Abstract
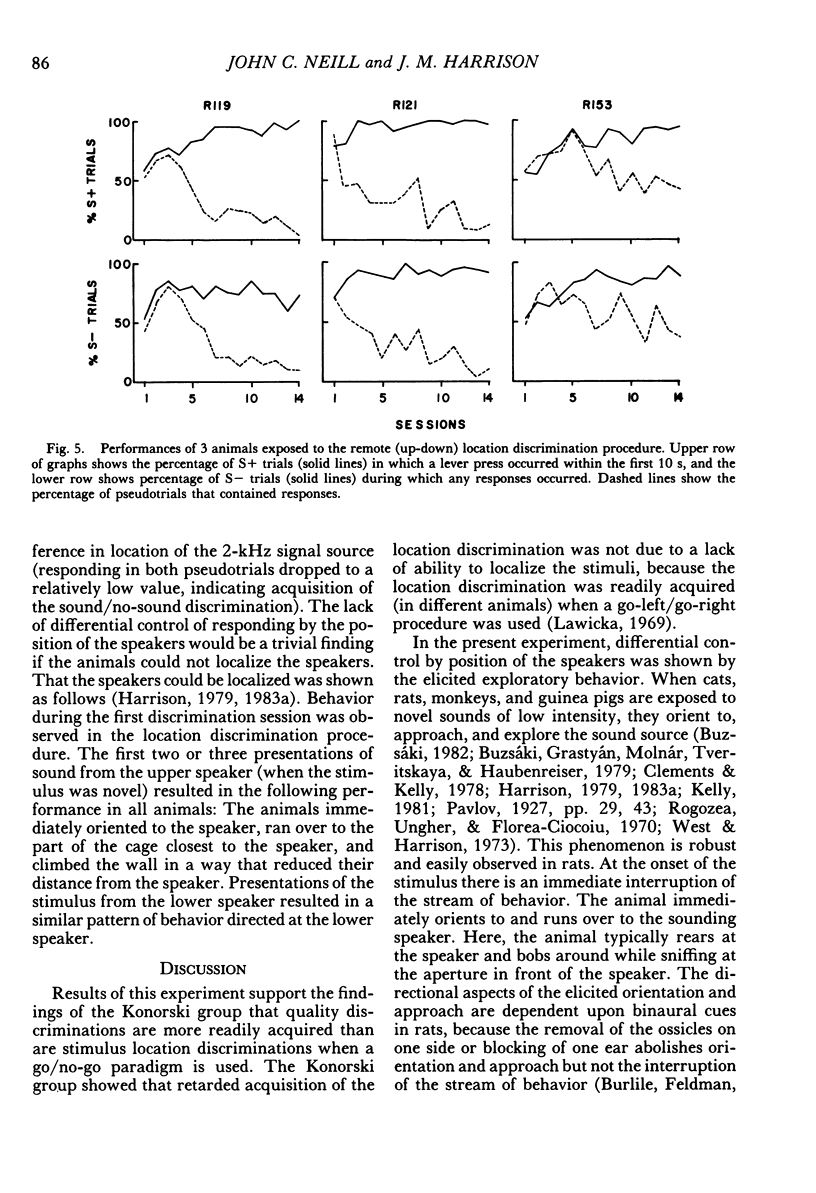
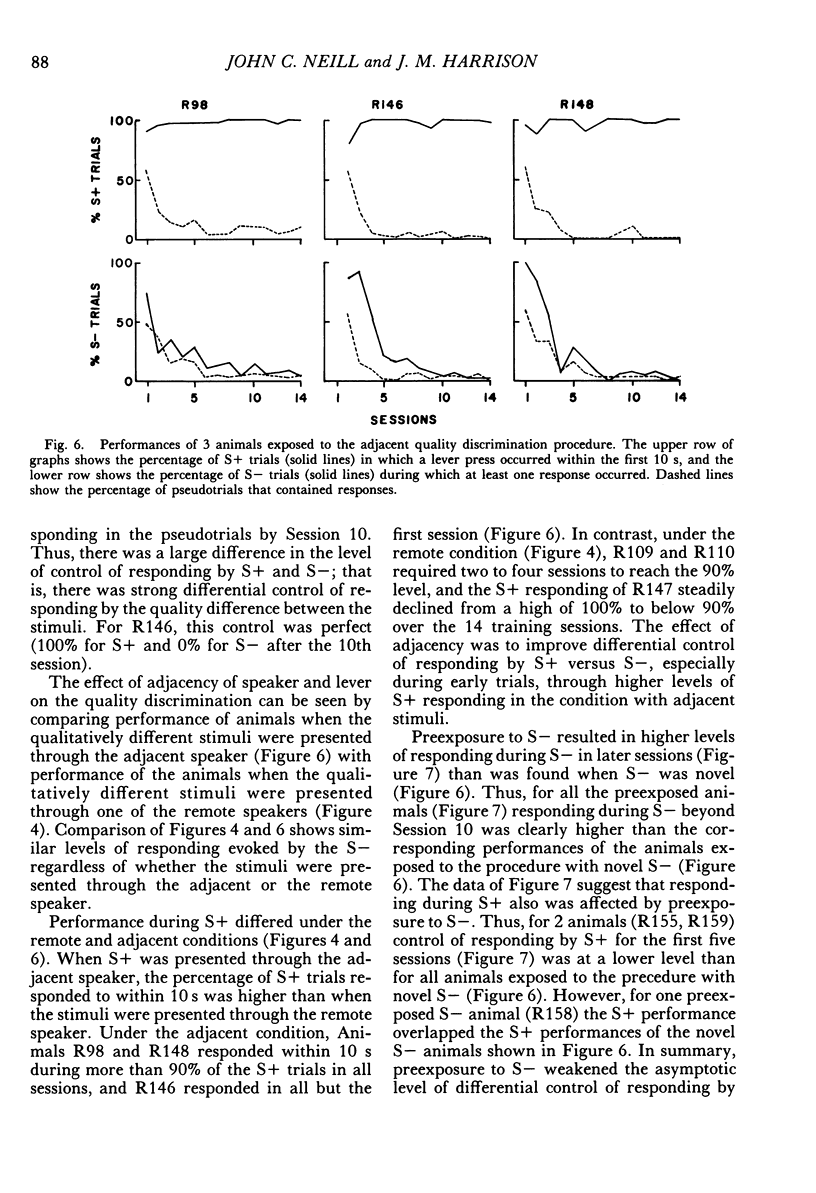
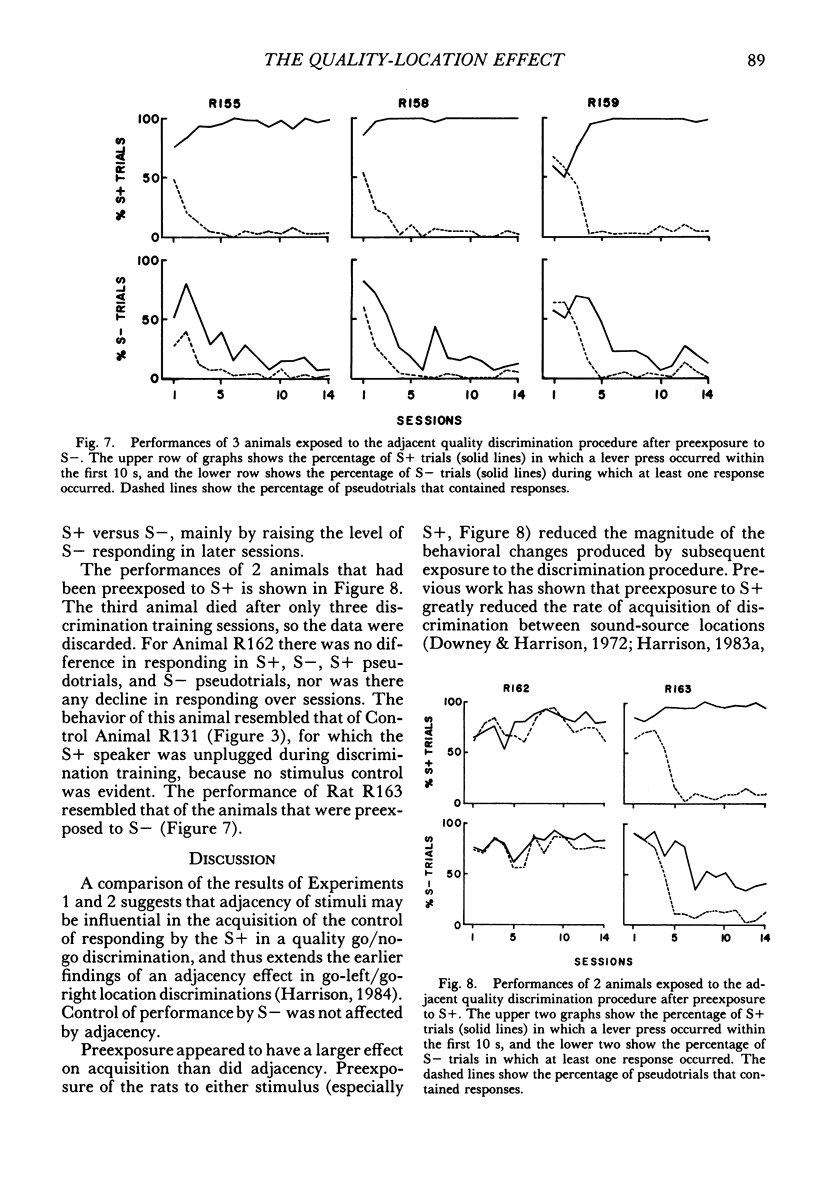
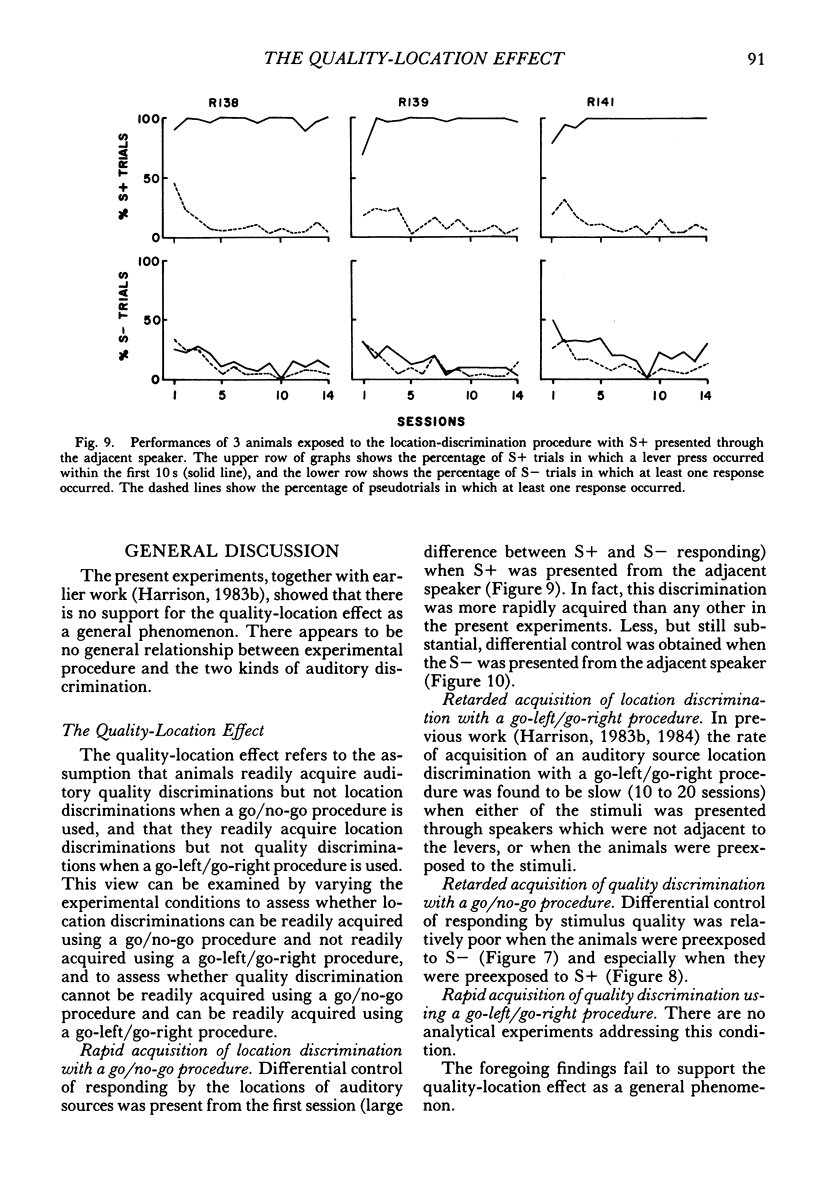
Konorski showed that when a go/no-go procedure was used, sound quality discriminations were rapidly acquired and sound location discriminations were slowly acquired. These findings have been interpreted as a general constraint on the acquisition of auditory discriminations (quality-location effect). However, experiments carried out within an evolutionary framework (Harrison, 1984) have shown that the rate of acquisition of sound location discriminations varies widely as a function of the inclusion or exclusion of naturalistic features. These data suggest that Konorski's findings were a function of the special conditions of the experiments. The first purpose of the present experiments was to assess whether rats showed the effects noted by Konorski when studied under similar conditions. The second purpose was to study the effect of manipulating two natural features (novelty and stimulus-response adjacency) to assess whether the acquisition rates of quality and location discriminations could be greatly modified or made approximately equal, or both. When a go/no-go procedure was used and the other conditions were similar to those of Konorski, rats acquired a quality discrimination but did not acquire a location discrimination. However, when the S+ or S- were presented through a closely adjacent speaker, the sound location discrimination was acquired as rapidly as the quality discrimination. Finally, preexposing the animal to either S+ or S- retarded the rate of or prevented the acquisition of the quality discrimination. The experiments showed that the quality-location effect was determined primarily by the conditions used in Konorski's experiments, and that the effect is not a general constraint on learning.
Full text
PDF






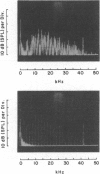
