Abstract
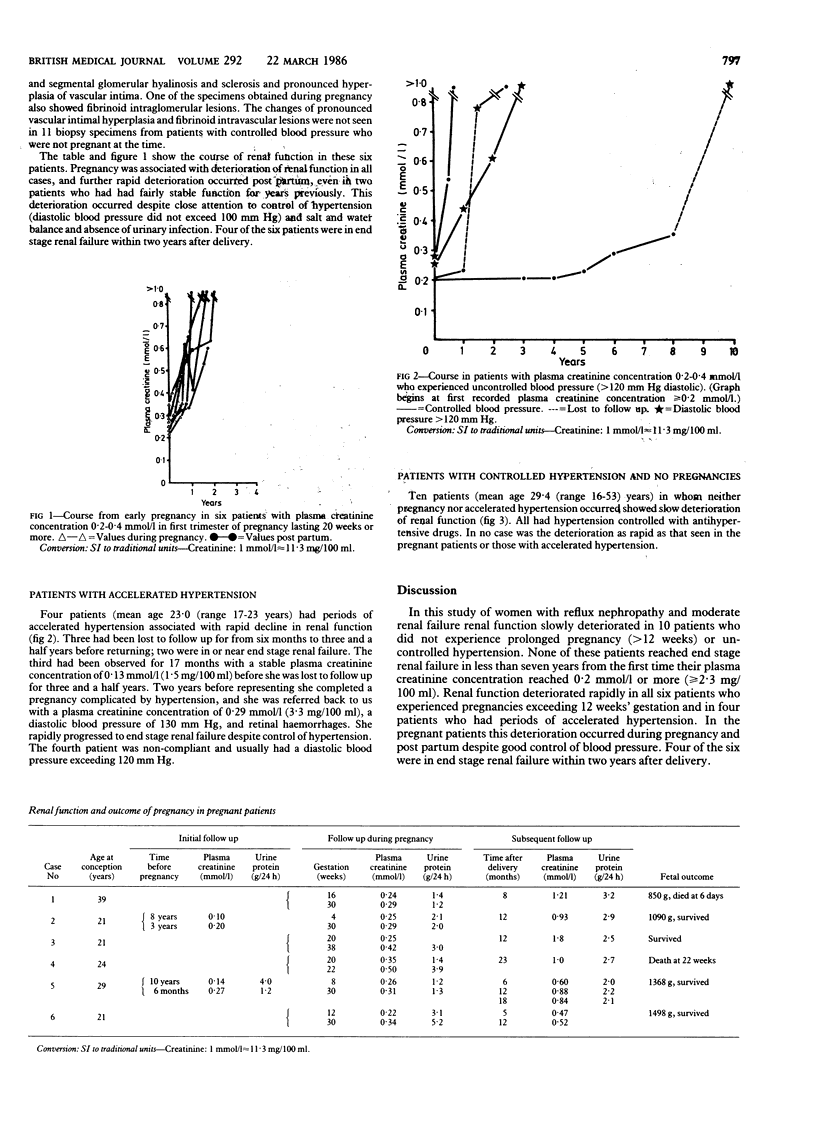
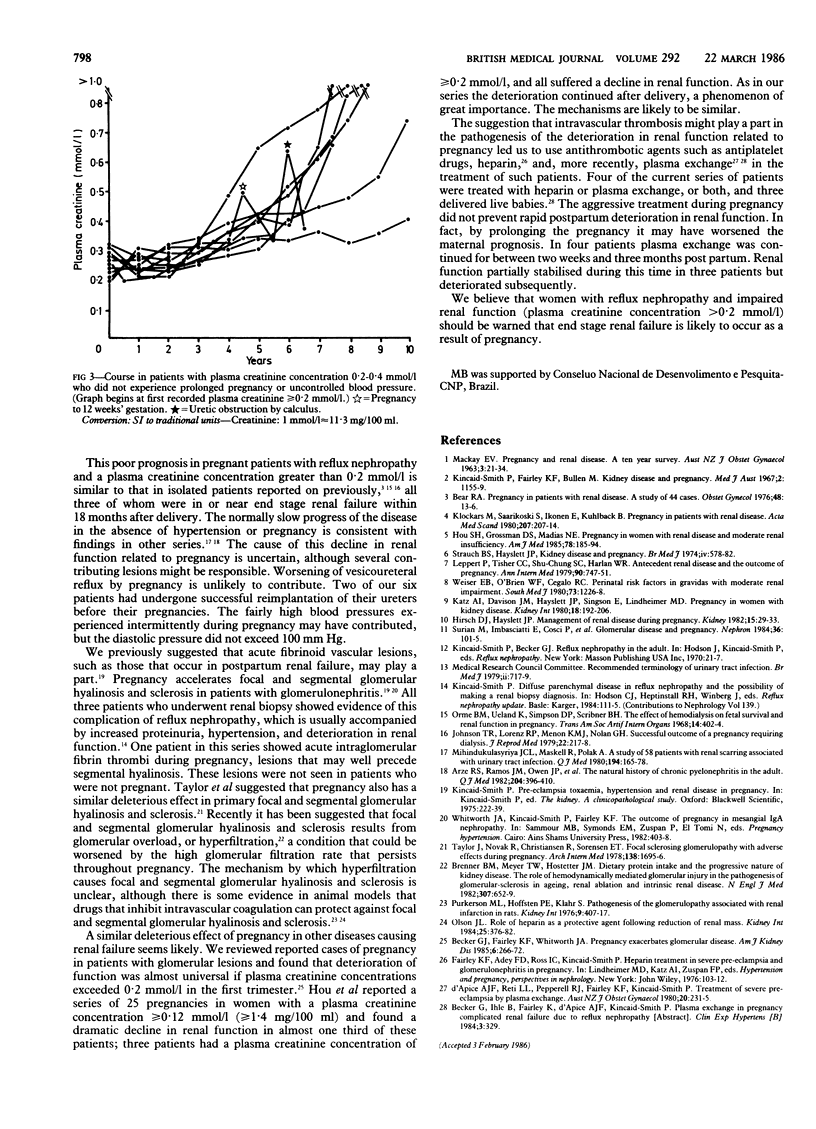
During a 10 year study of women with reflux nephropathy 20 women had plasma creatinine concentrations in the range 0.2-0.4 mmol/l (2.3-4.5 mg/100 ml). Six experienced pregnancies exceeding 12 weeks' gestation. Pregnancy was associated with rapid deterioration in function in all six, resulting in end stage renal failure in four women within two years after delivery despite adequate control of blood pressure. Of the 14 women who did not have a prolonged pregnancy, four had periods of uncontrolled hypertension, all of which were related to non-compliance or loss from follow up, or both. Uncontrolled hypertension was also associated with accelerated renal failure, and all four women progressed quickly to end stage renal failure. The remaining 10 women were observed for from five to 10 years; in all 10 renal function deteriorated slowly, and none reached end stage renal failure within seven years. It is concluded that pregnancy in patients with reflux nephropathy and moderately severe renal failure has a deleterious effect on renal function.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arze R. S., Ramos J. M., Owen J. P., Morley A. R., Elliott R. W., Wilkinson R., Ward M. K., Kerr D. N. The natural history of chronic pyelonephritis in the adult. Q J Med. 1982;51(204):396–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear R. A. Pregnancy in patients with renal disease. A study of 44 cases. Obstet Gynecol. 1976 Jul;48(1):13–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker G. J., Fairley K. F., Whitworth J. A. Pregnancy exacerbates glomerular disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 1985 Oct;6(4):266–272. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(85)80186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairley K. F., Adey F. D., Ross I. C., Kincaid-Smith P. Heparin treatment in severe preeclampsia and glomerulonephritis in pregnancy. Perspect Nephrol Hypertens. 1976;5:103–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou S. H., Grossman S. D., Madias N. E. Pregnancy in women with renal disease and moderate renal insufficiency. Am J Med. 1985 Feb;78(2):185–194. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90425-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson T. R., Jr, Lorenz R. P., Menon K. M., Nolan G. H. Successful outcome of a pregnancy requiring dialysis. Effects on serum progesterone and estrogens. J Reprod Med. 1979 Apr;22(4):217–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. I., Davison J. M., Hayslett J. P., Singson E., Lindheimer M. D. Pregnancy in women with kidney disease. Kidney Int. 1980 Aug;18(2):192–206. doi: 10.1038/ki.1980.