Abstract
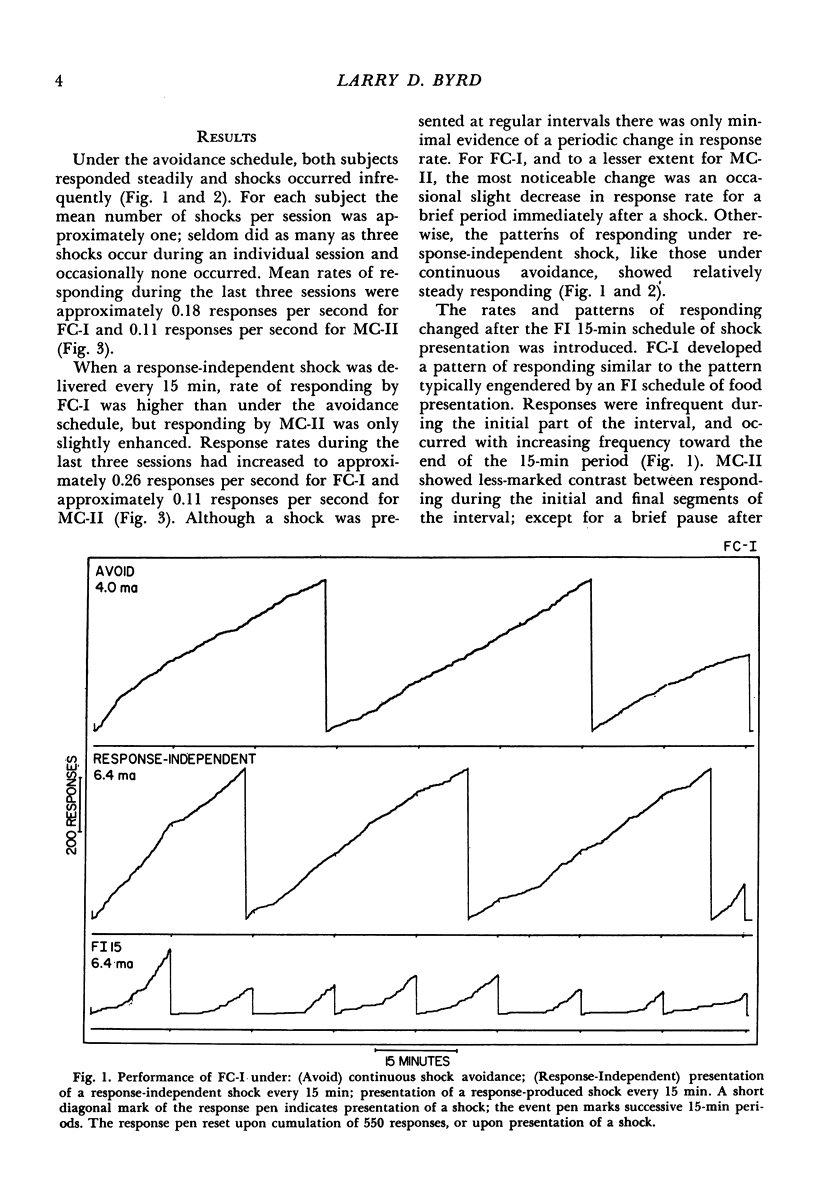
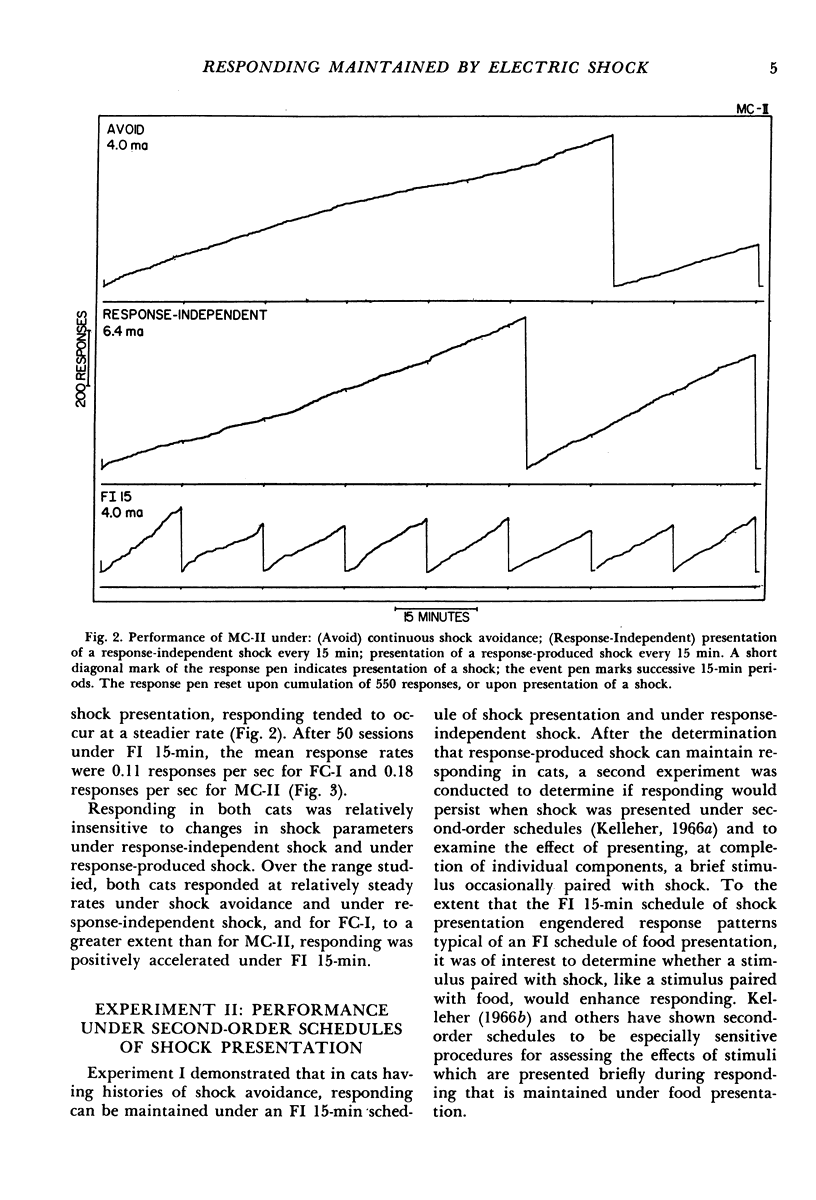
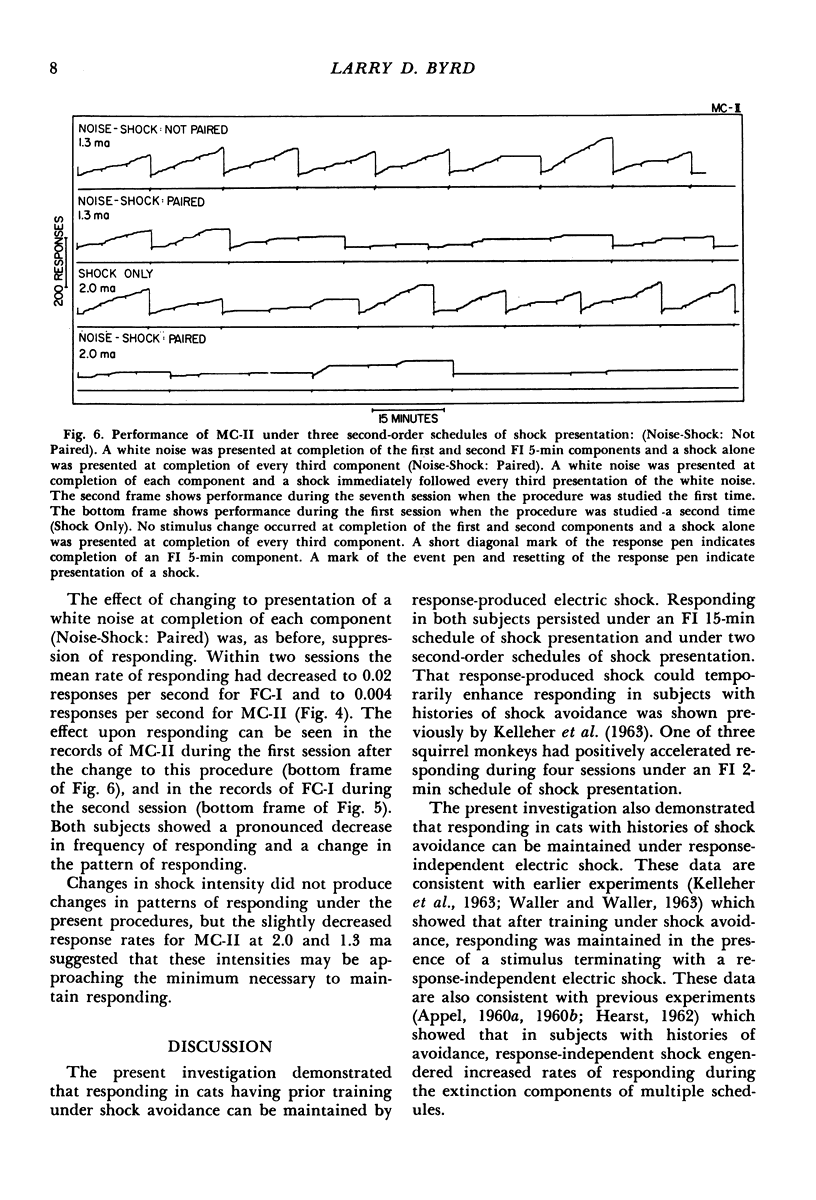
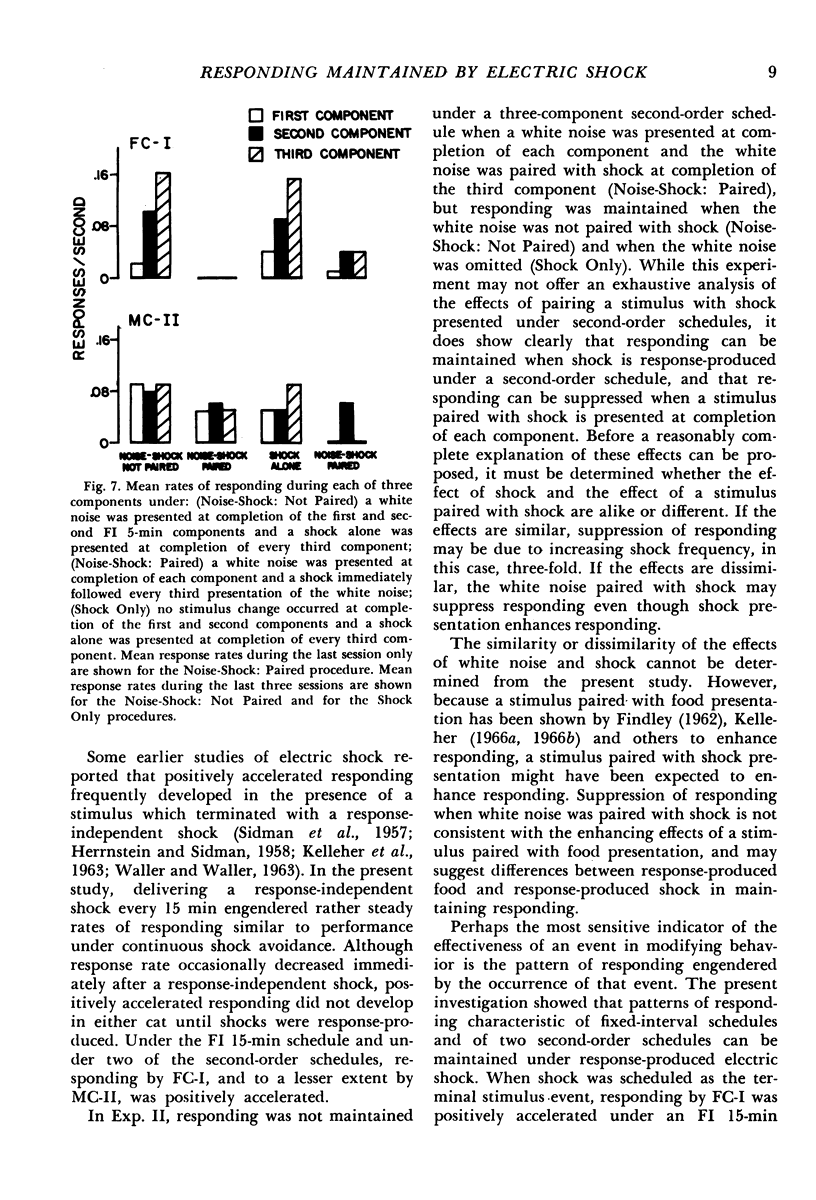
Key-pressing responses in the cat were maintained under conditions in which brief electric shock was first postponed by responses (avoidance), then periodically presented independently of responses, and finally produced by responses on a fixed-interval schedule of 15 min (FI 15-min). A steady rate of responding occurred under shock avoidance and under response-independent shock; positively accelerated responding was engendered by the FI 15-min schedule. A second experiment studied responding under second-order schedules composed of three FI 5-min components. Responding was suppressed when a stimulus was presented briefly at completion of each FI 5-min component and a shock followed the brief stimulus at completion of the third component. Responding was maintained when each of the first two components was completed either with or without presentation of a brief stimulus and a shock alone was presented at completion of the third FI 5-min component.