Abstract
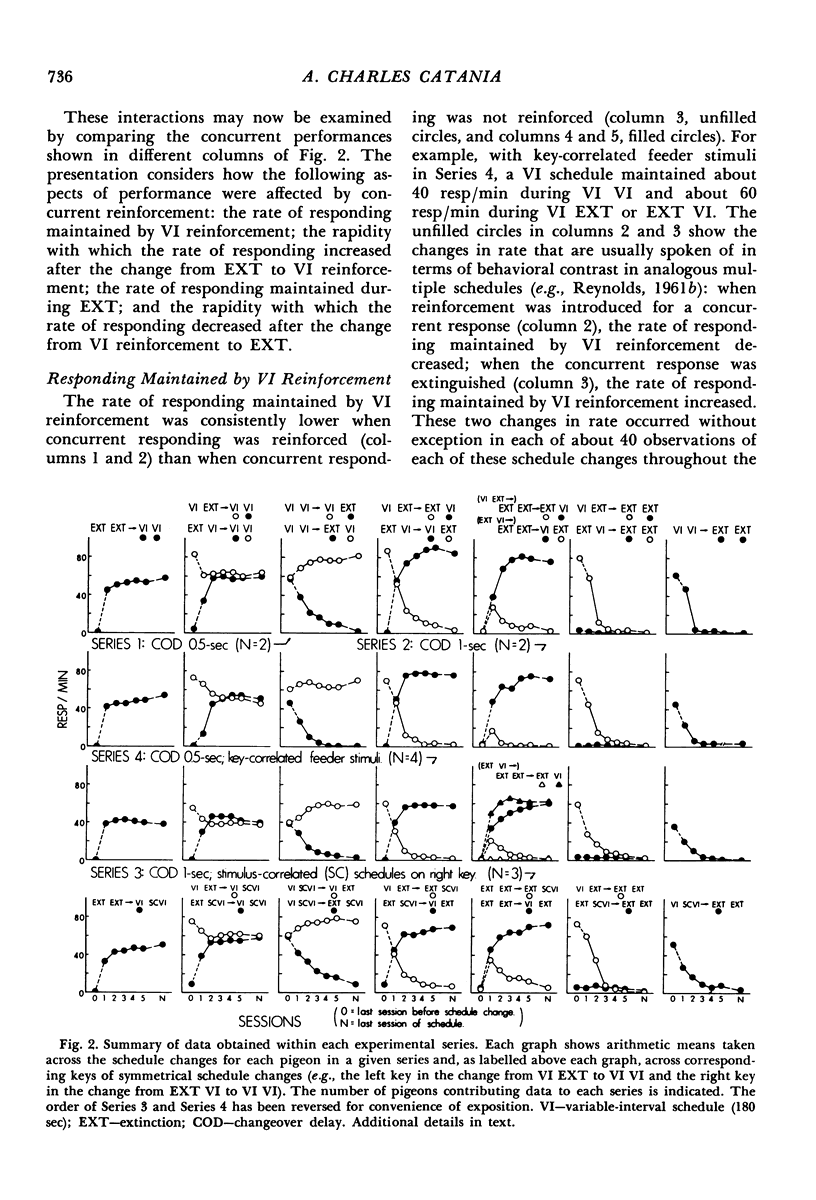
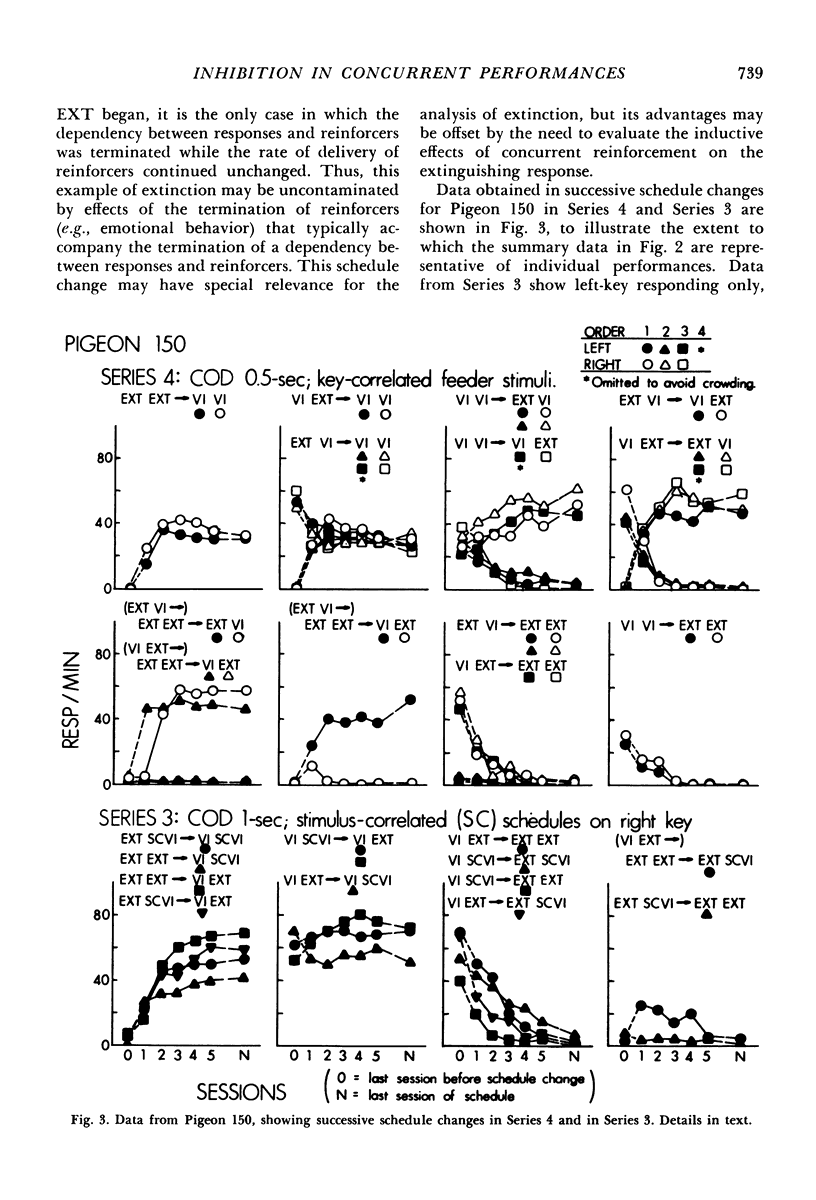
In an analysis of interactions between concurrent performances, variable-interval reinforcement was scheduled, in various sequences, for both keys, for only one key, or for neither key of a two-key pigeon chamber. With changeover delays of 0.5 or 1.0 sec, and with each key's reinforcements discriminated on the basis of key-correlated feeder stimuli, reinforcement of pecks on one key reduced the pecking maintained by reinforcement on the other key. The decrease in pecking early after reinforcement was discontinued on one key was not substantially affected by whether pecks on the other key were reinforced, but after reinforcement was discontinued on both keys, reinstatement of reinforcement for one key sometimes produced transient increases in pecking on the other key. Correlating the availability of right-key reinforcements with a stimulus, which maintained right-key reinforcement while reducing right-key pecking to negligible levels, demonstrated that these interactions depended on concurrent reinforcement, not concurrent responding. Thus, reinforcement of a response, but not necessarily the occurrence of the response, inhibits other reinforced responses. Compared with accounts in terms of excitatory effects of extinction, often invoked in treatments of behavioral contrast, this inhibitory account has the advantage of dealing only with observed dimensions of behavior.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRETHOWER D. M., REYNOLDS G. S. A facilitative effect of punishment on unpunished behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:191–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C., CUTTS D. Experimental control of superstitious responding inhumans. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:203–208. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Concurrent performances: reinforcement interaction and response independence. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:253–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATANIA A. C. Independence of concurrent responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:175–184. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Deegan J. F., Cook L. Concurrent fixed-ratio and avoidance responding in the squirrel monkey. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 May;9(3):227–231. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findley J. D. Preference and Switching under Concurrent Scheduling. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):123–144. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. SECONDARY REINFORCEMENT AND RATE OF PRIMARY REINFORCEMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Jan;7:27–36. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz W. C. Punishment and rate of positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):285–292. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovland C. I. Inhibition of Reinforcement' and Phenomena of Experimental Extinction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1936 Jun;22(6):430–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.22.6.