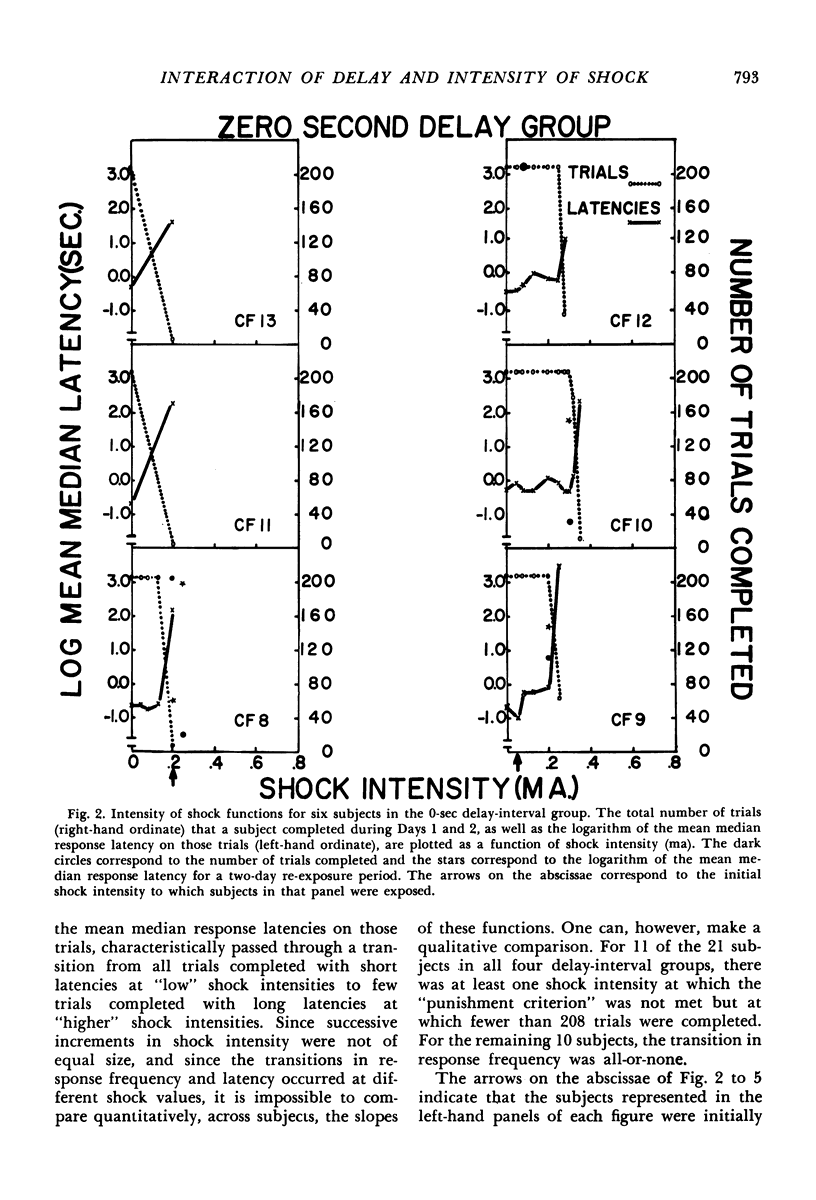
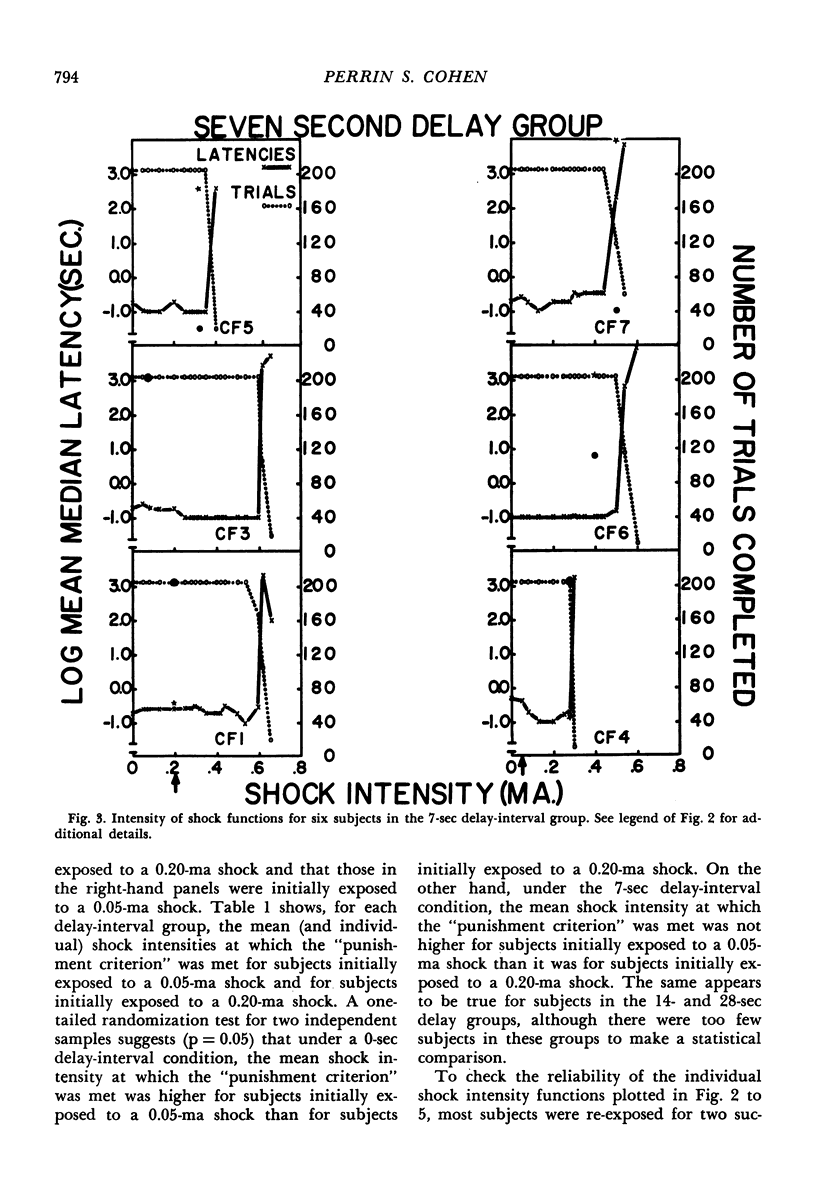
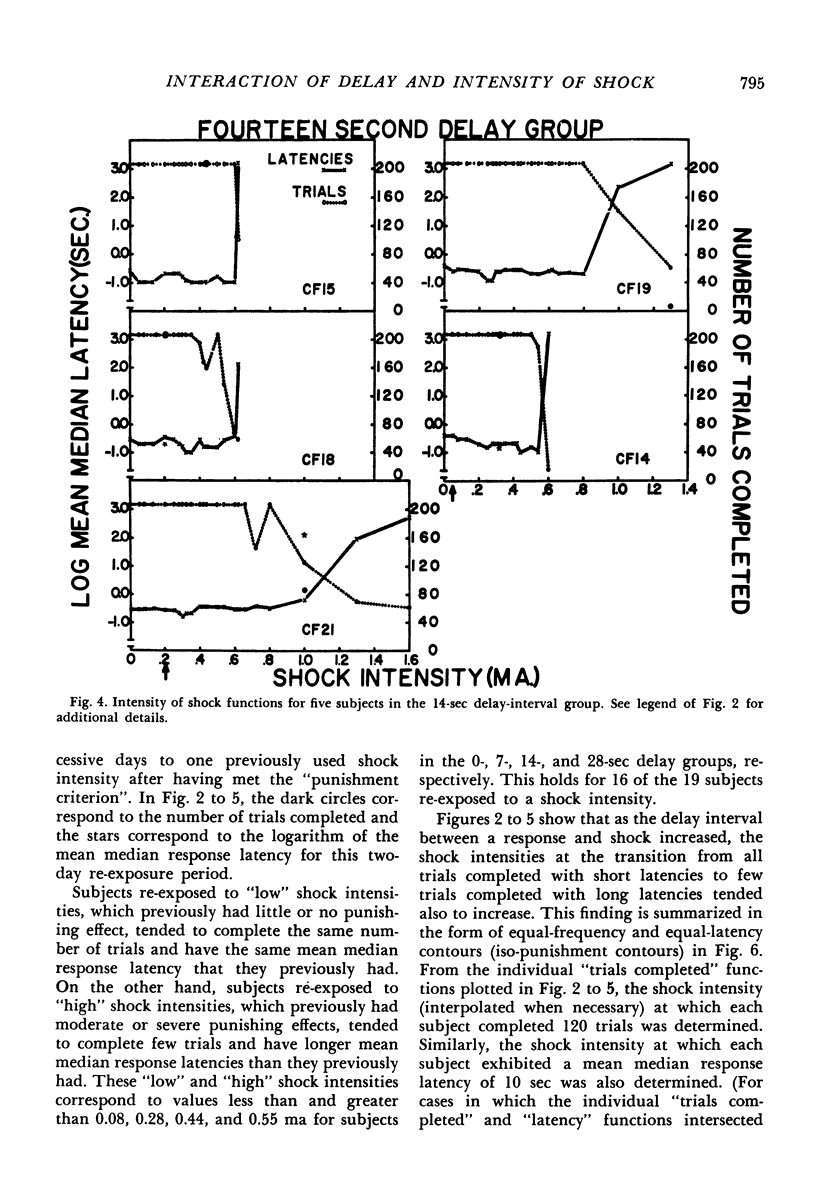
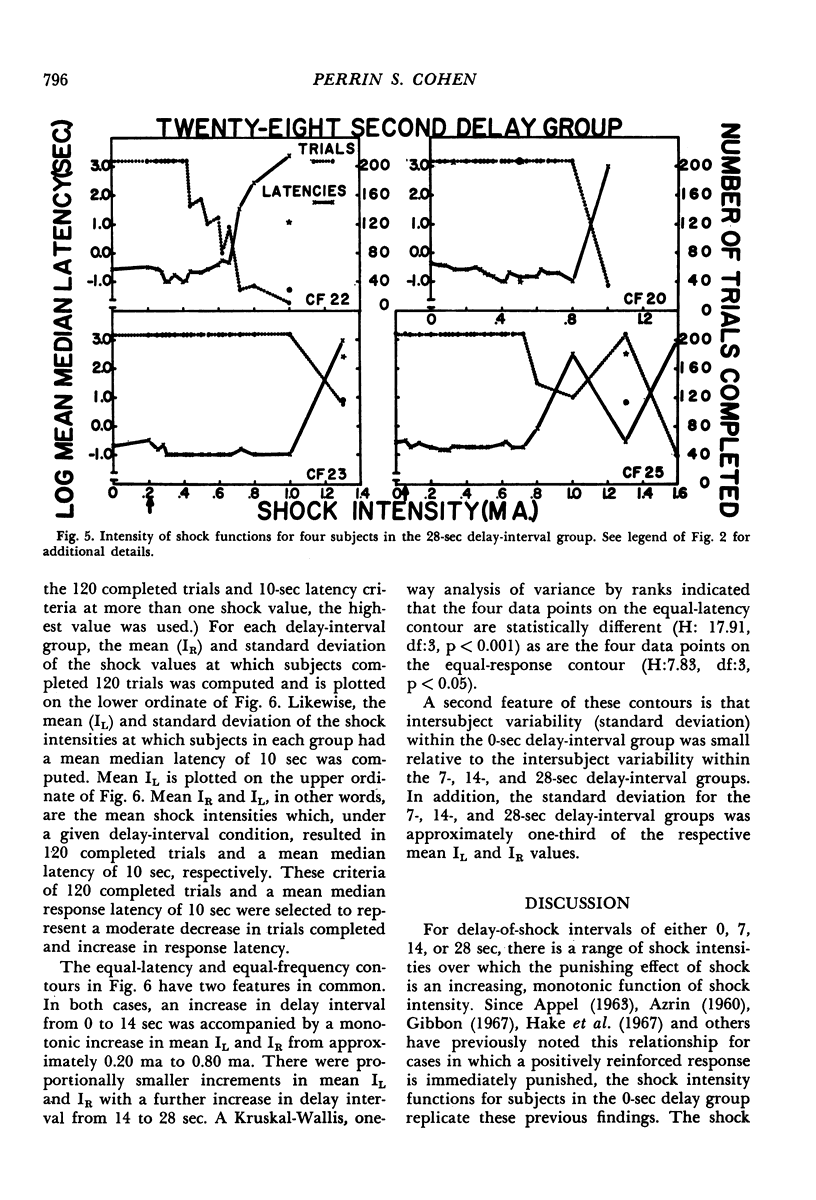
Abstract
A discrete-trial punishment procedure, with rats, was used to examine how delay-of-shock intervals of 0 to 28 sec and shock intensity interact to decrease the frequency and increase the latency of a positively reinforced response. For delay-of-shock intervals of 0, 7, 14, and 28 sec, there was a range of shock intensities, for some subjects, over which the punishing effect of shock was an increasing, monotonic function of shock intensity. For other subjects this transition was abrupt. Functions relating response frequency and latency measures to shock intensity were displaced toward higher values on the shock intensity axis with an increase in delay-of-shock interval. The effects of “gradual” and “abrupt” introduction to “severe” shock, as well as re-exposure to previously used shock intensities, were examined under both the immediate