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLEVILLE R. E., ROHLES F. H., GRUNZKE M. E., CLARK F. C. DEVELOPMENT OF A COMPLEX MULTIPLE SCHEDULE IN THE CHIMPANZEE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:549–556. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E. Concurrent generalization gradients for food-controlled and shock-controlled behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5:19–31. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J., SIDMAN M. Avoidance conditioning as a factor in the effects of unavoidable shocks on food-reinforced behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1958 Jun;51(3):380–385. doi: 10.1037/h0038487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., RIDDLE W. C., COOK L. PERSISTENT BEHAVIOR MAINTAINED BY UNAVOIDABLE SHOCKS. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:507–517. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T., Morse W. H. Schedules using noxious stimuli. III. Responding maintained with response-produced electric shocks. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):819–838. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearney J. W. Maintenance of responding under a fixed-interval schedule of electric shock-presentation. Science. 1968 Jun 14;160(3833):1249–1251. doi: 10.1126/science.160.3833.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Avoidance conditioning with brief shock and no exteroceptive warning signal. Science. 1953 Aug 7;118(3058):157–158. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3058.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M., HERRNSTEIN R. J., CONRAD D. G. Maintenance of avoidance behavior by unavoidable shocks. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1957 Dec;50(6):553–557. doi: 10.1037/h0043500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLER M. B., WALLER P. F. The effects of unavoidable shocks on a multiple schedule having an avoidance component. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jan;6:29–37. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



