Abstract
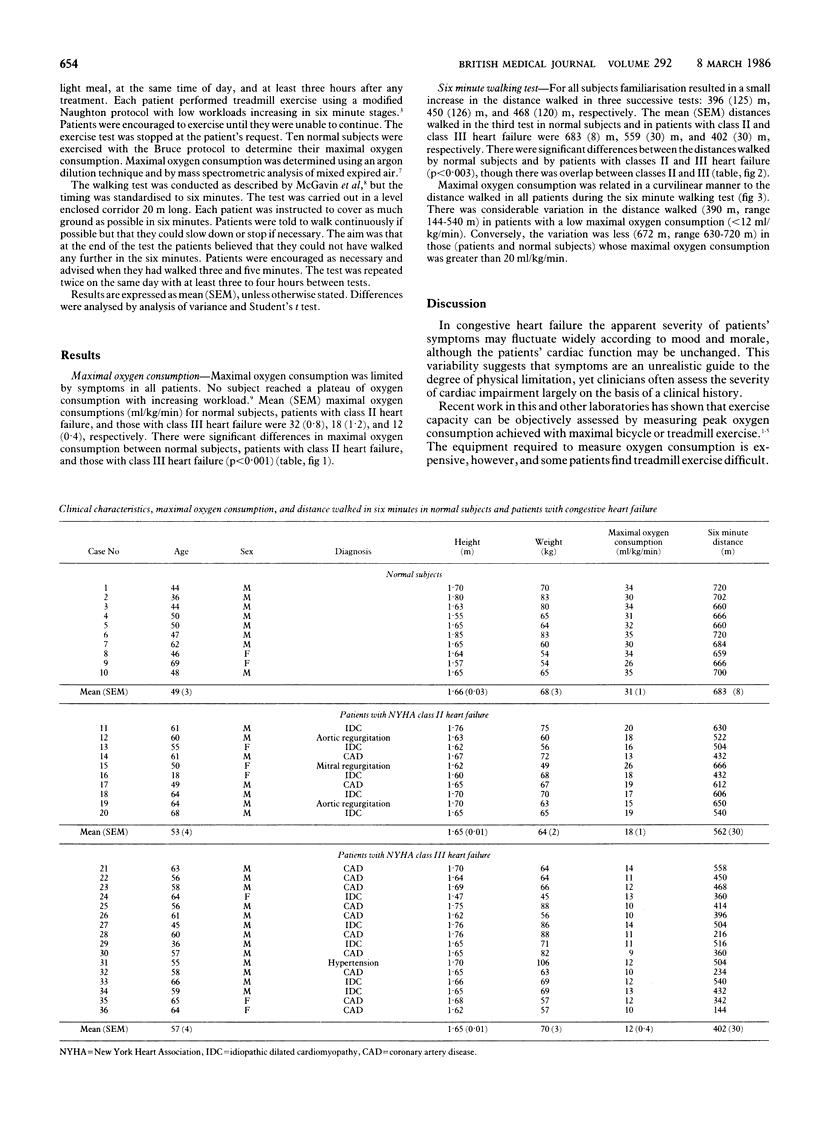
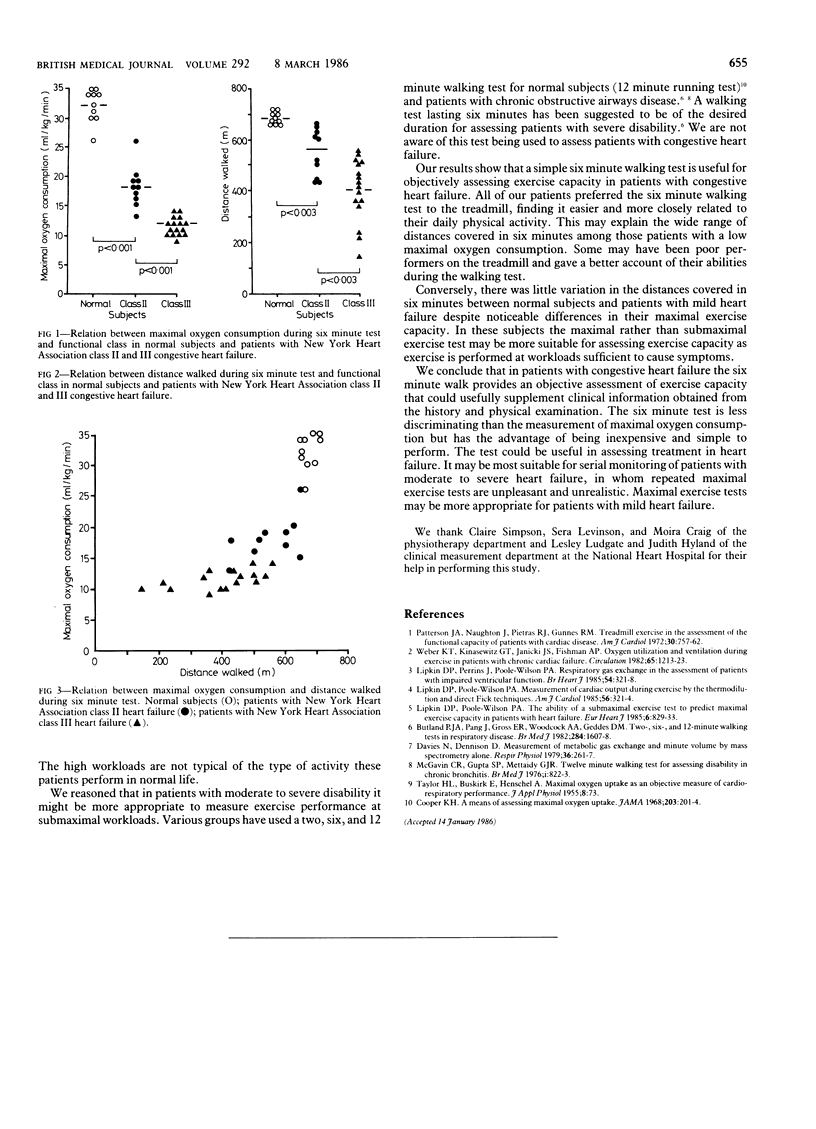
Twenty six patients, mean age 58 years (range 36-68), with stable chronic heart failure, New York Heart Association class II-III, and 10 normal subjects of a similar age range were studied. Exercise capacity was assessed by determining oxygen consumption reached during a maximal treadmill exercise test and by measuring the distance each patient walked in six minutes. There were significant differences in the distance walked in six minutes between normal subjects, patients with heart failure, class II, and those with class III heart failure (683 m, 558 m, and 402 m, respectively (p less than 0.003)). The relation between maximal oxygen consumption and the distance walked in six minutes was curvilinear; thus the distance walked varied considerably in those with a low maximal oxygen consumption but varied little in patients and normal subjects with a high maximal oxygen consumption. All subjects preferred performing the six minute walking test to the treadmill exercise test, considering it to be more closely related to their daily physical activity. The six minute test is a simple objective guide to disability in patients with chronic heart failure and could be of particular value in assessing patients with severe heart failure but less useful in assessing patients with mild heart failure.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butland R. J., Pang J., Gross E. R., Woodcock A. A., Geddes D. M. Two-, six-, and 12-minute walking tests in respiratory disease. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 May 29;284(6329):1607–1608. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6329.1607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. H. A means of assessing maximal oxygen intake. Correlation between field and treadmill testing. JAMA. 1968 Jan 15;203(3):201–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin D. P., Bayliss J., Poole-Wilson P. A. The ability of a submaximal exercise test to predict maximal exercise capacity in patients with heart failure. Eur Heart J. 1985 Oct;6(10):829–833. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin D. P., Perrins J., Poole-Wilson P. A. Respiratory gas exchange in the assessment of patients with impaired ventricular function. Br Heart J. 1985 Sep;54(3):321–328. doi: 10.1136/hrt.54.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin D. P., Poole-Wilson P. A. Measurement of cardiac output during exercise by the thermodilution and direct Fick techniques in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 1985 Aug 1;56(4):321–324. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGavin C. R., Gupta S. P., McHardy G. J. Twelve-minute walking test for assessing disability in chronic bronchitis. Br Med J. 1976 Apr 3;1(6013):822–823. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6013.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. A., Naughton J., Pietras R. J., Gunnar R. M. Treadmill exercise in assessment of the functional capacity of patients with cardiac disease. Am J Cardiol. 1972 Nov;30(7):757–762. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR H. L., BUSKIRK E., HENSCHEL A. Maximal oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):73–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K. T., Kinasewitz G. T., Janicki J. S., Fishman A. P. Oxygen utilization and ventilation during exercise in patients with chronic cardiac failure. Circulation. 1982 Jun;65(6):1213–1223. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.6.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


