Abstract
Choice behavior in college students was examined in two experiments using the concurrent-chains procedure. In both experiments, the concurrent chains were presented on a microcomputer in the form of an air-defense game in which subjects used two radar systems to detect and subsequently destroy enemy aircraft. Access to one of two radar systems was controlled by a pair of independent concurrent variable-interval 60-s schedules with a 4-s changeover delay always in effect. In the terminal link, the appearance of an enemy aircraft was determined by a pair of differentially segmented fixed-time schedules (Experiment 1) or fixed-interval schedules (Experiment 2) of equal overall duration. In Experiment 1, the terminal-link duration was either 20 s or 40 s, and subjects preferred the unsegmented to the segmented intervals. In Experiment 2, the duration was either 10 s or 60 s, and the reinforcement contingencies required responding during the terminal link. Prior to the reinstatement of the initial link, subjects estimated the duration of the terminal-link schedule. Segmentation affected choice in the 60-s conditions but not in the 10-s ones. Preference for the unsegmented schedule was correlated with an overestimation of the durations for the segmented schedules. These results replicated those found in animal experiments and support the notion of increasing the psychological distance to reward by segmenting a time-based schedule of reinforcement.
Keywords: preference, choice, segmentation, interval schedules, psychological distance, concurrent chains, computer game, humans
Full text
PDF

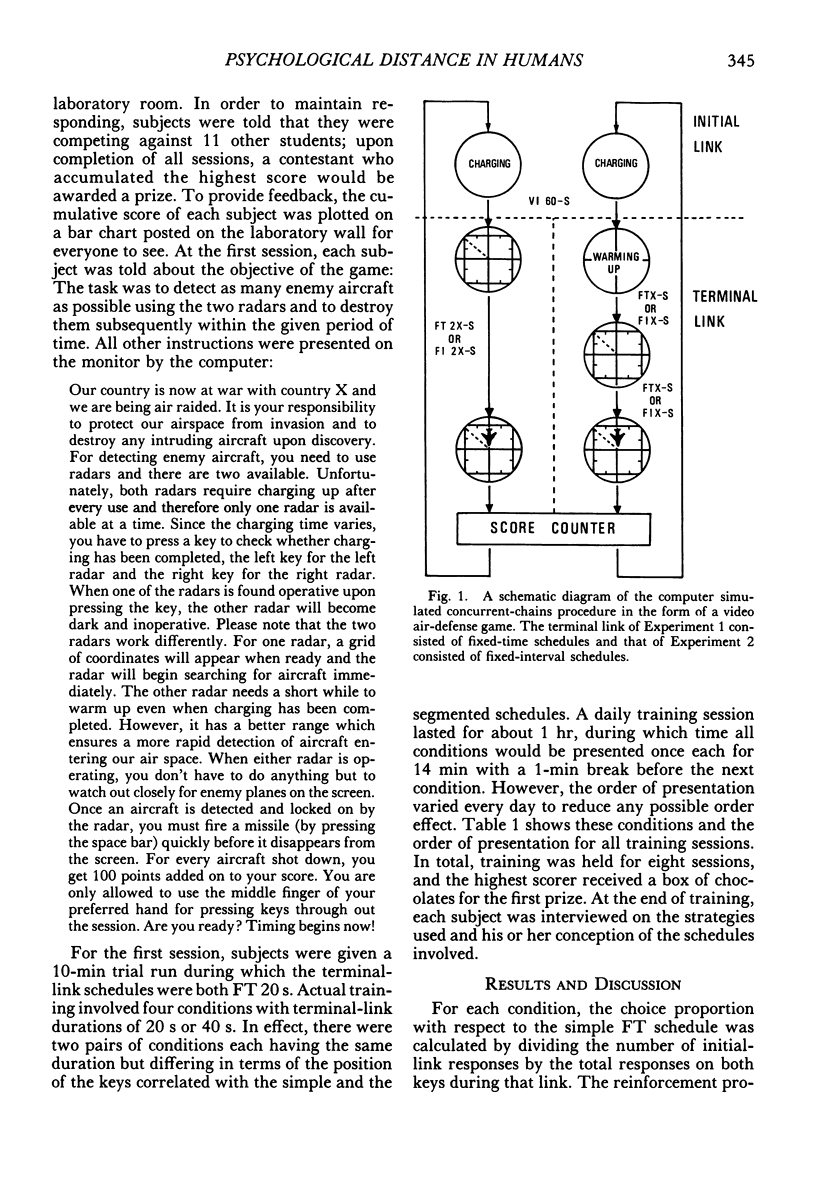
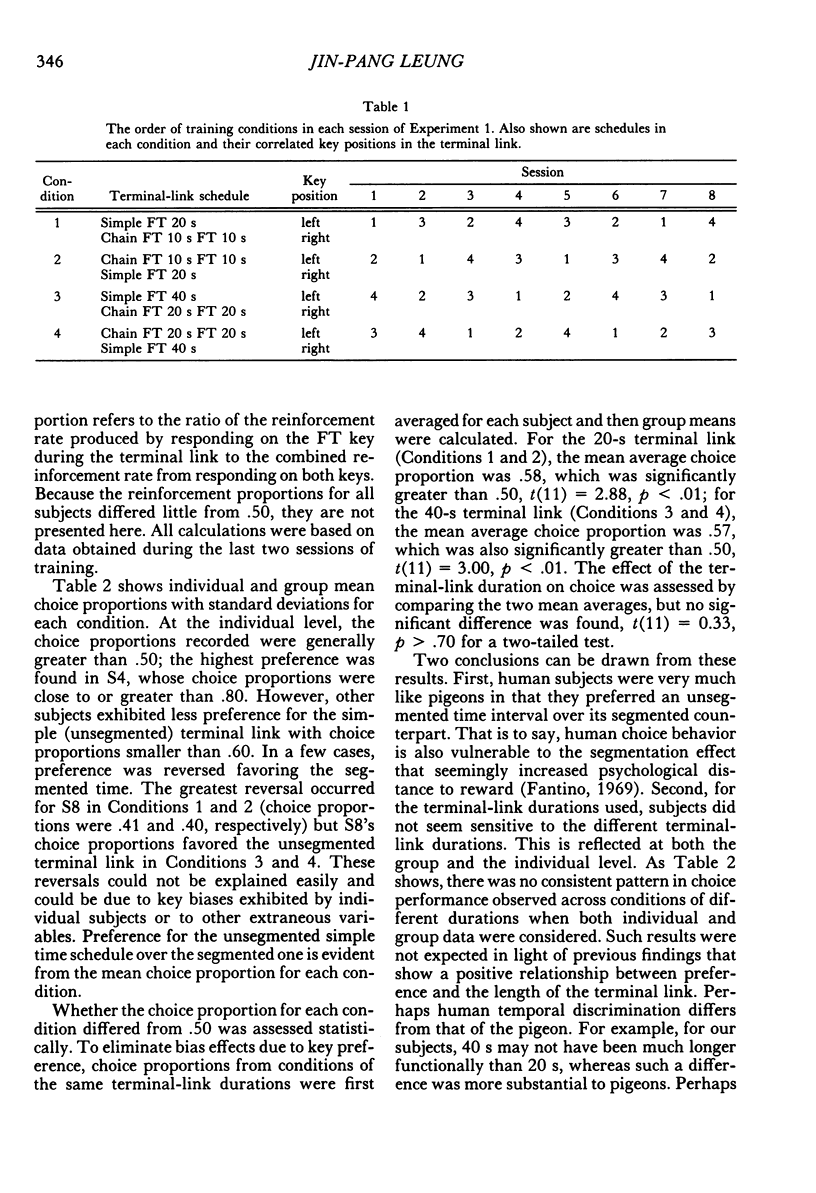
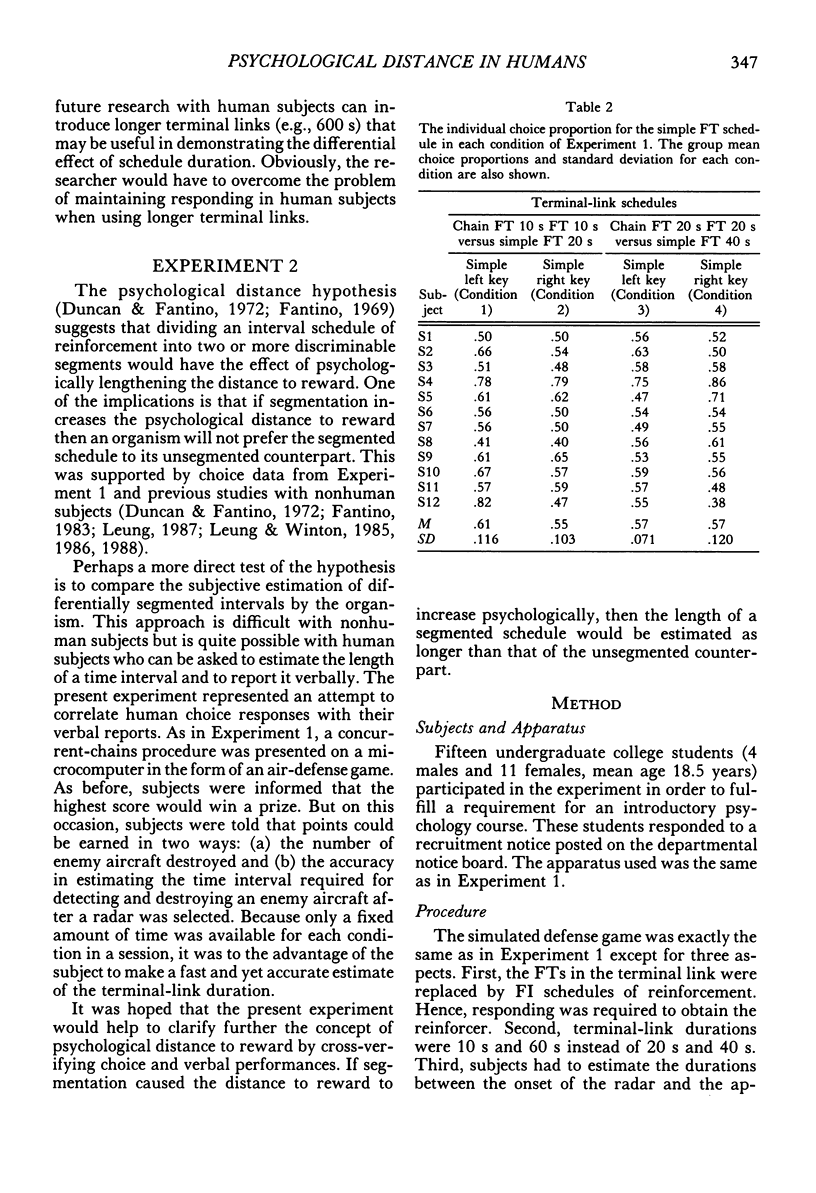

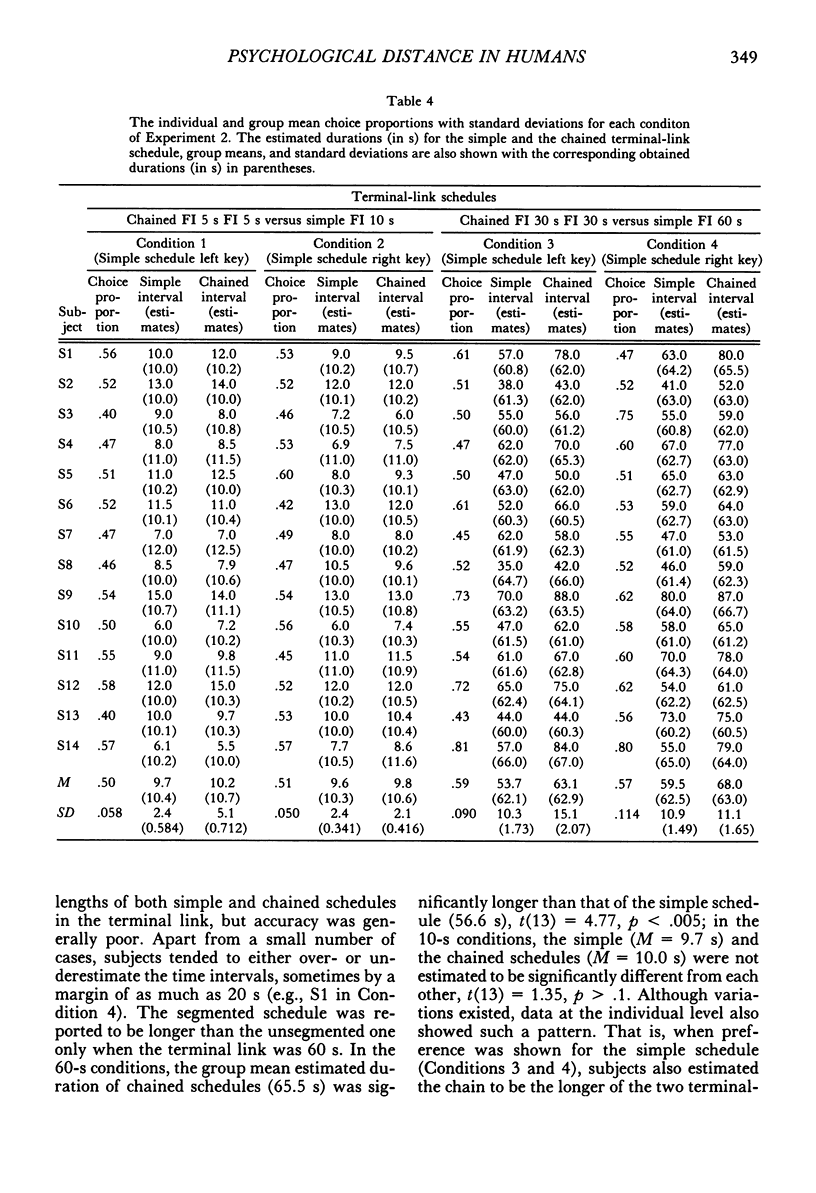



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Duncan B., Fantino E. The psychological distance to reward. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):23–34. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E., Duncan B. Some effects of interreinforcement time upon choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):3–14. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Effects of required rates of responding upon choice. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Jan;11(1):15–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERRNSTEIN R. J. Relative and absolute strength of response as a function of frequency of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jul;4:267–272. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. P., Winton A. S. Preference for less segmented fixed-time components in concurrent-chain schedules of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Sep;46(2):175–183. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.46-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. P., Winton A. S. Preference for simple interval schedules of reinforcement in concurrent chains: Effects of segmentation ratio. J Exp Anal Behav. 1988 Jan;49(1):9–20. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1988.49-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. P., Winton A. S. Preference for unsegmented interreinforcement intervals in concurrent chains. J Exp Anal Behav. 1985 Jul;44(1):89–101. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1985.44-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. A., Shimoff E., Catania A. C., Sagvolden T. Uninstructed human responding: sensitivity to ratio and interval contingencies. J Exp Anal Behav. 1977 May;27(3):453–467. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1977.27-453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J. Delayed reinforcement versus reinforcement after a fixed interval. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):375–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuringer A. J., Schneider B. A. Separating the effects of interreinforcement time and number of interreinforcement responses. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):661–667. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W. Choice between two-component chained and tandem schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):45–60. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