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beecher M. D., Harrison J. M. Rapid acquisition of an auditory localization discrimination by rats. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Sep;16(2):193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.16-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdick C. K. Auditory discrimination learning by the chinchilla: comparison of go/no go and two-choice procedures. J Aud Res. 1980 Jan;20(1):1–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdick C. K. The effect of behavioral paradigm on auditory discrimination learning: a literature review. J Aud Res. 1979 Jan;19(1):59–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlile C. J., Feldman M. L., Craig C., Harrison J. M. Control of responding by the location of sound: role of binaural cues. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):315–319. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G., Grastyán E., Molnár P., Tveritskaya I. N., Haubenreiser J. Auto-shaping or orienting? Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1979;39(4):179–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G., Grastyán E., Winiczai Z., Mód L. Maintenance of signal directed behavior in a response dependent paradigm: a systems approach. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1979;39(4):201–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzsáki G. The "where is it?" reflex: autoshaping the orienting response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 May;37(3):461–484. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton P. L., Vogel J. R. Habituation and conditioning. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Apr;63(2):348–351. doi: 10.1037/h0024372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casseday J. H., Neff W. D. Auditory localization: role of auditory pathways in brain stem of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1975 Jul;38(4):842–858. doi: 10.1152/jn.1975.38.4.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements M., Kelly J. B. Auditory spatial responses of young guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus) during and after ear blocking. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1978 Feb;92(1):34–44. doi: 10.1037/h0077424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowell C. R., Anderson D. C. Variations in intensity, interstimulus interval, and interval between preconditioning CS exposures and conditioning with rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1972 May;79(2):291–298. doi: 10.1037/h0032550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzecka C., Konorski J. Qualitative versus directional cues in differential conditioning. I. Left leg-right leg differentiation to cues on a mixed character. Acta Biol Exp (Warsz) 1967;27(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzecka C., Konorski J. Qualitative versus directional cues in differential conditioning. IV. Left leg-right leg differentiation to non-directional cues. Acta Biol Exp (Warsz) 1968;28(2):61–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobrzecka C., Szejkowska G., Konorski J. Qualitative versus directional cues in two forms of differentiation. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):87–89. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downey P., Harrison J. M. Control of responding by location of auditory stimuli: role of differential and non-differential reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Nov;18(3):453–463. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. N., Trahiotis C. Cortical lesions and auditory discrimination. Psychol Bull. 1972 Mar;77(3):198–222. doi: 10.1037/h0032281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grastyán E., Vereczkei L. Effects of spatial separation of the conditioned signal from the reinforcement: a demonstration of the conditioned character of the orienting response or the orientational character of conditioning. Behav Biol. 1974 Feb;10(2):121–146. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(74)91725-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall G., Pearce J. M. Latent inhibition of a CS during CS-US pairings. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1979 Jan;5(1):31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M., Downey P., Segal M., Howe M. Control of responding by location of auditory stimuli: rapid acquisition in monkey and rat. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 May;15(3):379–386. