Abstract
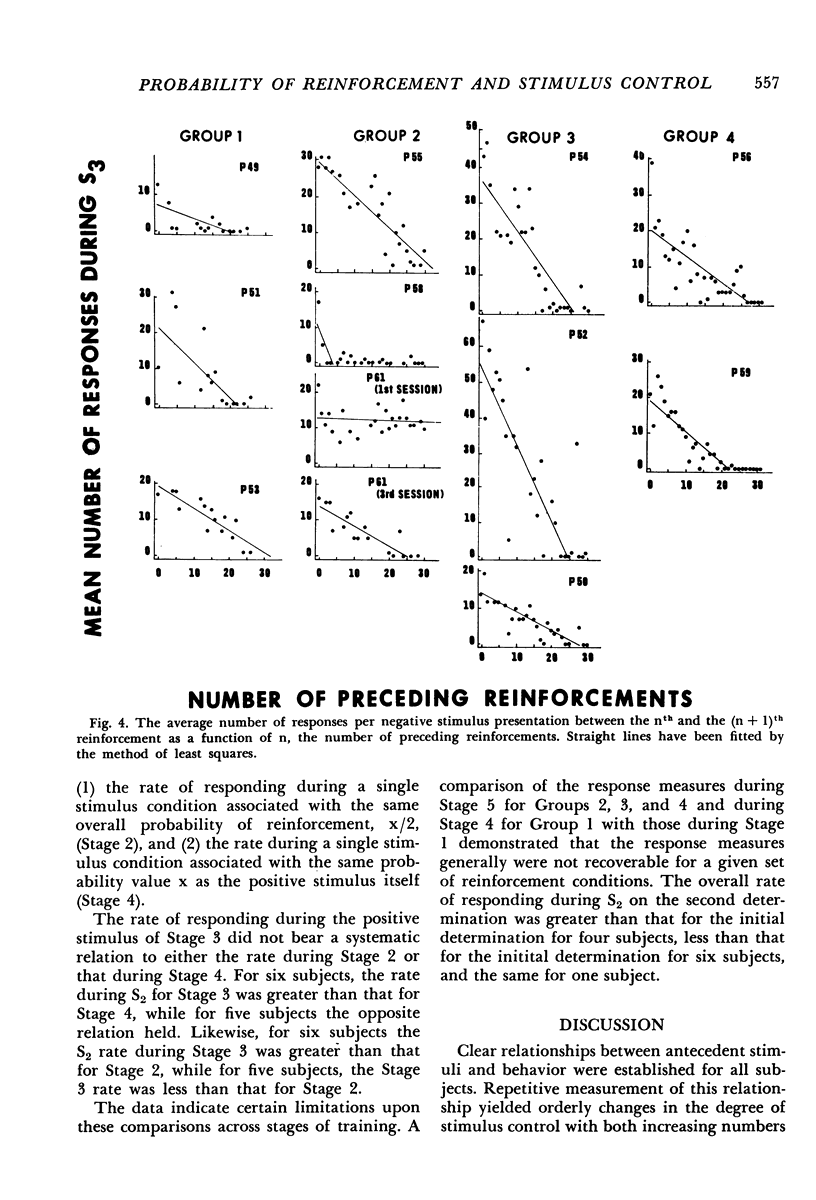
Pigeons were trained with a successive discrimination procedure in which responding during the negative stimulus was never reinforced and responding during the positive stimulus was reinforced according to one of four probability values. This discrimination training followed extensive training with a single, neutral stimulus and the same temporal distribution of reinforcements. The development of stimulus control was studied by tracing the difference in rate of responding between the positive and negative stimuli over the course of discrimination training. Response rate during the positive stimulus remained constant, while that during the negative stimulus decreased to zero. The probability of reinforcement associated with the positive stimulus affected both the total number of responses emitted during the negative stimulus and the number of negative stimulus presentations during which responding occurred. However, the number of reinforcements during the positive stimulus preceding the attainment of various degrees of stimulus control was similar for all probability values.
