Abstract
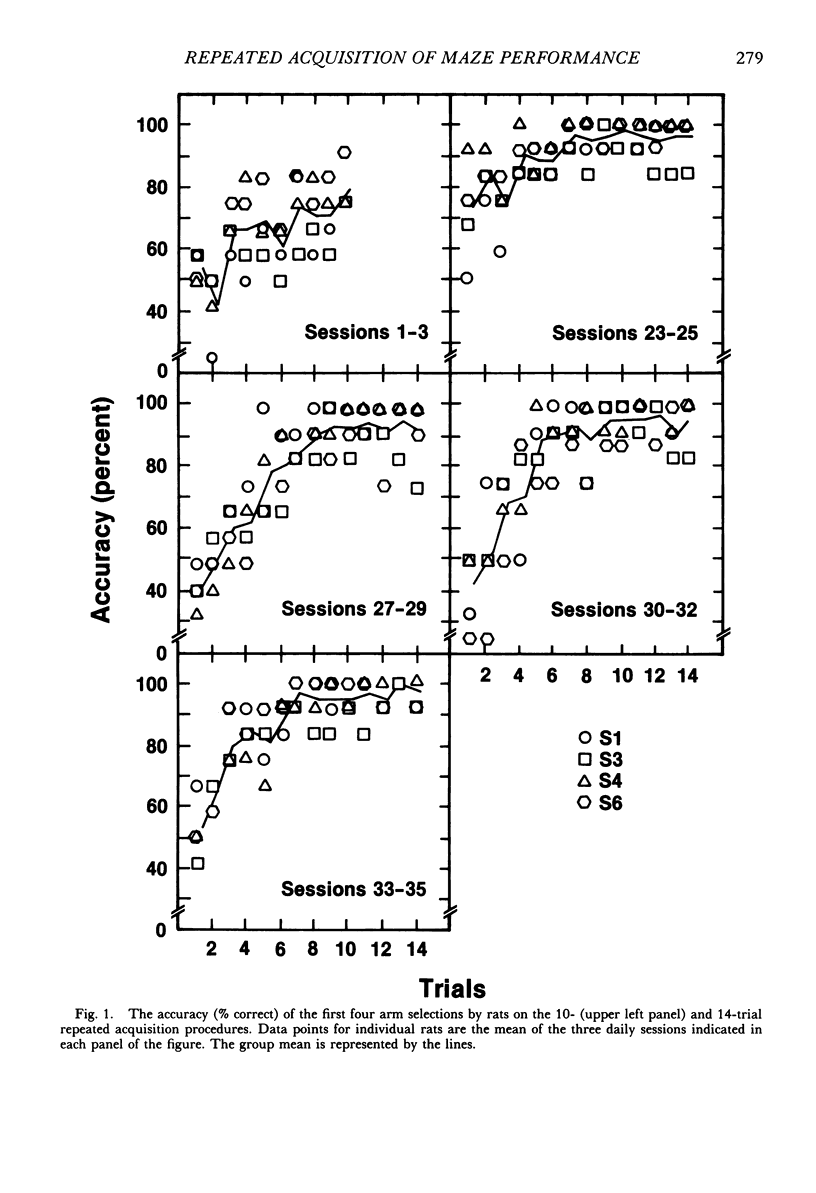
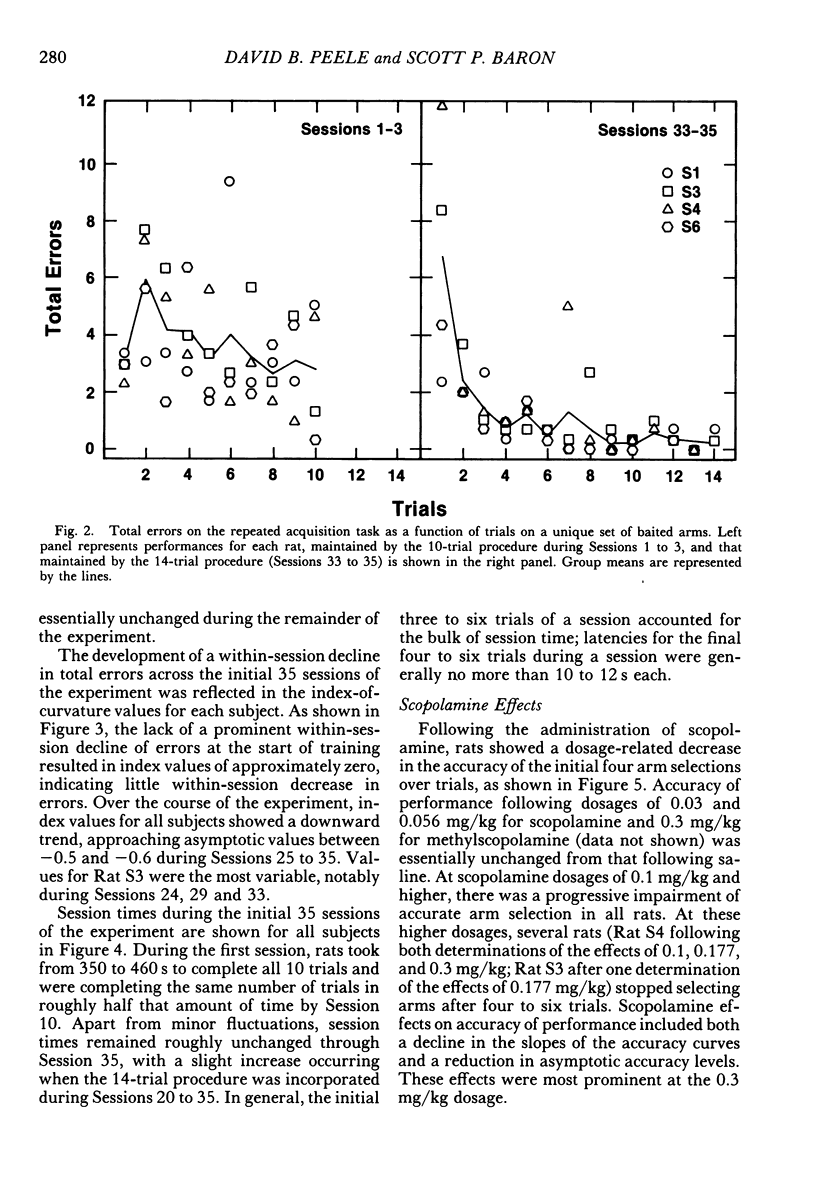
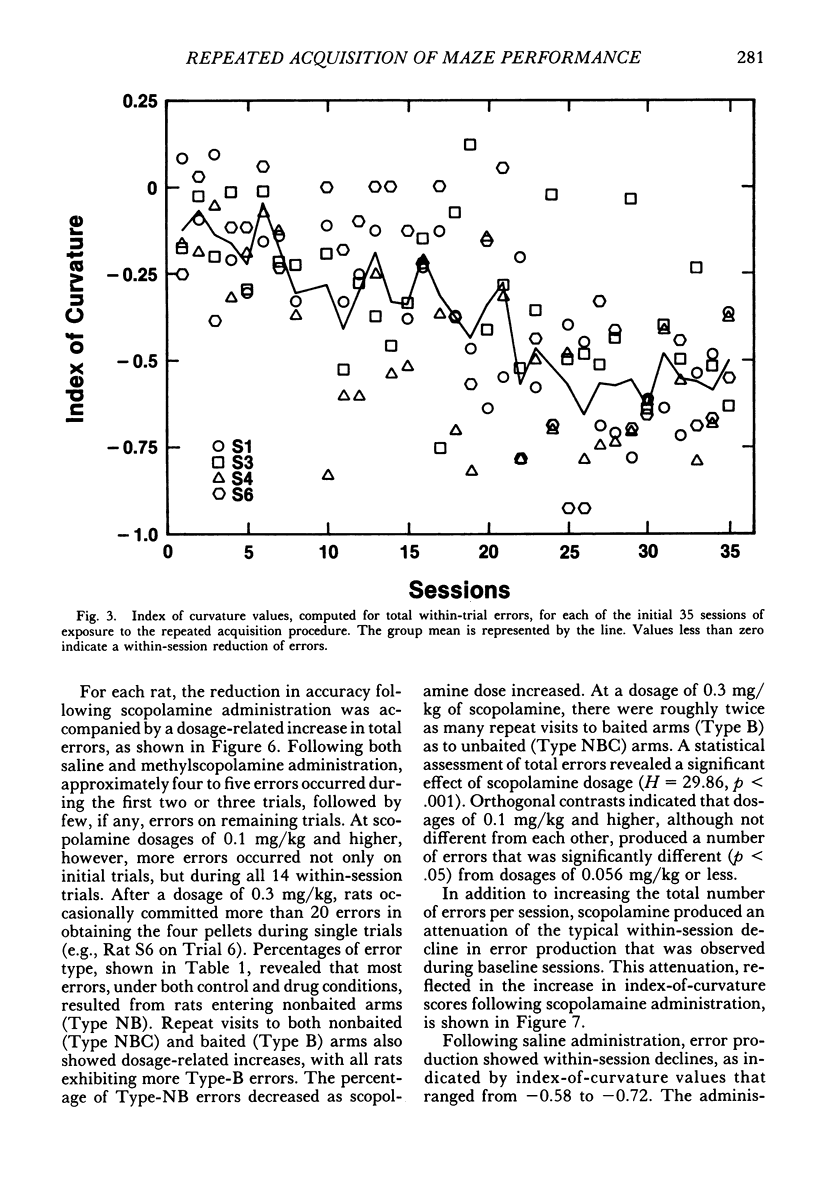
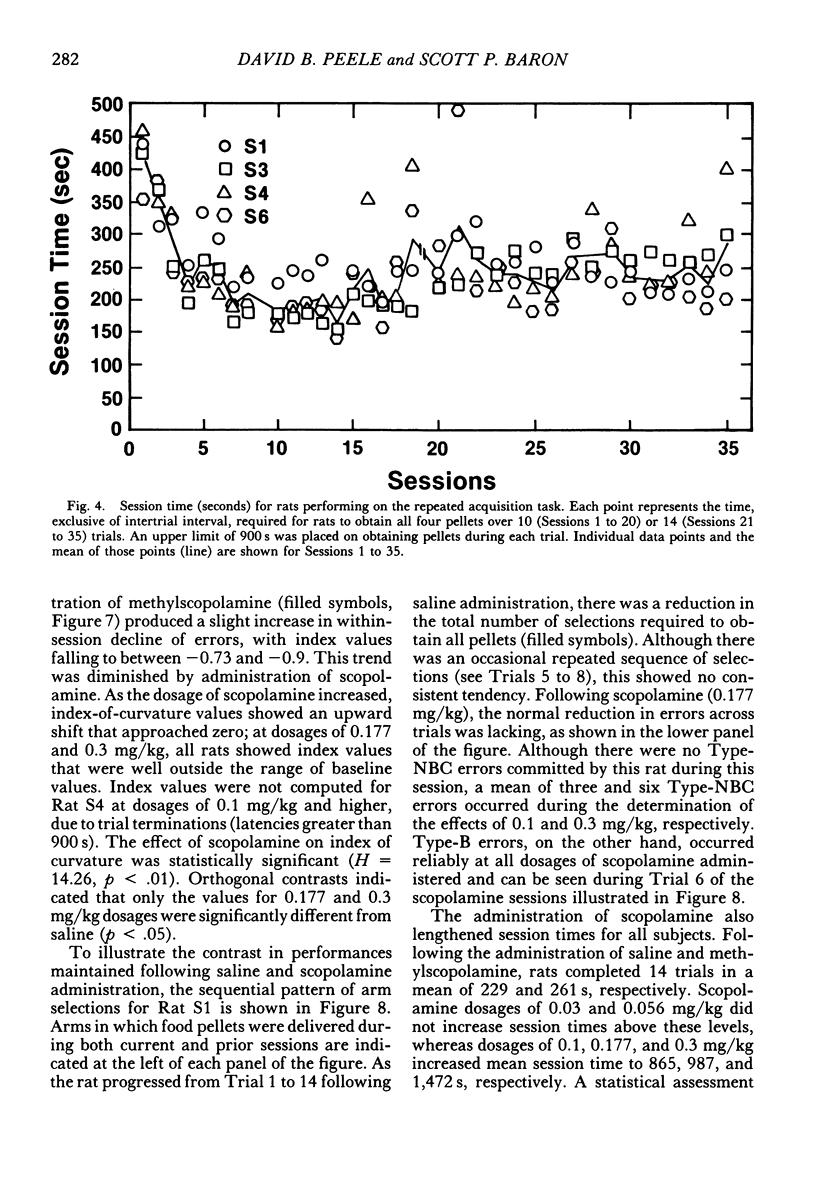
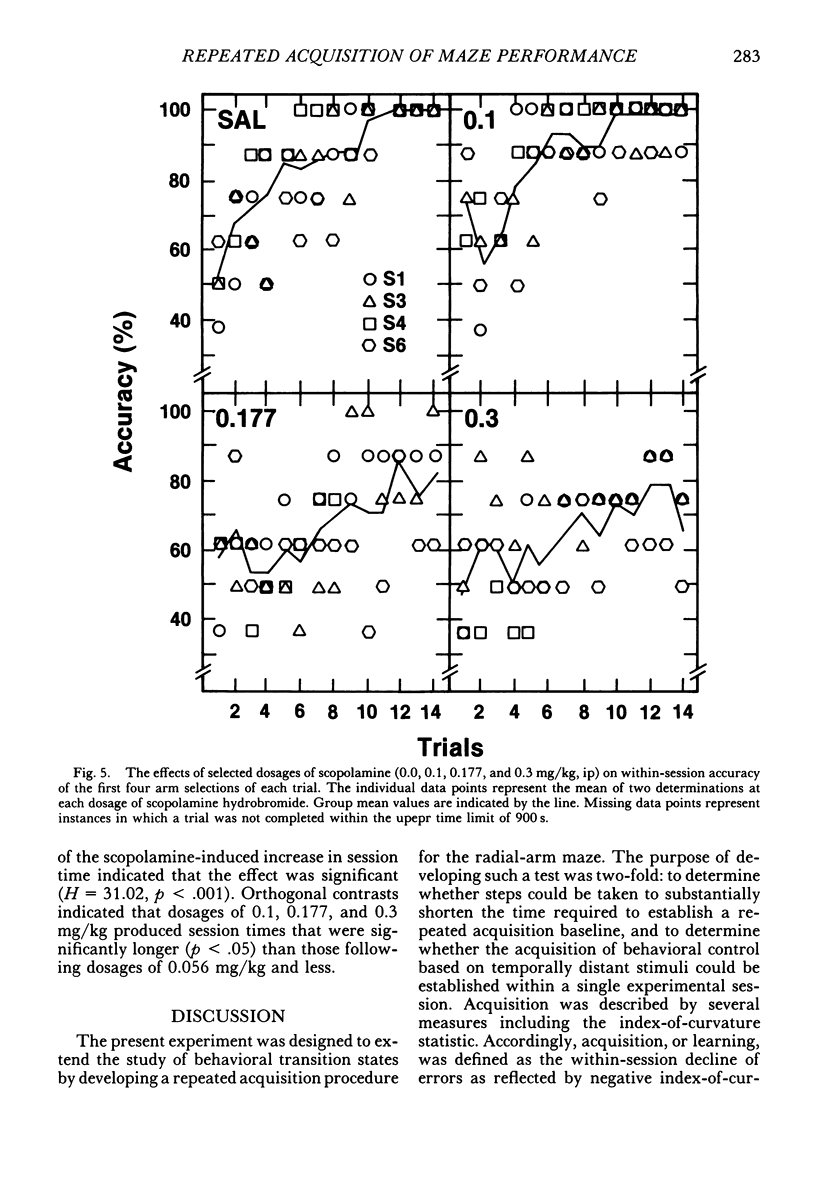
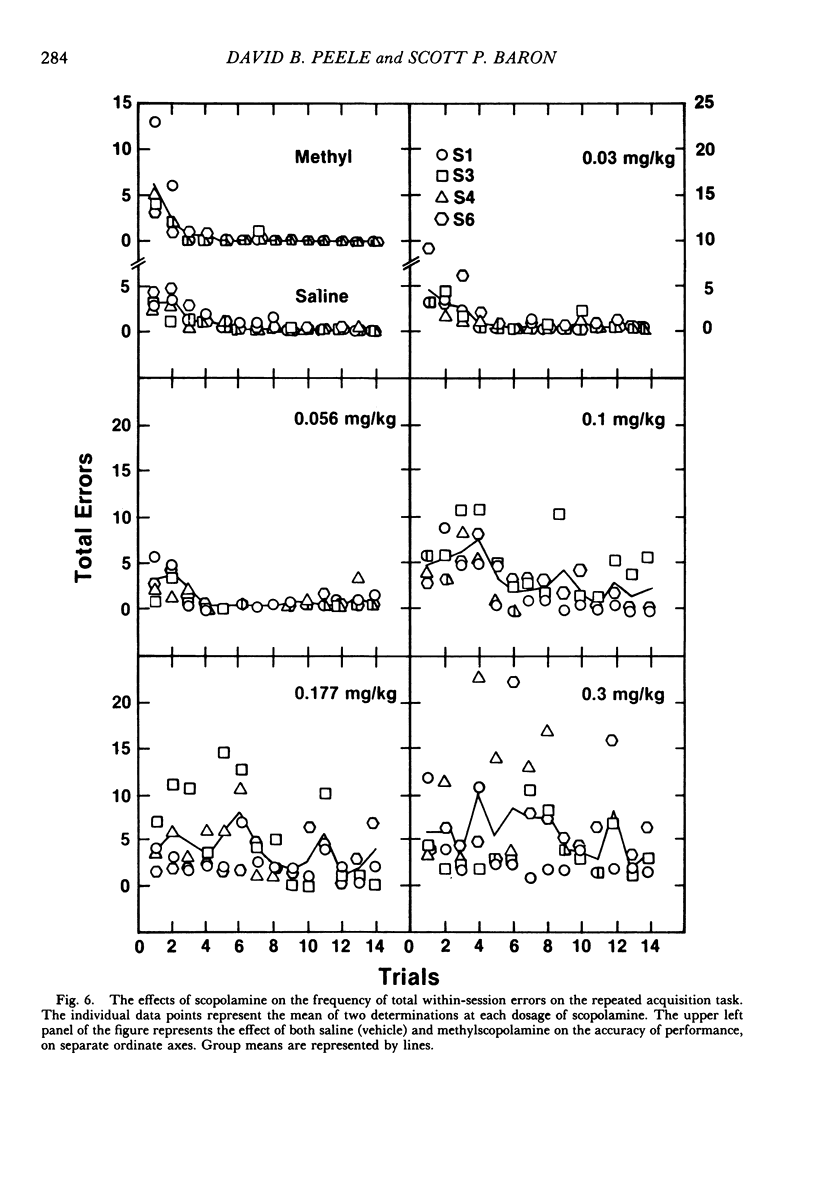
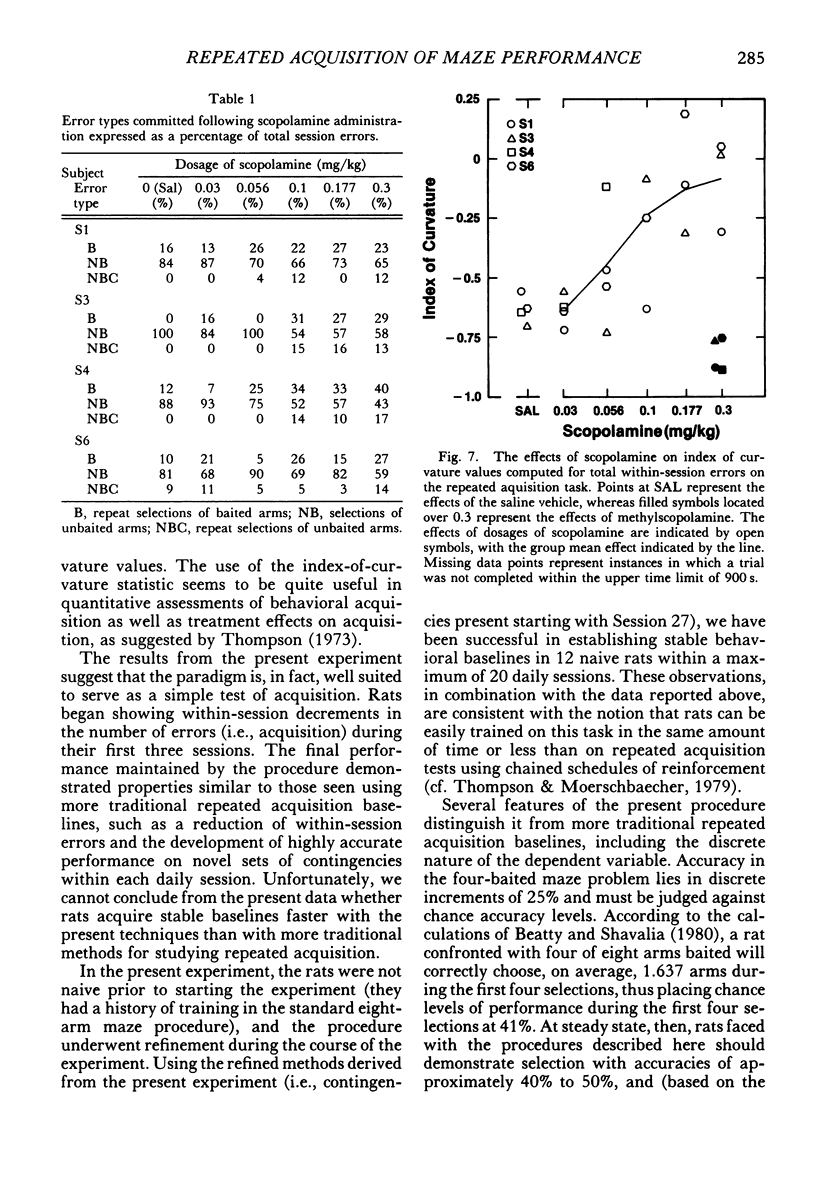
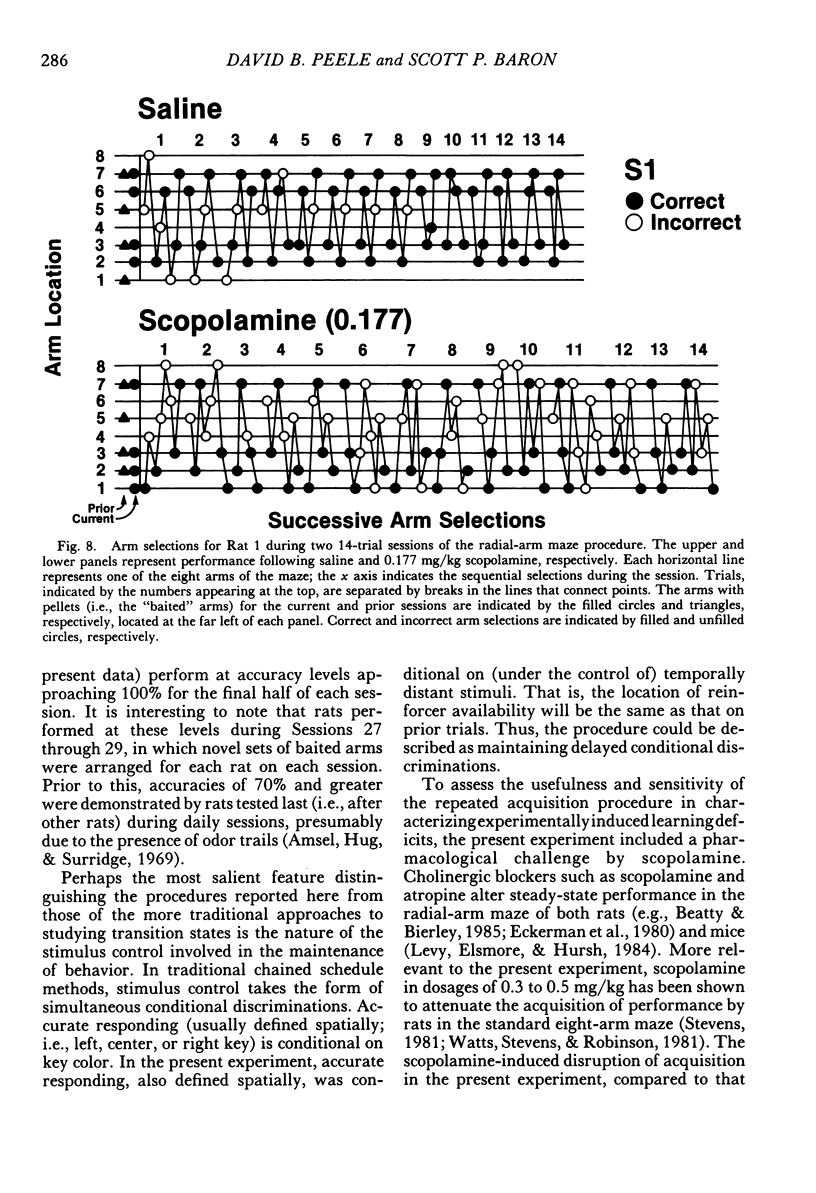
Rats repeatedly acquired the performance of selecting only the four baited arms in an automated eight-arm radial maze, with the arms containing food pellets randomly assigned prior to each session. During each 14-trial (trial: obtain all four pellets) daily session, the number of errors (selecting nonbaited arms or repeating arm selections) showed a within-session decline, and choice accuracy for the first four arm selections showed a positive acceleration across trials for all rats. An index-of-curvature statistic, calculated for total errors, was used to quantify both the within- and between-session improvement of performance. Scopolamine (0.03 to 0.3 mg/kg, ip), but not methylscopolamine (0.3 mg/kg), reduced the accuracy of the first four selections of each trial and increased total within-session errors for all rats. Session times also were increased by scopolamine. An examination of within-session accuracy showed only