Abstract
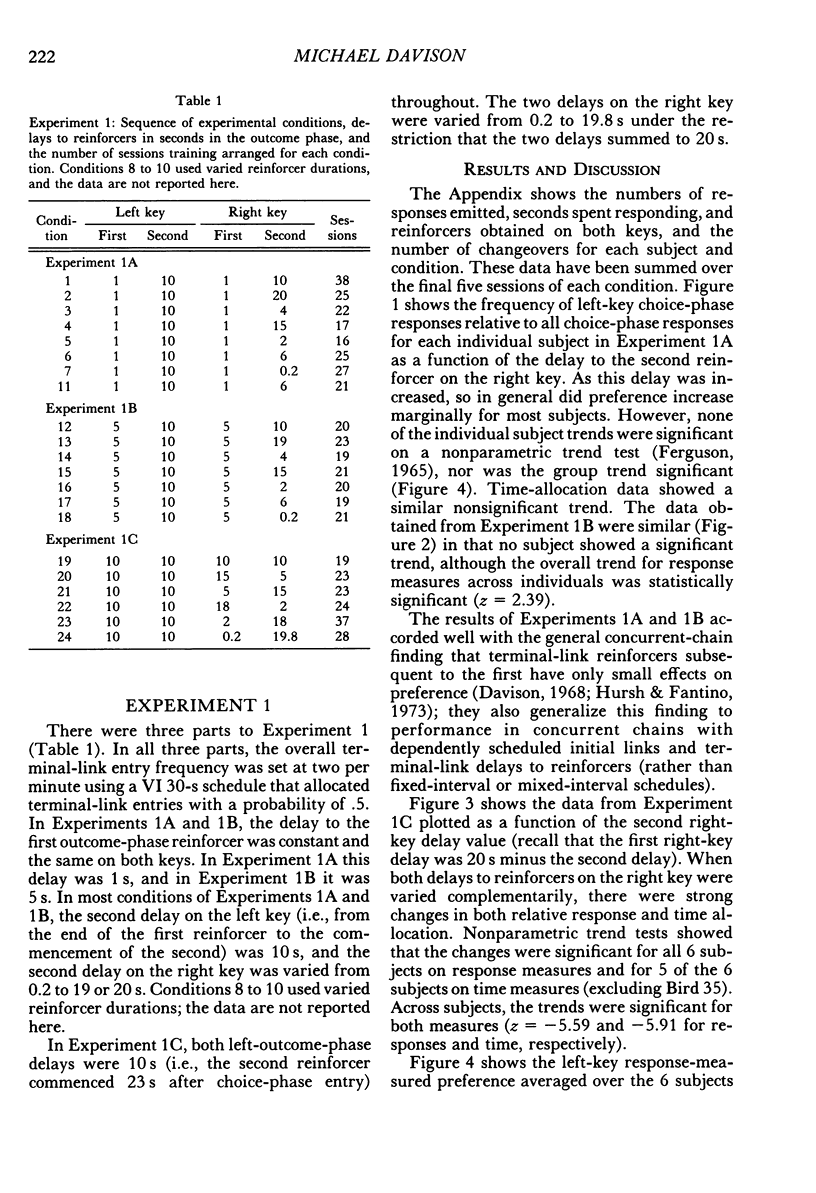
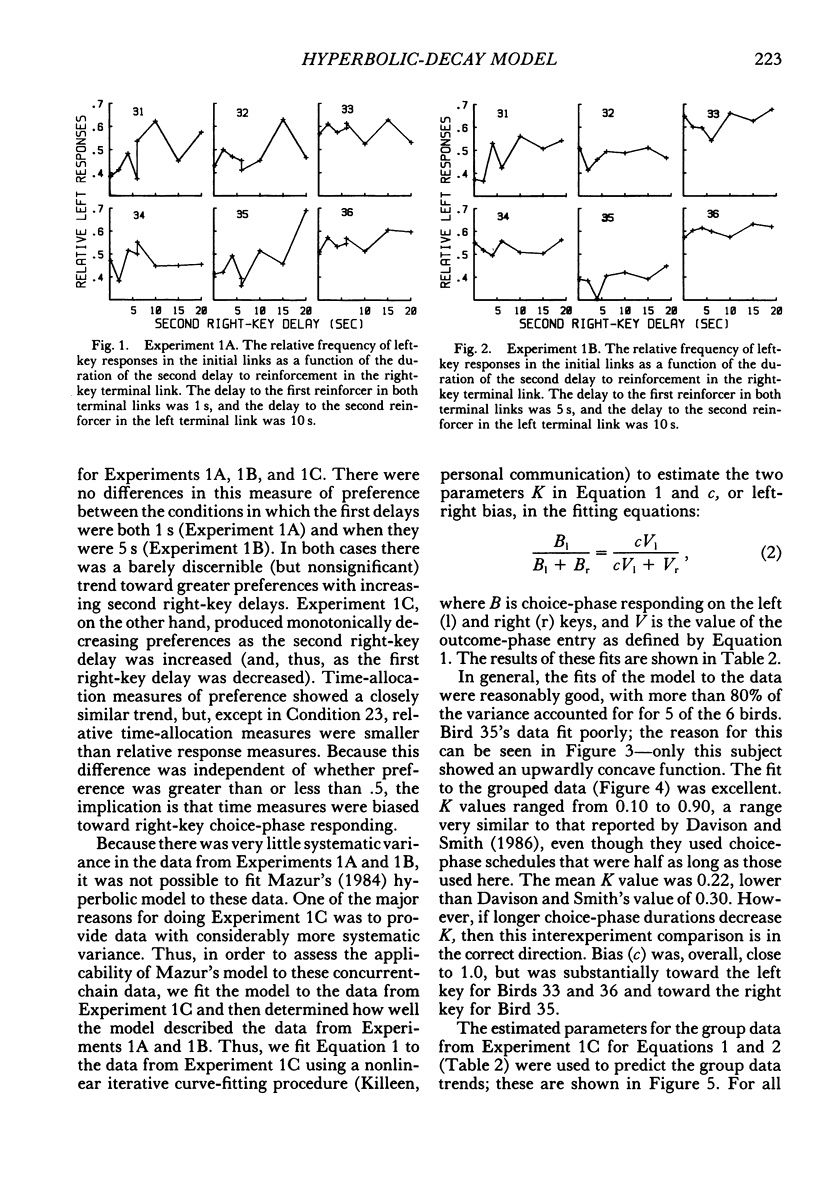
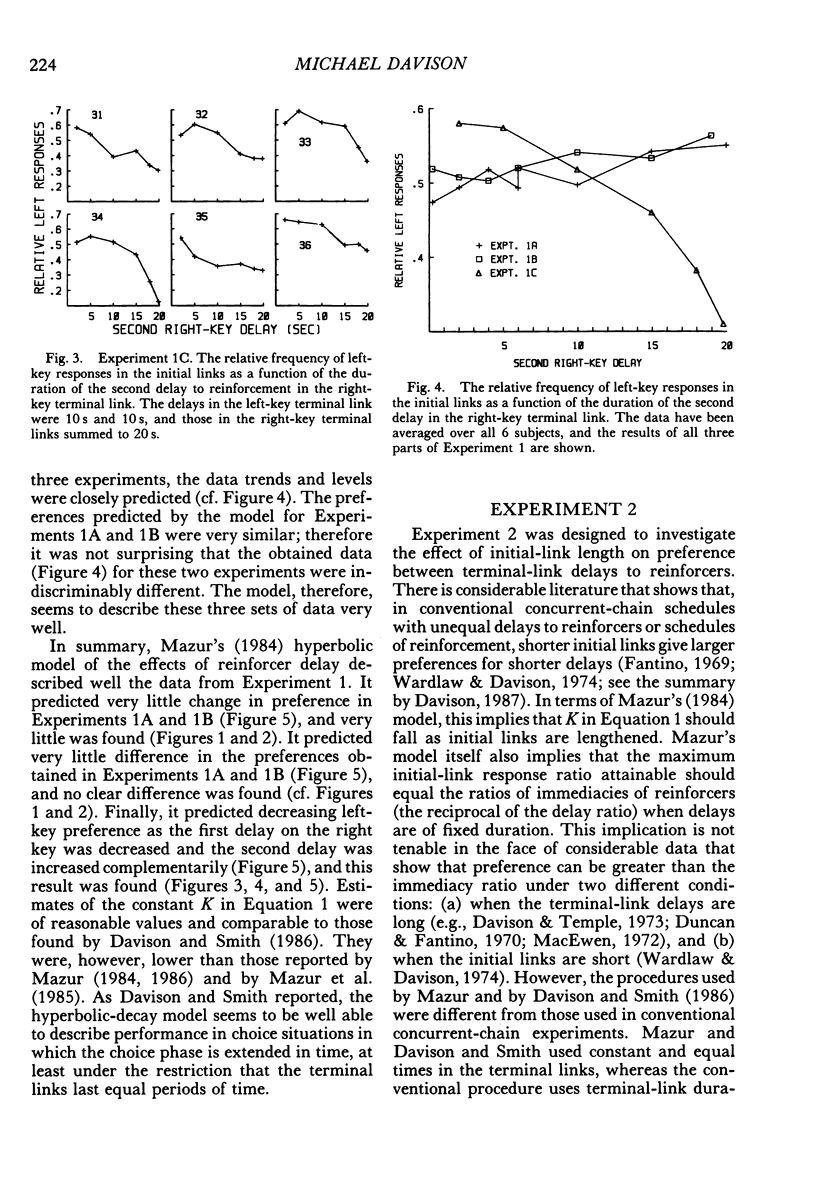
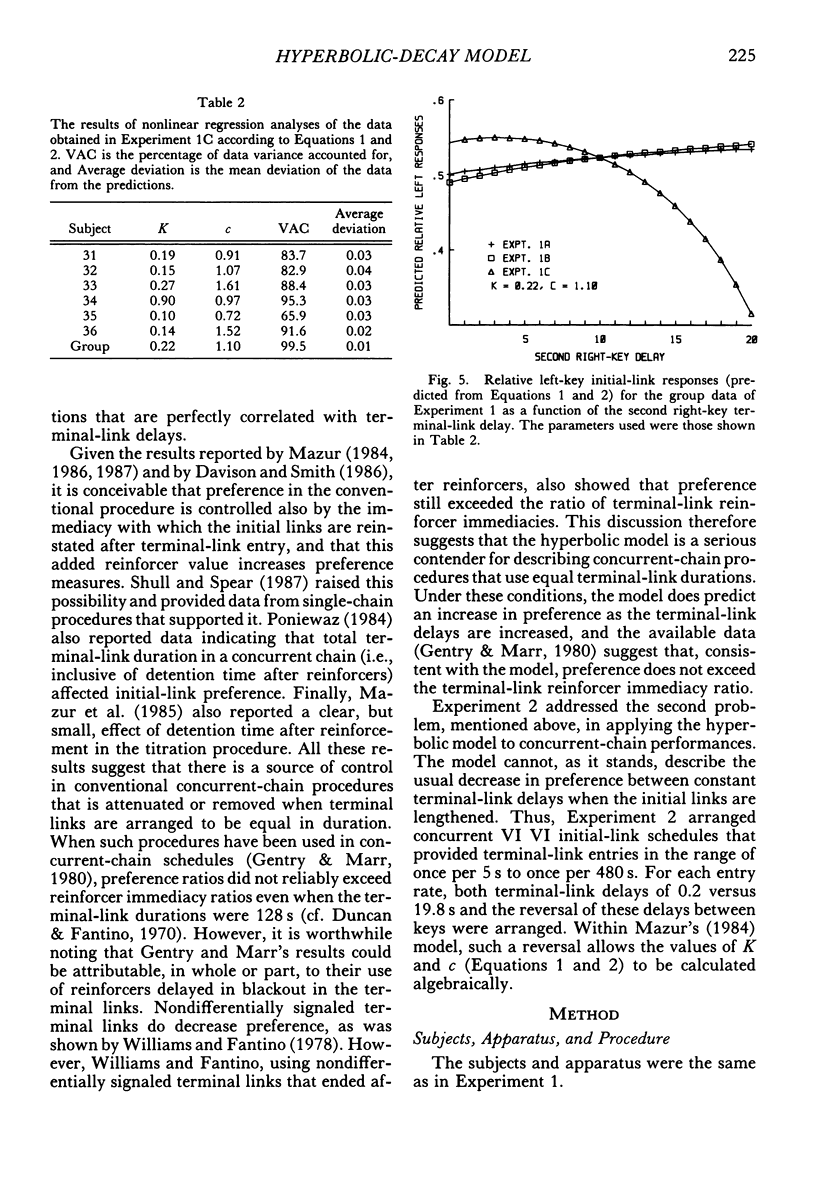
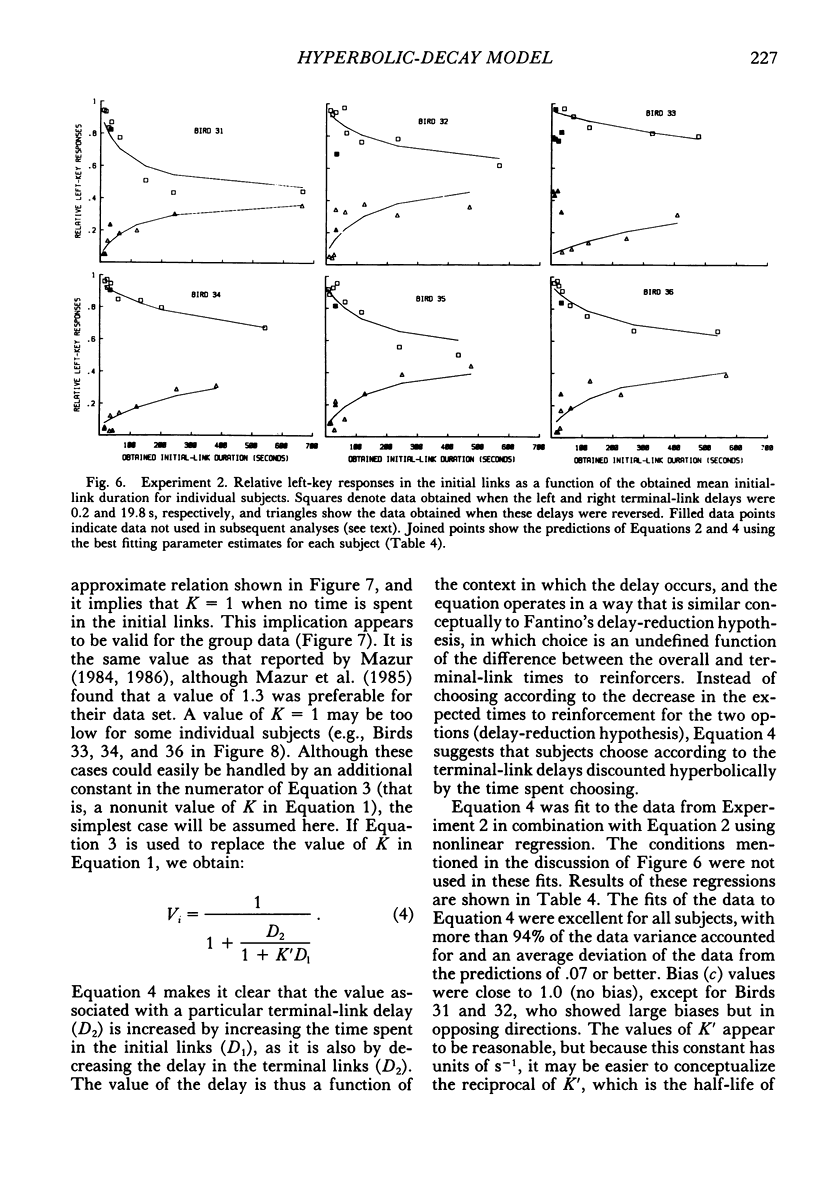
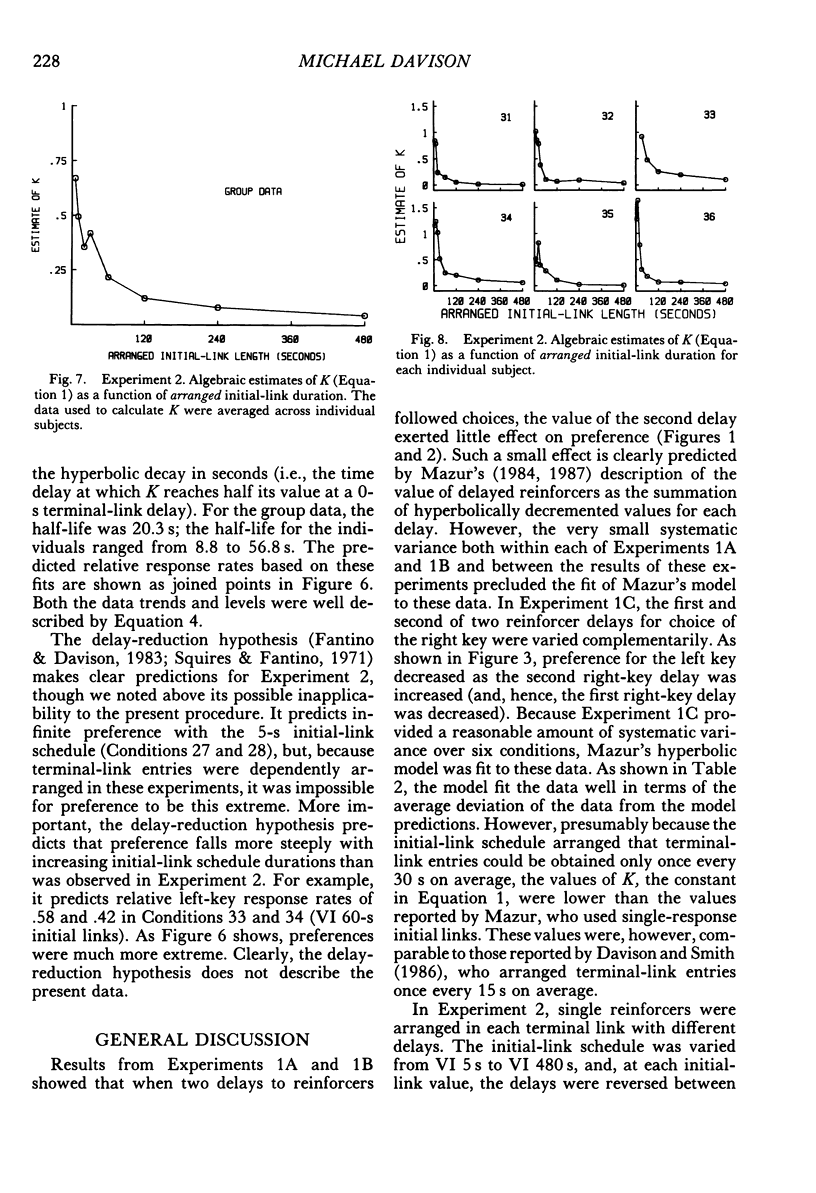
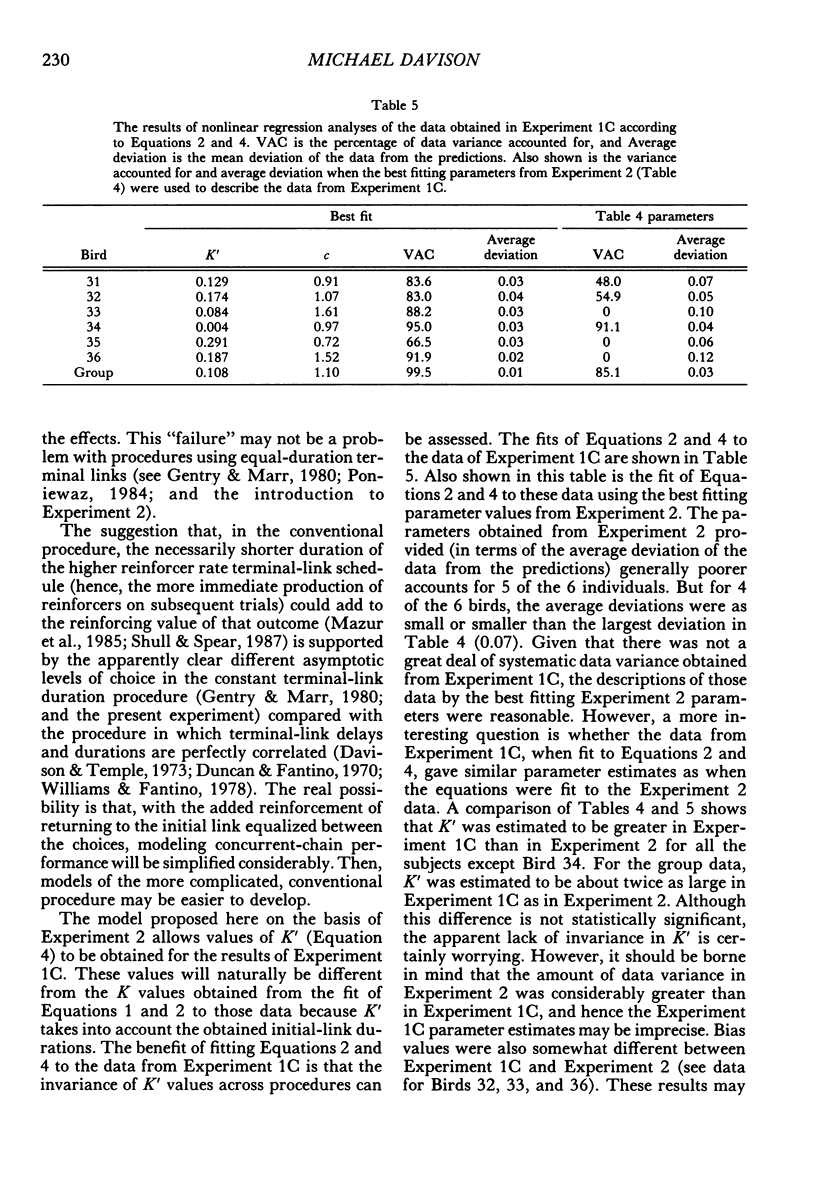
Six pigeons were trained in concurrent-chain schedules with equal aperiodic initial links and delays to reinforcers in the terminal links. The terminal links always lasted 30 s. In Experiment 1, two reinforcers were delivered in each terminal link, with the first reinforcer delivered either 1 s (Experiment 1A) or 5 s (Experiment 1B) after choice. In these experiments, the delay between the first and second reinforcers in one terminal link was 10 s, and the delay between the first and second reinforcers on the other key was varied. This variation produced little change in preference. In Experiment 1C, the first and second