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander D. G., Irwin R. J. Multiple schedules: effects of the distribution of reinforcements between component on the distribution of responses between conponents. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):517–524. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A. Differential reinforcement and stimulus control of not responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):715–726. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Shettleworth S. J. An analysis of contrast effects in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):305–315. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID R. L. The role of the reinforcer as a stimulus. Br J Psychol. 1958 Aug;49(3):202–209. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1958.tb00658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. Behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:57–71. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS G. S. OPERANT EXTINCTION NEAR ZERO. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:173–176. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Baum W. M. Response rate as a function of amount of reinforcement for a signalled concurrent response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Jan;12(1):11–16. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. Induction, contrast, and resistance to extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jul;11(4):453–457. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S., Limpo A. J. On some causes of behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):543–547. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. S. Potency of Conditioned Reinforcers Based on Food and on Food and Punishment. Science. 1963 Mar 1;139(3557):838–839. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3557.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEGAL E. F. Behavioral interaction under concurrent spaced-responding, variable-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:263–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Pliskoff S. S. Changeover delay and concurrent schedules: some effects on relative performance measures. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Nov;10(6):517–527. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staddon J. E. Attention and temporal discrimination: factors controlling responding under a cyclic-interval schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Jul;10(4):349–359. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRACE H. S. Errorless transfer of a discrimination across two continua. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:223–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning, the peak shift, and behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):727–741. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis C., Walters G. Punished and unpunished responding in multiple variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Mar;11(2):147–152. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