slight signs of improvement at the higher dosages of scopolamine. The results indicate that behavior in transition states maintained by reinforcement contingencies in the radial maze is similar to that maintained by extended chained schedules, despite the fact that some of the stimuli controlling behavior in the maze are absent at the moment behavior is emitted.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anger W. K., Setzer J. V. Effects of oral and intramuscular carbaryl administrations on repeated chain acquisition in monkeys. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1979 Sep;5(5):793–808. doi: 10.1080/15287397909529790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty W. W., Bierley R. A. Scopolamine degrades spatial working memory but spares spatial reference memory: dissimilarity of anticholinergic effect and restriction of distal visual cues. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 Jul;23(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beatty W. W., Shavalia D. A. Spatial memory in rats: time course of working memory and effect of anesthetics. Behav Neural Biol. 1980 Apr;28(4):454–462. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(80)91806-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boren J. J., Devine D. D. The repeated acquisition of behavioral chains. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):651–660. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun W. H., Jones E. A. Methamphetamine's effect on repeated acquisitions with serial discrimination reversals. Psychopharmacologia. 1974;39(4):303–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00422969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins P. J., Moerschbaecher J. M., Thompson D. M., Thomas J. R. Intravenous diazepam in humans: effects on acquisition and performance of response chains. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1982 Nov;17(5):1055–1059. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(82)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz D. D., McMillan D. E., Mushak P. Effects of chronic lead administration on acquisition and performance of serial position sequences by pigeons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Feb;47(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(79)90333-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckerman D. A., Gordon W. A., Edwards J. D., MacPhail R. C., Gage M. I. Effects of scopolamine, pentobarbital, and amphetamine on radial arm maze performance