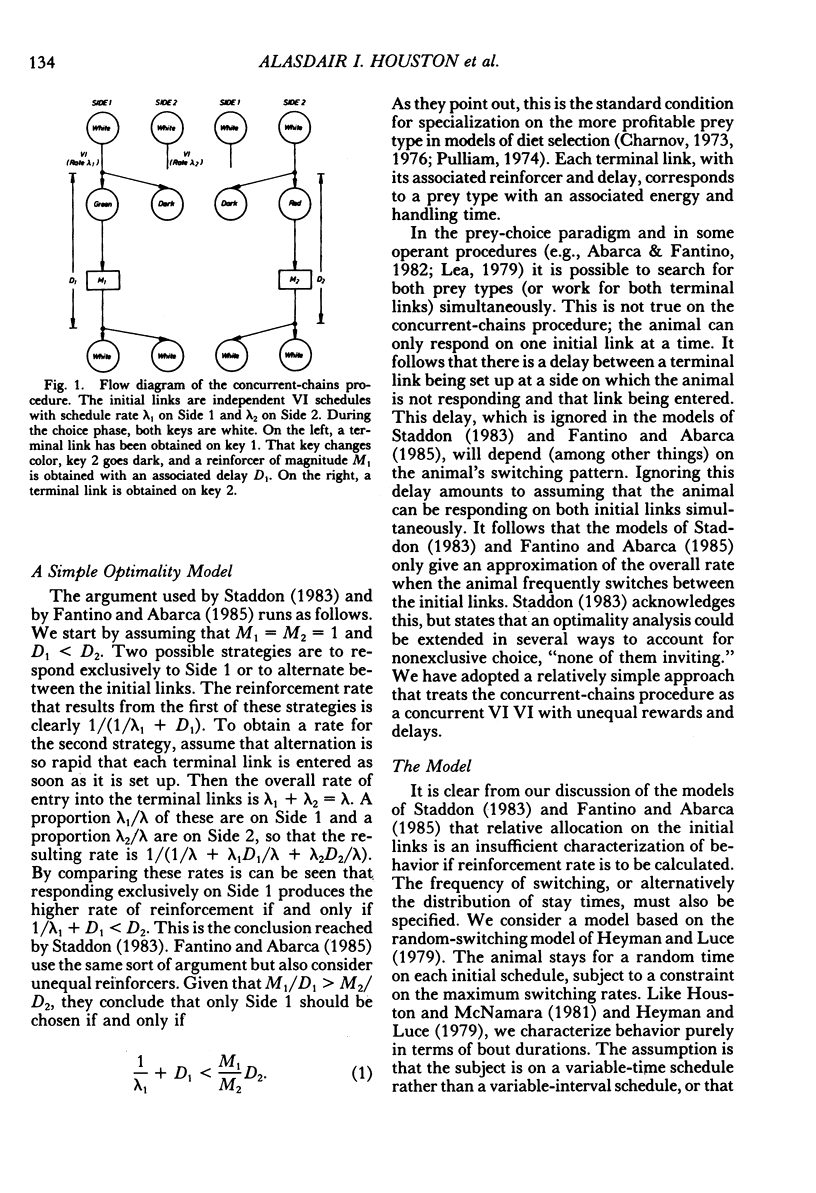
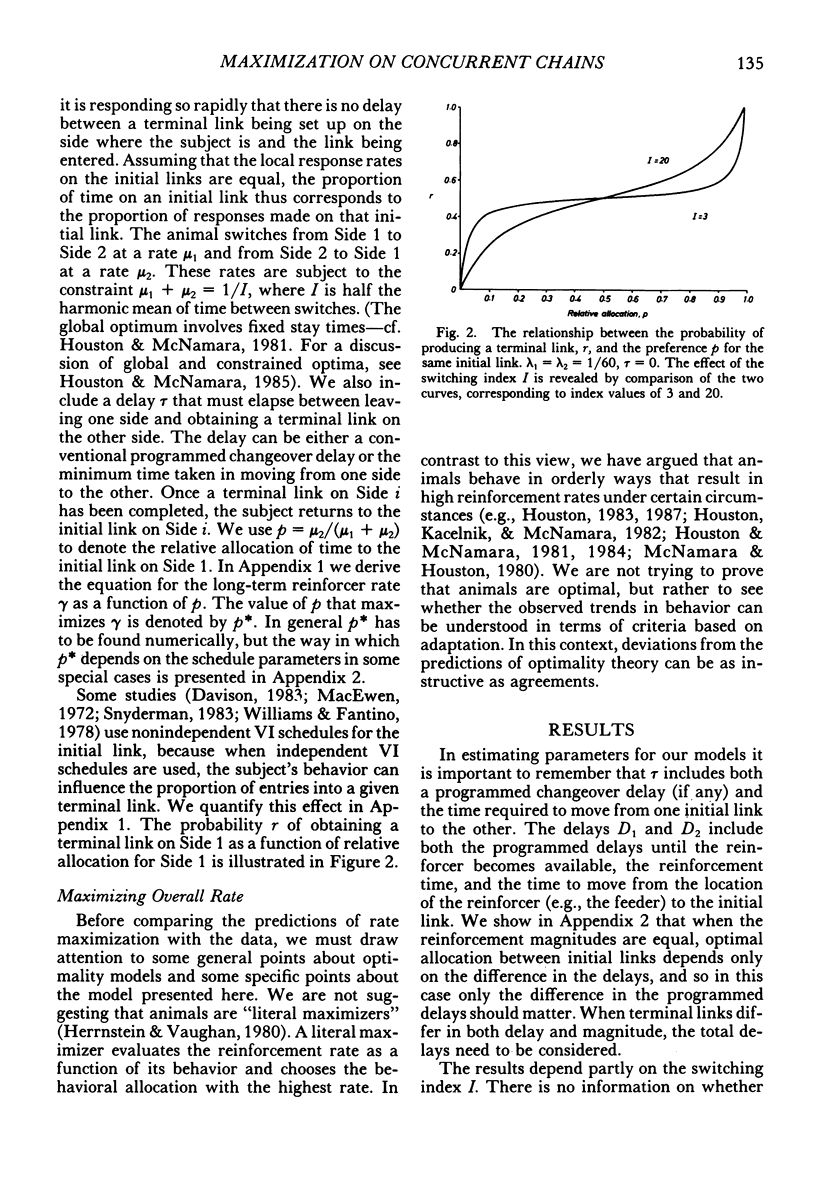
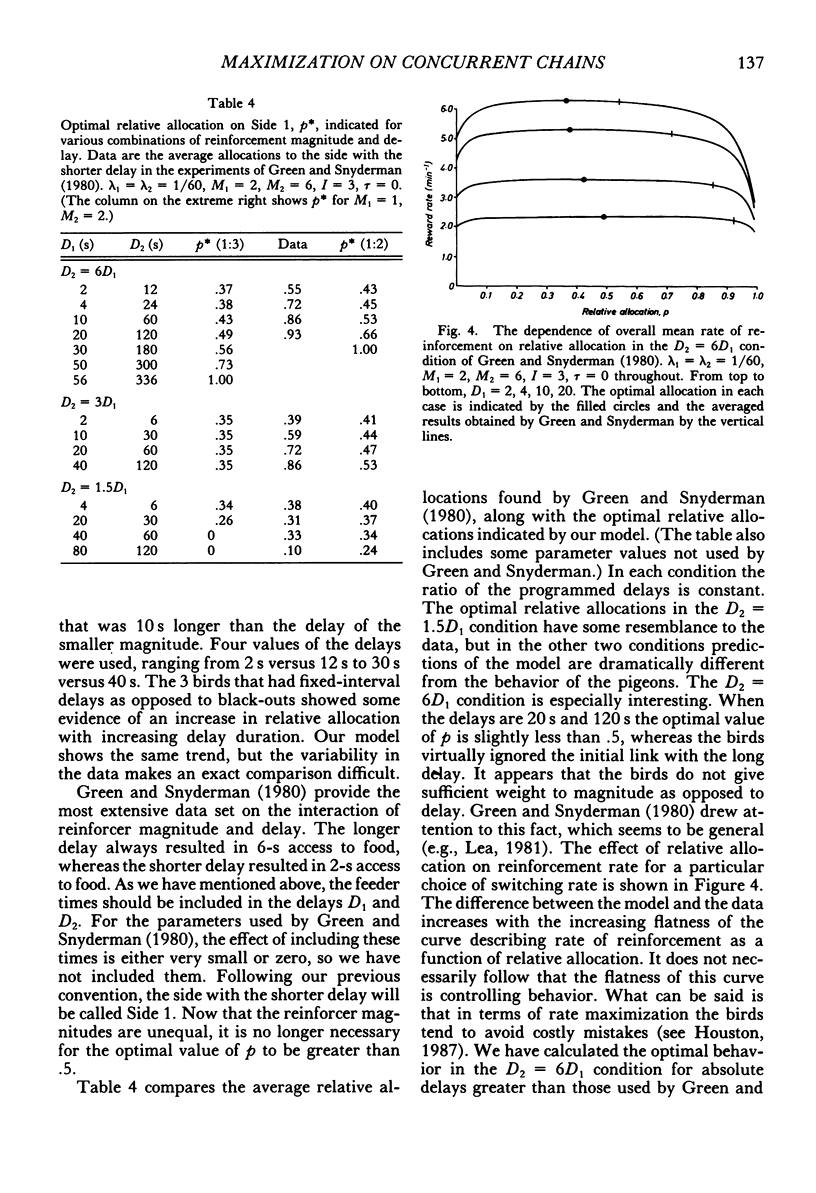
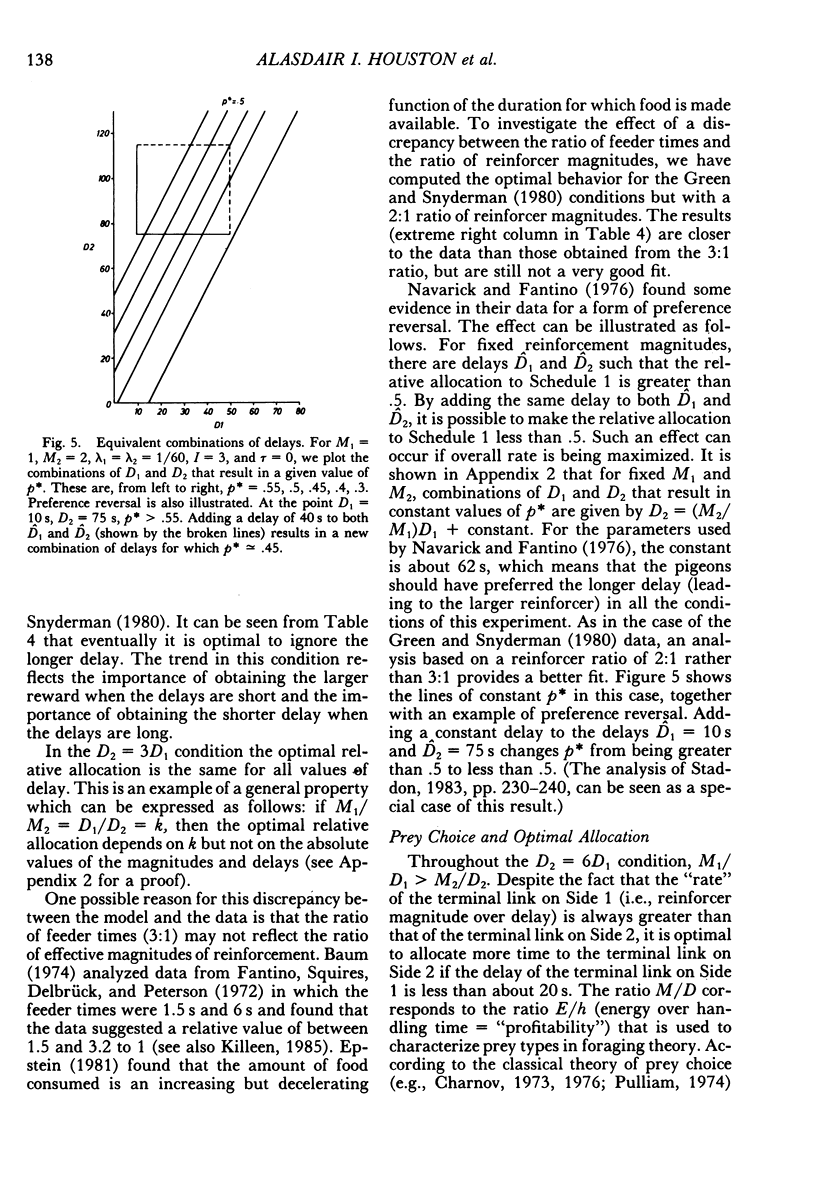
Abstract
We model behavioral allocation on concurrent chains in which the initial links are independent variable-interval schedules. We also quantify the relationship between behavior during the initial links and the probability of entering a terminal link. The behavior that maximizes overall reinforcement rate is then considered and compared with published experimental data. Although all the trends in the data are predicted by rate maximization, there are considerable deviations from the predictions of rate maximization when reward magnitudes are unequal. We argue from our results that optimal allocation on concurrent chains, and prey choice as used in the theory of optimal diets, are distinct concepts. We show that the maximization of overall rate can lead to apparent violations of stochastic transitivity.
Keywords: concurrent chains, relative allocation, reinforcement rate, maximization, diet theory, stochastic transitivity
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abarca N., Fantino E. Choice and foraging. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Sep;38(2):117–123. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C. Preference for mixed-interval versus fixed-interval schedules: number of component intervals. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Mar;17(2):169–176. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. Bias and sensitivity to reinforcement in a concurrent-chain schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):15–34. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Davison M. Choice: Some quantitative relations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):1–13. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Squires N., Delbrück N., Peterson C. Choice behavior and the accessibility of the reinforcer. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):35–43. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Snyderman M. Choice between rewards differing in amount and delay: Toward a choice model of self control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):135–147. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. APERIODICITY AS A FACTOR IN CHOICE. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:179–182. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston A. I., McNamara J. How to maximize reward rate on two variable-interval paradigms. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 May;35(3):367–396. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R., Fantino E. Relative delay of reinforcement and choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):437–450. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. R. Incentive theory: II. Models for choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Sep;38(2):217–232. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. R. Incentive theory: IV. Magnitude of reward. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 May;43(3):407–417. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.43-407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killeen P. On the measurement of reinforcement frequency in the study of preference. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3):263–269. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macewen D. The effects of terminal-link fixed-interval and variable-interval schedules on responding under concurrent chained schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):253–261. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara J., Houston A. The application of statistical decision theory to animal behaviour. J Theor Biol. 1980 Aug 21;85(4):673–690. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(80)90265-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman M. Delay and amount of reward in a concurrent chain. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 May;39(3):437–447. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Fantino E. Effects on choice of reinforcement delay and conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jan;29(1):77–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