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. S. Diffuse parenchymal lesions in reflux nephropathy and the possibility of making a renal biopsy diagnosis in reflux nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;39:111–115. doi: 10.1159/000409240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klockars M., Saarikoski S., Ikonen E., Kuhlbäck B. Pregnancy in patients with renal disease. Acta Med Scand. 1980;207(3):207–214. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1980.tb09707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert P., Tisher C. C., Cheng S. C., Harlan W. R. Antecedent renal disease and the outcome of pregnancy. Ann Intern Med. 1979 May;90(5):747–751. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L. Role of heparin as a protective agent following reduction of renal mass. Kidney Int. 1984 Feb;25(2):376–382. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme B. M., Ueland K., Simpson D. P., Scribner B. H. The effect of hemodialysis on fetal survival and renal function in pregnancy. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1968;14:402–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purkerson M. L., Hoffsten P. E., Klahr S. Pathogenesis of the glomerulopathy associated with renal infarction in rats. Kidney Int. 1976 May;9(5):407–417. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch B. S., Hayslett J. P. Kidney disease and pregnancy. Br Med J. 1974 Dec 7;4(5944):578–582. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5944.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surian M., Imbasciati E., Cosci P., Banfi G., Barbiano di Belgiojoso G., Brancaccio D., Minetti L., Ponticelli C. Glomerular disease and pregnancy. A study of 123 pregnancies in patients with primary and secondary glomerular diseases. Nephron. 1984;36(2):101–105. doi: 10.1159/000183126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J., Novak R., Christiansen R., Sorensen E. T. Focal sclerosing glomerulopathy with adverse effects during pregnancy. Arch Intern Med. 1978 Nov;138(11):1695–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser E. B., O'Brien W. F., Cefalo R. C. Perinatal risk factors in gravidas with moderate renal impairment. South Med J. 1980 Sep;73(9):1226–1228. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198009000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Apice A. J., Reti L. L., Pepperell R. J., Fairley K. F., Kincaid-Smith P. Treatment of severe pre-eclampsia by plasma exchange. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 1980 Nov;20(4):231–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1479-828x.1980.tb00773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


