Abstract
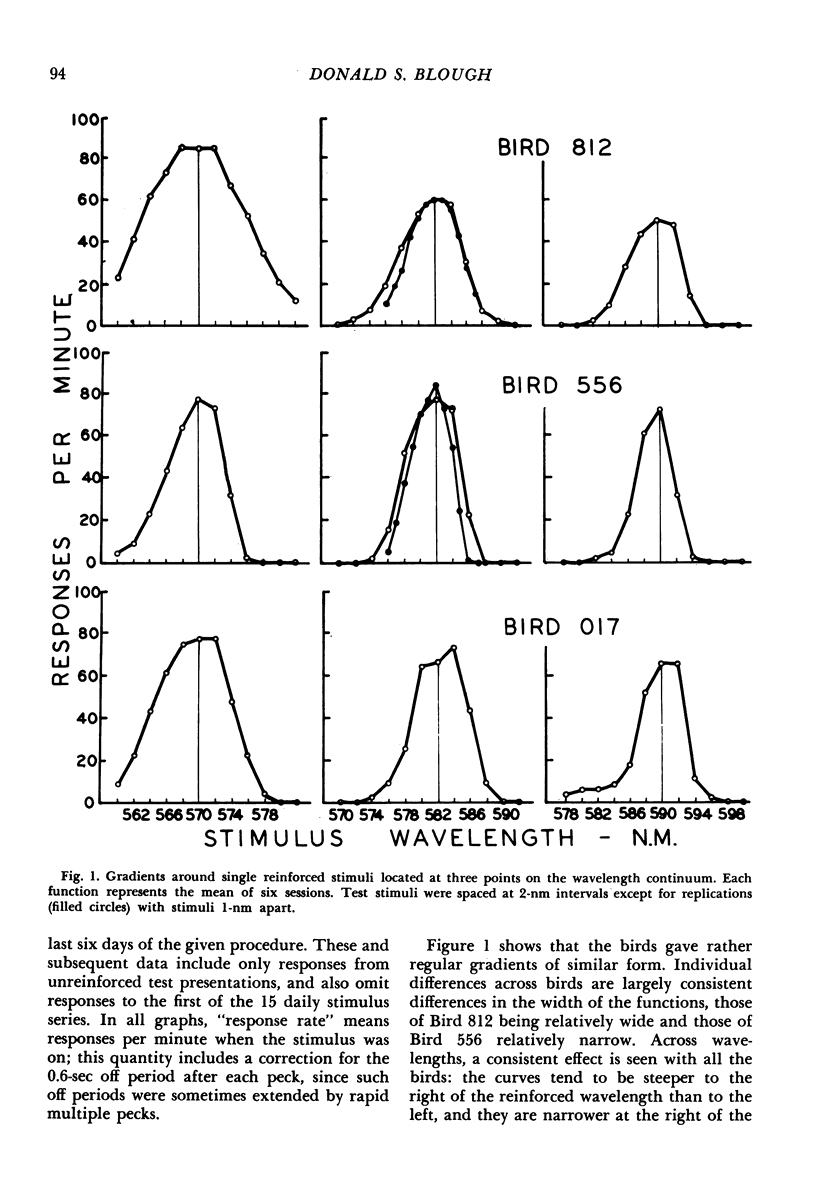
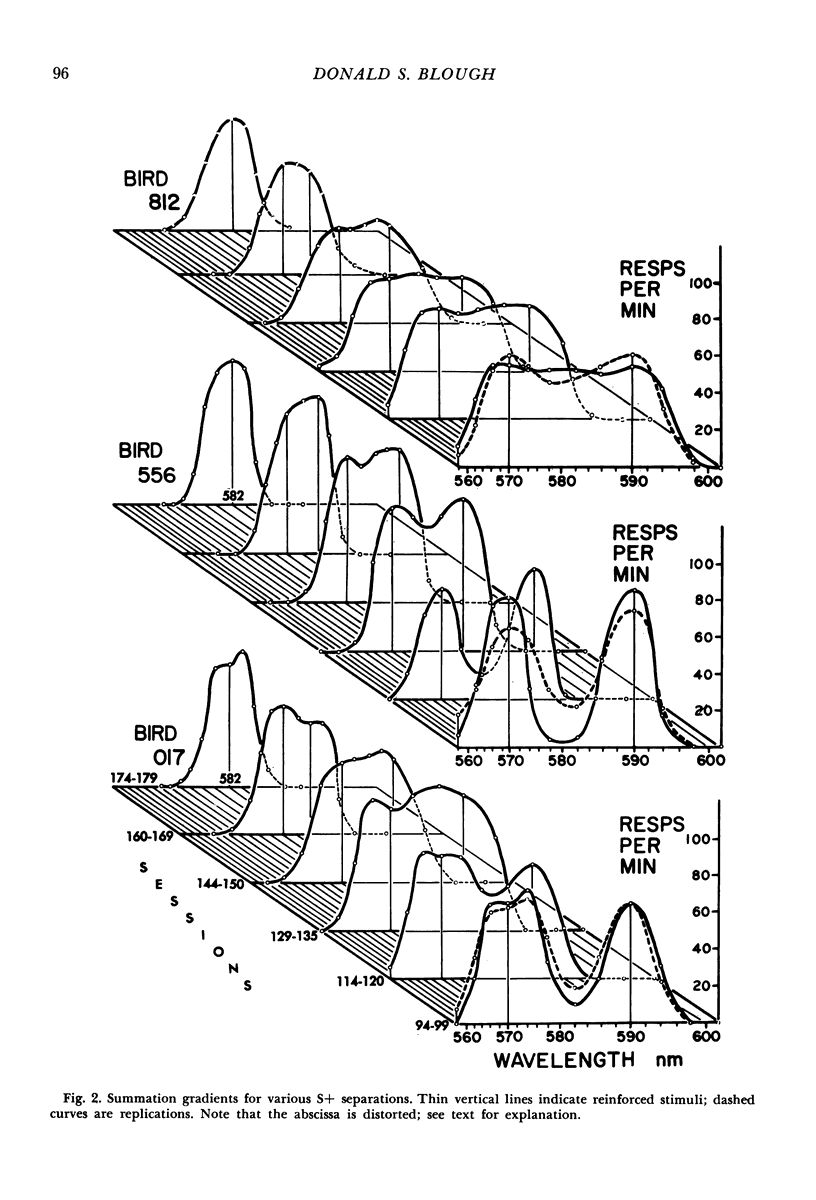
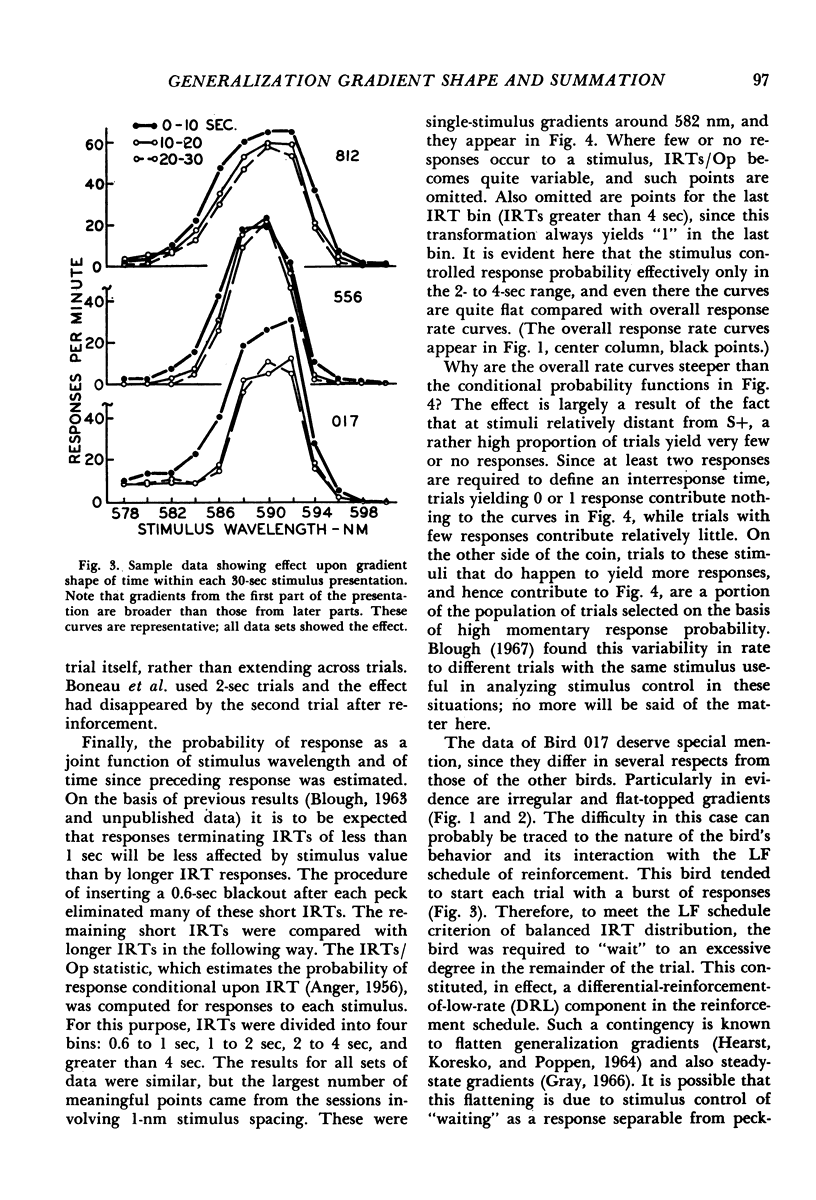
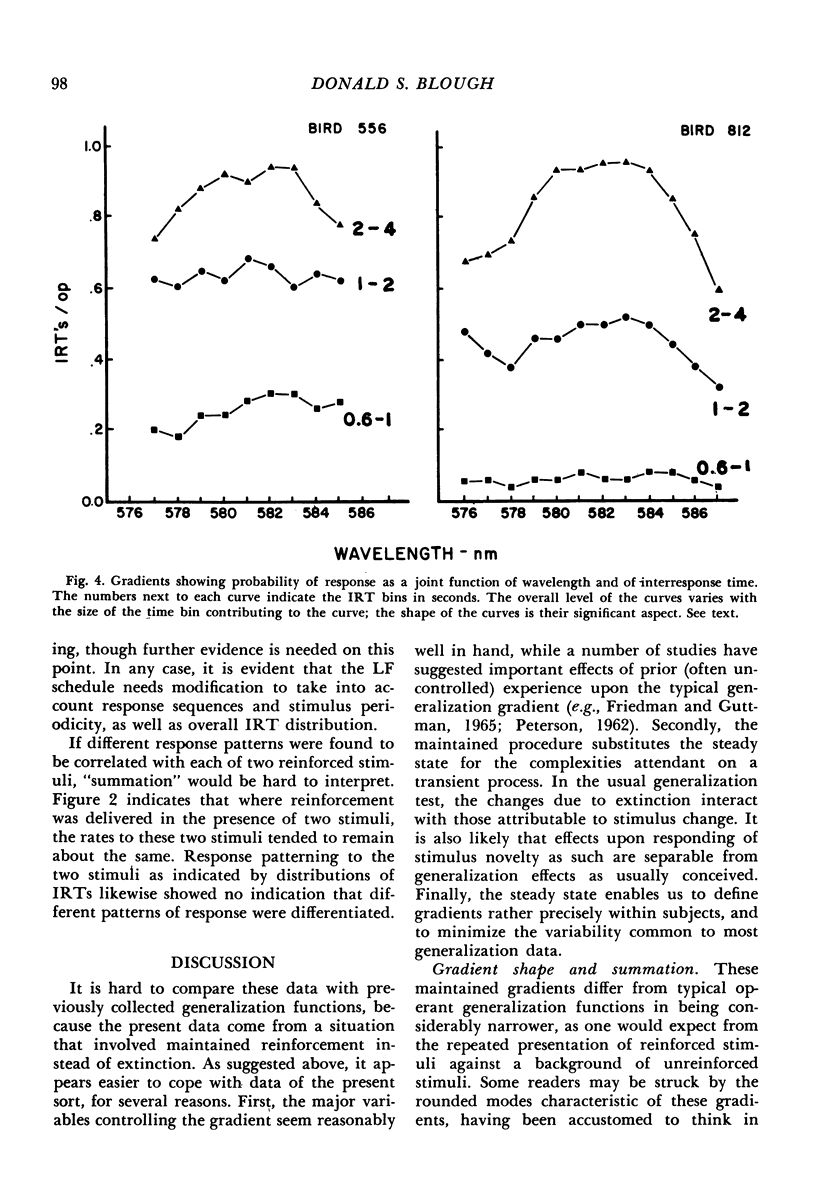
Pigeons' pecks at one or two wavelengths were reinforced intermittently. Random series of adjacent wavelengths appeared without reinforcement. Gradients of responding around the reinforced wavelengths were allowed to stabilize over a number of sessions. The single (one reinforced stimulus) and summation (two reinforced stimuli) gradients were consistent with a statistical decision account of the generalization process.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGER D. The dependence of interresponse times upon the relative reinforcement of different interresponse times. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Sep;52(3):145–161. doi: 10.1037/h0041255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOUGH D. S. Spectral sensitivity in the pigeon. J Opt Soc Am. 1957 Sep;47(9):827–833. doi: 10.1364/josa.47.000827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. Interresponse time as a function of continuous variables: a new method and some data. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6(2):237–246. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. Stimulus generalization as signal detection in pigeons. Science. 1967 Nov 17;158(3803):940–941. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3803.940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough D. S. The reinforcement of least-frequent interresponse times. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):581–591. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boneau C. A., Cole J. L. Decision theory, the pigeon, and the psychophysical function. Psychol Rev. 1967 Mar;74(2):123–135. doi: 10.1037/h0024287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boneau C. A., Holland M. K., Baker W. M. Color-discrimination performance of pigeons: effects of reward. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1113–1114. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARK W. A., MOLNAR C. E. THE LINC: A DESCRIPTION OF THE LABORATORY INSTRUMENT COMPUTER. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Jul 31;115:653–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTTMAN N., KALISH H. I. Discriminability and stimulus generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1956 Jan;51(1):79–88. doi: 10.1037/h0046219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON H. M. Effects of discrimination training on stimulus generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Nov;58:321–334. doi: 10.1037/h0042606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E., KORESKO M. B., POPPEN R. STIMULUS GENERALIZATION AND THE RESPONSE-REINFORCEMENT CONTINGENCY. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Sep;7:369–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALISH H. I., GUTTMAN N. Stimulus generalization after equal training on two stimuli. J Exp Psychol. 1957 Feb;53(2):139–144. doi: 10.1037/h0047916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALISH H. I., GUTTMAN N. Stimulus generalization after training on three stimuli: a test of the summation hypothesis. J Exp Psychol. 1959 Apr;57(4):268–272. doi: 10.1037/h0046433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LABERGE D., MARTIN D. R. AN ANALYSIS OF SUMMATED GENERALIZATION. J Exp Psychol. 1964 Jul;68:71–79. doi: 10.1037/h0044690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE W. H., SKINNER B. F. A second type of superstition in the pigeon. Am J Psychol. 1957 Jun;70(2):308–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON N. Effect of monochromatic rearing on the control of responding by wavelength. Science. 1962 Jun 1;136(3518):774–775. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3518.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrel R. A generalization gradient for auditory intensity in the rat. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Oct;1(4):303–313. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switalski R. W., Lyons J., Thomas D. R. Effects of interdimensional training on stimulus generalization. J Exp Psychol. 1966 Nov;72(5):661–666. doi: 10.1037/h0023795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