in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1980 Apr;12(4):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(80)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRY W., KELLEHER R. T., COOK L. A mathematical index of performance on fixed-interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1960 Jul;3:193–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1960.3-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway W. D. Microwave dose-response relationships on two behavioral tasks. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;247:410–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb36016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley G. W., Calhoun W. H. The effects of methylphenidate on repeated acquisition of serial discrimination reversals. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1978 Apr 14;57(1):115–117. doi: 10.1007/BF00426967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harting J., Mcmillian D. E. Effects of pentobarbital and d-amphetamine on the repeated acquisition of response sequences by pigeons. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1976 Sep 29;49(3):245–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00426823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton B., McGowan M., Olton D. S. Hippocampal stimulation disrupts spatial working memory even 8 h after acquisition. Behav Neural Biol. 1985 Sep;44(2):325–337. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(85)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leander J. D., McMillan D. E., Barlow T. S. Chronic mercuric chloride: Behavioral effects in pigeons. Environ Res. 1977 Dec;14(3):424–435. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(77)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy A., Elsmore T. F., Hursh S. R. Central vs peripheral anticholinergic effects on repeated acquisition of behavioral chains. Behav Neural Biol. 1984 Jan;40(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(84)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moerschbaecher J. M., Thompson D. M. Effects of d-amphetamine, cocaine, and phencyclidine on the acquisition of response sequences with and without stimulus fading. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 May;33(3):369–381. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.33-369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olton D. S., Papas B. C. Spatial memory and hippocampal function. Neuropsychologia. 1979;17(6):669–682. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(79)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olton D. S., Wolf W. A. Hippocampal seizures produce retrograde amnesia without a temporal gradient when they reset working memory. Behav Neural Biol. 1981 Dec;33(4):437–452. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(81)91797-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paule M. G., McMillan D. E. Effects of trimethyltin on incremental repeated acquisition (learning) in the rat. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1986 May-Jun;8(3):245–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieper W. A. Great apes and rhesus monkeys as subjects for psychopharmacological studies of stimulants and depressants. Fed Proc. 1976 Sep;35(11):2254–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poschel B. P. The hippocampally stimulated rat as a model for Korsakoff-type amnesias. Lab Anim Sci. 1977 Oct;27(5 Pt 2):738–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrot J., Boren J. J., Moerschbaecher J. M. Sequential reacquisition as a function of timeout from avoidance. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):303–310. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrot J., Boren J. J., Moerschbaecher J. M., Simoes Fontes J. C. Effects of d-amphetamine and cocaine on repeated acquisition with timeout from avoidance. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1978 Nov;9(5):659–663. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(78)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrot J., Thomas J. R., Banvard R. A. Modification of the repeated acquisition of response sequences in rats by low-level microwave exposure. Bioelectromagnetics. 1980;1(1):89–99. doi: 10.1002/bem.2250010109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrot J., Thomas J. R., Robertson R. F. Temporal changes in repeated acquisition behavior after carbon monoxide exposure. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):23–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens R. Scopolamine impairs spatial maze performance in rats. Physiol Behav. 1981 Aug;27(2):385–386. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(81)90285-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Repeated acquisition as a behavioral base line for studying drug effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):506–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson D. M. Repeated acquisition of behavioral chains: effects of methylphenidate and imipramine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1976 Jun;4(6):671–677. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(76)90218-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilson H. A., Mitchell C. L. Neurobehavioral techniques to assess the effects of chemicals on the nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1984;24:425–450. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.24.040184.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J., Stevens R., Robinson C. Effects of scopolamine on radial maze performance in rats. Physiol Behav. 1981 May;26(5):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(81)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whishaw I. Q. Formation of a place learning-set by the rat: a new paradigm for neurobehavioral studies. Physiol Behav. 1985 Jul;35(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(85)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirsching B. A., Beninger R. J., Jhamandas K., Boegman R. J., El-Defrawy S. R. Differential effects of scopolamine on working and reference memory of rats in the radial maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1984 May;20(5):659–662. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(84)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