and delay-of-shock conditions. With delay-of-shock intervals of 7, 14, or 28 sec, shock intensities of approximately 0.50 milliamperes or greater were necessary to decrease substantially the number and increase the latency of the lever-pressing response. For the immediate punishment group this intensity was approximately 0.20 ma. These facts were related to Annau and Kamin's (1961) conditioned emotional response experiment in which a shock intensity of 0.49 ma or greater was required to suppress the rate of a positively reinforced response.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNAU Z., KAMIN L. J. The conditioned emotional response as a function of intensity of the US. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1961 Aug;54:428–432. doi: 10.1037/h0042199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL J. B. Punishment and shock intensity. Science. 1963 Aug 9;141(3580):528–529. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3580.528-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AZRIN N. H. Effects of punishment intensity during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Apr;3:123–142. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp D. S., Raymond G. A., Church R. M. Temporal relationship between response and punishment. J Exp Psychol. 1967 May;74(1):114–123. doi: 10.1037/h0024518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DINSMOOR J. A. Punishment. I. The avoidance hypothesis. Psychol Rev. 1954 Jan;61(1):34–46. doi: 10.1037/h0062725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbon J. Discriminated punishment: avoidable and unavoidable shock. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):451–460. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT H. F., BRADY J. V. Some effects of punishment and intercurrent anxiety on a simple operant. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1955 Aug;48(4):305–310. doi: 10.1037/h0042529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hake D. F., Azrin N. H., Oxford R. The effects of punishment intensity on squirrel monkeys. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jan;10(1):95–107. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. M. Measurement of stimulus control during discriminative operant conditioning. Psychol Bull. 1965 Nov;64(5):365–376. doi: 10.1037/h0022537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMIN L. J. The delay-of-punishment gradient. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1959 Aug;52:434–437. doi: 10.1037/h0045089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsh E. B. Changes in Intensity of Punishment: Effect on Running Behavior of Rats. Science. 1963 Jun 7;140(3571):1084–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3571.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER N. E. Learning resistance to pain and fear: effects of overlearning, exposure, and rewarded expsure in context. J Exp Psychol. 1960 Sep;60:137–145. doi: 10.1037/h0043321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