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M. Effects of age on acquisition and maintenance of a location discrimination in rats. Exp Aging Res. 1981 Winter;7(4):467–476. doi: 10.1080/03610738108259825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M. Effects of age on some behavioral characteristics of novel auditory stimuli in the rat. Exp Aging Res. 1983 Spring;9(1):35–39. doi: 10.1080/03610738308258418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M., Iversen S. D., Pratt S. R. Control of responding by location of auditory stimuli: adjacency of sound and response. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 Nov;28(3):243–251. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.28-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M. The control of responding by sounds: unusual effect of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1979 Sep;32(2):167–181. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1979.32-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. M. The functional analysis of auditory discrimination. J Acoust Soc Am. 1984 Jun;75(6):1848–1854. doi: 10.1121/1.390985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. B., Masterton B. Auditory sensitivity of the albino rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1977 Aug;91(4):930–936. doi: 10.1037/h0077356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawicka W. Auditory targeting reflexes: their determining role in directional instrumental responding. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1979;39(6):537–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawicka W. Differing effectiveness of auditory quality and location cues in two forms of differentiation learning. Acta Biol Exp (Warsz) 1969;29(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawicka W., Mishkin M., Rosvold H. E. Dissociation of deficits on auditory tasks following partial prefrontal lesions in monkeys. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1975;35(5-6):581–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawicka W., Szczechura J. Stimulus-response spatial contiguity vs. S-R spatial discontiguity in auditory spatial tasks. I. Acquisition by normal dogs. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1979;39(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubow R. E. Latent inhibition. Psychol Bull. 1973 Jun;79(6):398–407. doi: 10.1037/h0034425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterton B., Jane J. A., Diamond I. T. Role of brainstem auditory structures in sound localization. I. Trapezoid body, superior olive, and lateral lemniscus. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Mar;30(2):341–359. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. D., Bowe C. A. Roles of the qualities and locations of stimuli and responses in simple associative learning. The quality-location hypothesis. Pavlov J Biol Sci. 1982 Jul-Sep;17(3):129–139. doi: 10.1007/BF03001207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla R. A. Summation and retardation tests of latent inhibition. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1971 Apr;75(1):77–81. doi: 10.1037/h0030694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogozea R., Ungher J., Florea-Ciocoiu V. Effect of ablation of auditory and "associative" cortex on the orienting reflex. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1970;30(3):263–277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szwejkowska G. Qualitative versus directional cues in differential conditioning. 3. The role of qualitative and directional cues in differentiation of salivary conditioned reflexes. Acta Biol Exp (Warsz) 1967;27(4):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szwejkowska G., Sychowa B. The effects of lesions of auditory cortex on discrimination of sound localization in dog. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 1971;31(3):237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISKRANTZ L., MISHKIN M. Effects of temporal and frontal cortical lesions on auditory discrimination in monkeys. Brain. 1958 Sep;81(3):406–414. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.3.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. D., Harrison J. M. Transneuronal cell atrophy in the congenitally deaf white cat. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Oct 15;151(4):377–398. doi: 10.1002/cne.901510406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]