delays on one key were 10 s, and on the other key they were varied within the restriction that the sum of delays was 20 s. Preference for the varied terminal link increased as the first delay was decreased. A hyperbolic model of the value of reinforcer delay provided a good description of the data from Experiment 1. In Experiment 2, a single reinforcer was delivered in each terminal link after a delay of either 0.2 or 19.8 s, and these delays were reversed between conditions. The initial-link schedule providing terminal-link access was varied from means of 5 s to 480 s. As the initial-link duration was increased, preference for the shorter delay became less extreme. An extension of the hyperbolic-decay model, in which the decay constant was a hyperbolic function of the initial-link duration, described the results well. Differences between the procedure used here (constant-duration terminal links) and that used in conventional concurrent-chain research precludes use of the model as a general account of concurrent-chain performance.
Keywords: delay of reinforcement, concurrent-chain schedules, preference, hyperbolic decay, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Reynolds G. S. A quantitative analysis of the responding maintained by interval schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 May;11(3 Suppl):327–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-s327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Temple W. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: an alternative model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):393–403. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan B., Fantino E. Choice for periodic schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):73–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Davison M. Choice: Some quantitative relations. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jul;40(1):1–13. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.40-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Royalty P. A molecular analysis of choice on concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1987 Jul;48(1):145–159. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1987.48-145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. D., Marr M. J. Choice and reinforcement delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Jan;33(1):27–37. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.33-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R., Fantino E. Relative delay of reinforcement and choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 May;19(3):437–450. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.19-437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macewen D. The effects of terminal-link fixed-interval and variable-interval schedules on responding under concurrent chained schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):253–261. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur J. E. Fixed and variable ratios and delays: further tests of an equivalence rule. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1986 Apr;12(2):116–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur J. E., Snyderman M., Coe D. Influences of delay and rate of reinforcement on discrete-trial choice. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1985 Oct;11(4):565–575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poniewaz W. R. Effects on preference of reinforcement delay, number of reinforcers, and terminal-link duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Sep;42(2):255–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.42-255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull R. L., Spear D. J., Bryson A. E. Delay or rate of food delivery as determiners of response rate. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Mar;35(2):129–143. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squires N., Fantino E. A model for choice in simple concurrent and concurrent-chains schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Jan;15(1):27–38. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw G. R., Davison M. C. Preference for fixed-interval schedules: effects of initial-link length. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Mar;21(2):331–340. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A., Fantino E. Effects on choice of reinforcement delay and conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jan;29(1):77–86. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.29-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