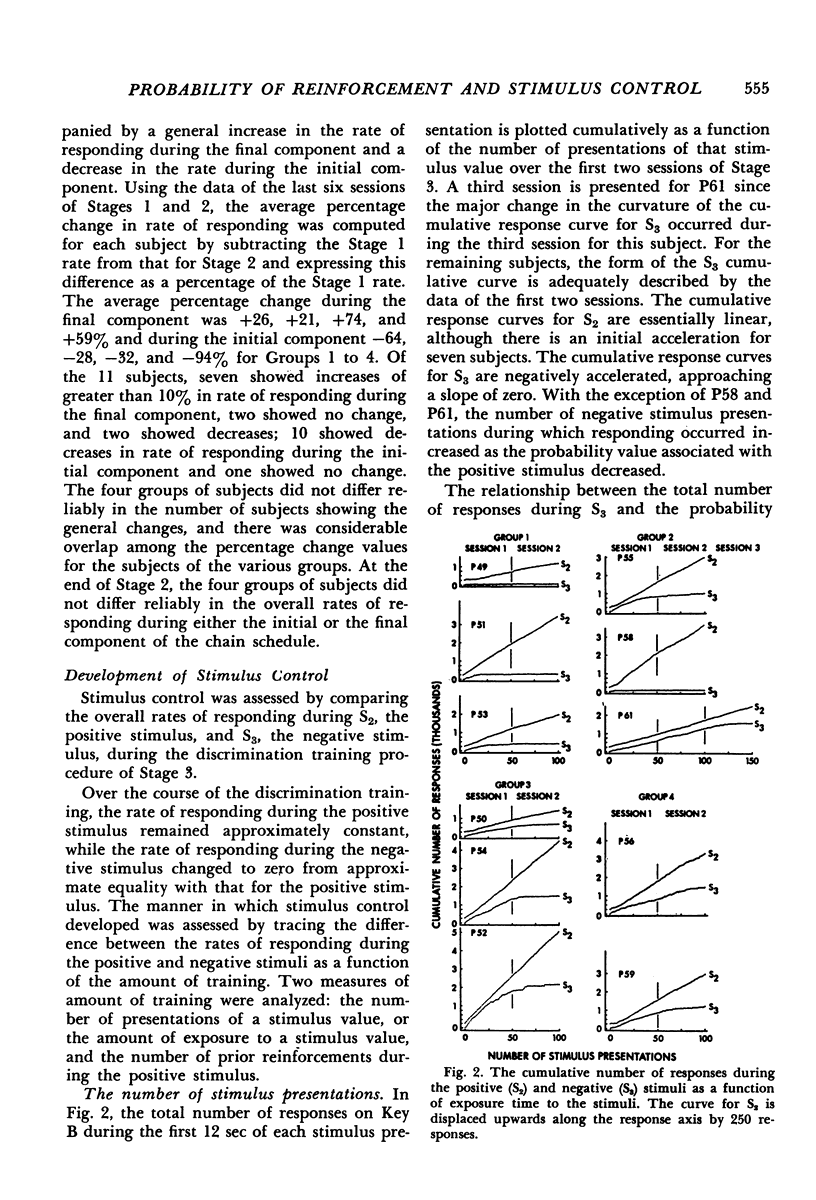
Full text
PDF

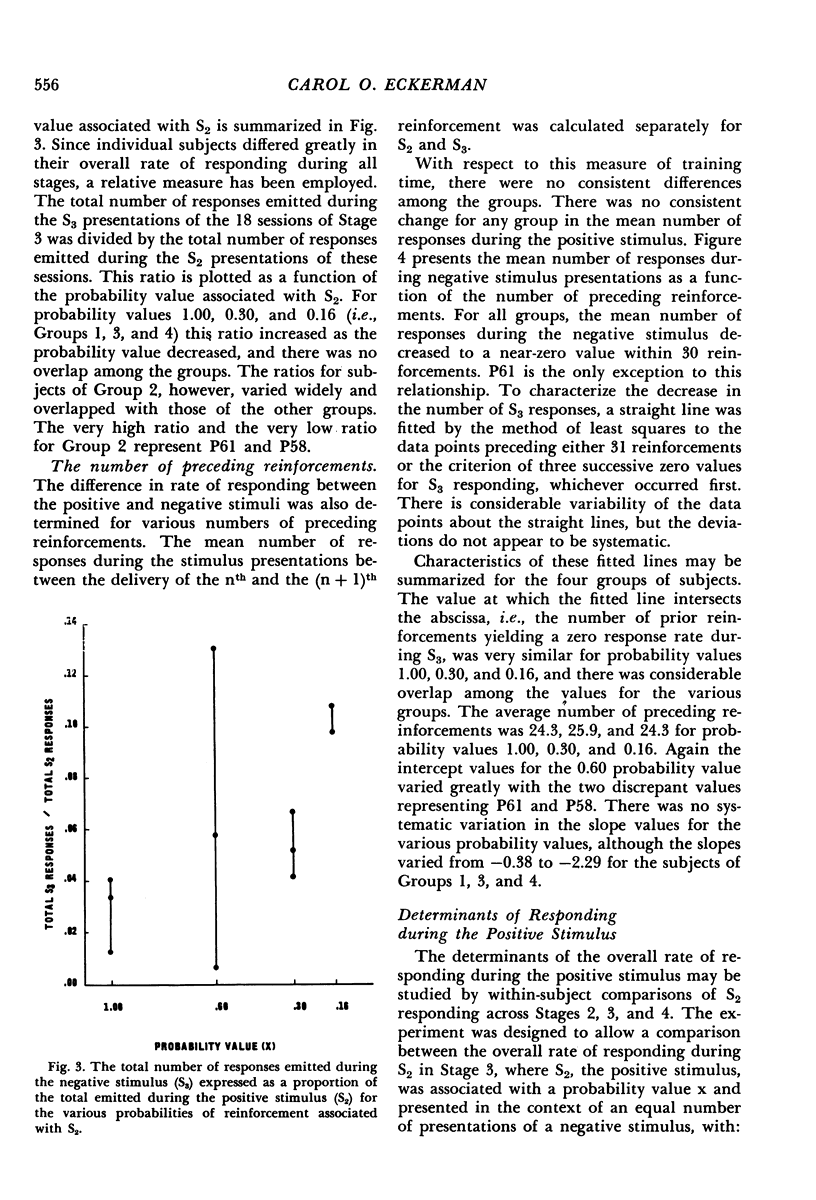


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Farmer J., Schoenfeld W. N. Varying temporal placement of an added stimulus in a fixed-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):369–375. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABER A., KALISH H. I. PREDICTION OF DISCRIMINATION FROM GENERALIZATION AFTER VARIATIONS IN SCHEDULE OF REINFORCEMENT. Science. 1963 Oct 18;142(3590):412–413. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3590.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E. Concurrent generalization gradients for food-controlled and shock-controlled behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Jan;5:19–31. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARST E., KORESKO M. B., POPPEN R. STIMULUS GENERALIZATION AND THE RESPONSE-REINFORCEMENT CONTINGENCY. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Sep;7:369–380. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins H. M. Measurement of stimulus control during discriminative operant conditioning. Psychol Bull. 1965 Nov;64(5):365–376. doi: 10.1037/h0022537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKINTOSH N. J. SELECTIVE ATTENTION IN ANIMAL DISCRIMINATION LEARNING. Psychol Bull. 1965 Aug;64:124–150. doi: 10.1037/h0022347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
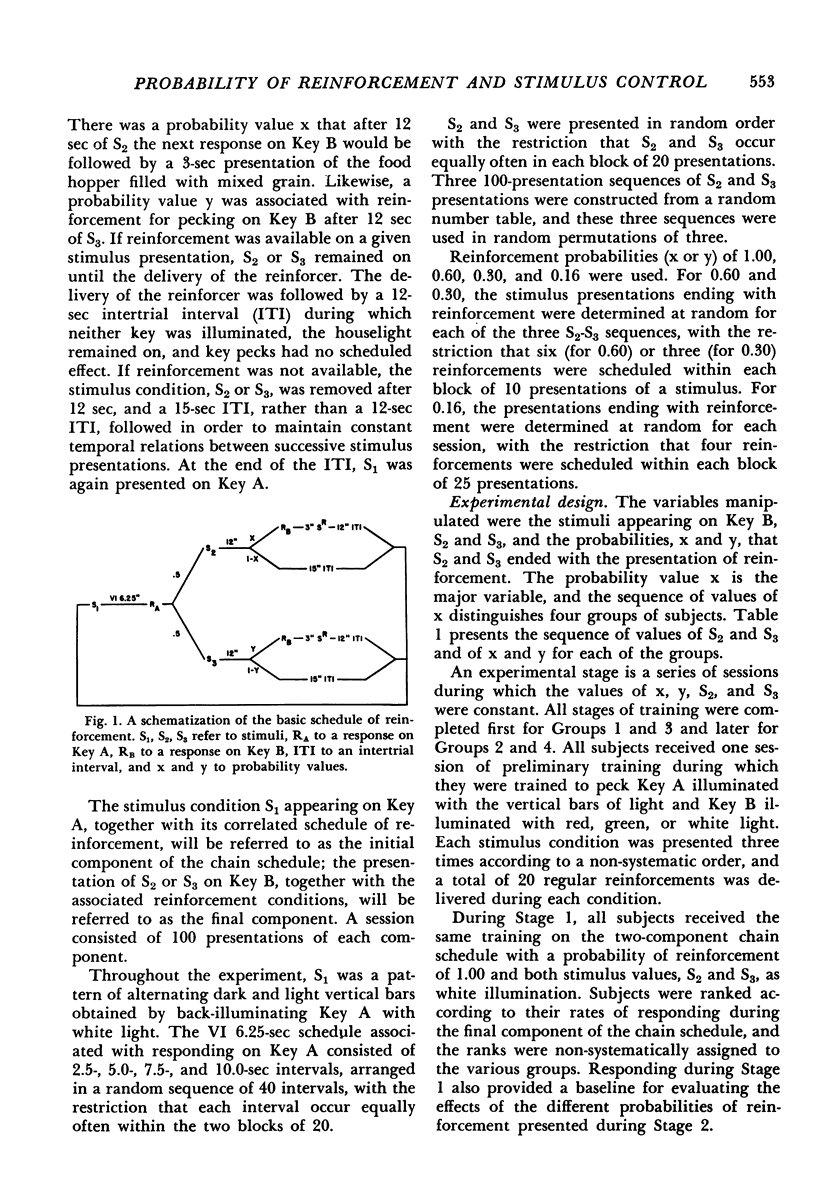
- Nevin J. A. Effects of reinforcement scheduling on simultaneous discrimination performance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 May;10(3):251–260. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


