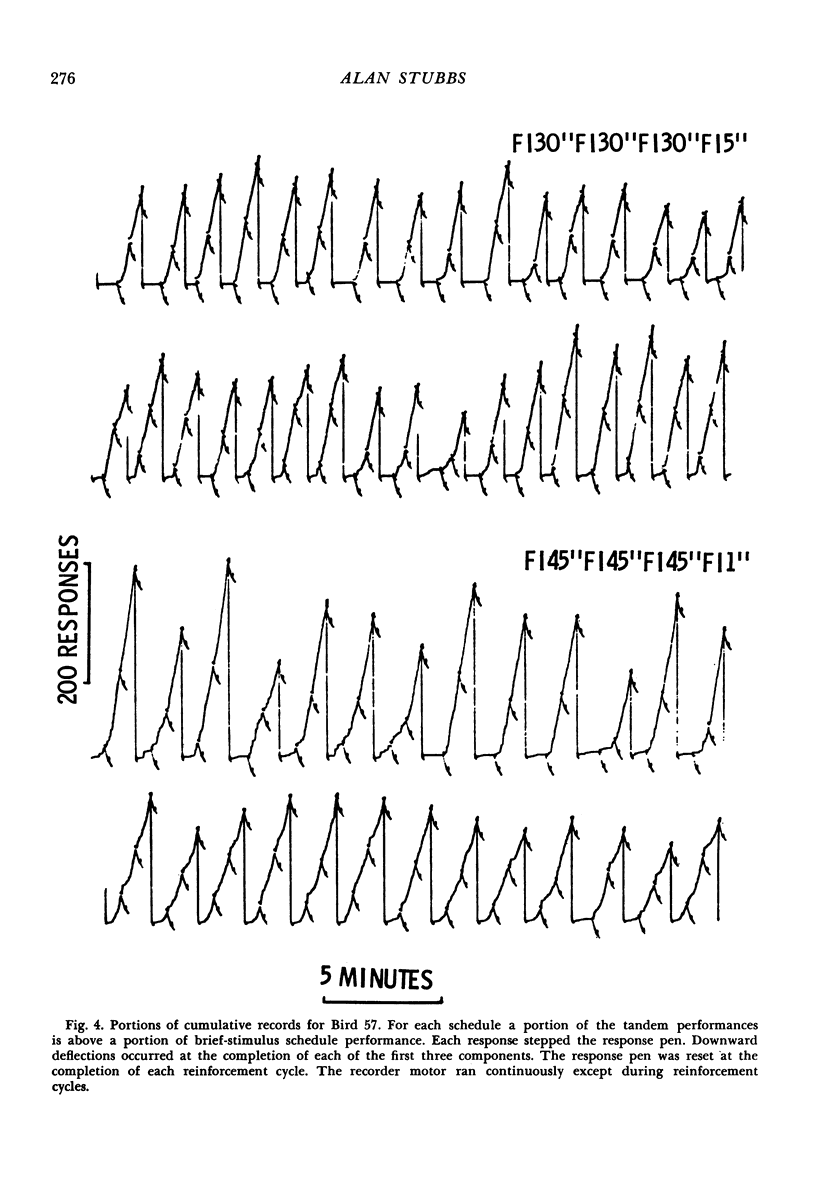
Pigeons performed on second-order schedules of reinforcement consisting of four fixed-interval components. Only the terminal component ended with food. Performance was studied both when a brief stimulus followed the completion of each of the first three fixed intervals (brief-stimulus schedule) and when the stimulus was omitted (tandem schedule). Variations in the temporal contiguity of the last presentation of the stimulus and the presentation of food indicated that the shorter the delay, the greater was the enhancement of rate of responding in comparison with tandem performance. A positively accelerated pattern of responding within fixed-interval components was a function of the contiguity of the brief stimulus and reinforcement; this pattern was absent for all tandem-schedule performance.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSH P. J. The influence of two variables upon the establishment of a secondary reinforcer for operant responses. J Exp Psychol. 1951 Jan;41(1):62–73. doi: 10.1037/h0059386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lorge J. Fixed-interval behavior maintained by conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 May;10(3):271–276. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINDLEY J. D., BRADY J. V. FACILITATION OF LARGE RATIO PERFORMANCE BY USE OF CONDITIONED REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Mar;8:125–129. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKINS W. O. A temporal gradient of derived reinforcement. Am J Psychol. 1950 Apr;63(2):237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T. Conditioned reinforcement in second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):475–485. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Chung S. H. Quasi-reinforcement: control of responding by a percentage-reinforcement schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):45–54. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R., Stubbs A. Stimulus control of temporally spaced responding in second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Mar;10(2):175–183. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman D. W. Intermittent Reinforcement of Discriminatively Controlled Responses and Runs of Responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jan;3(1):83–91. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


