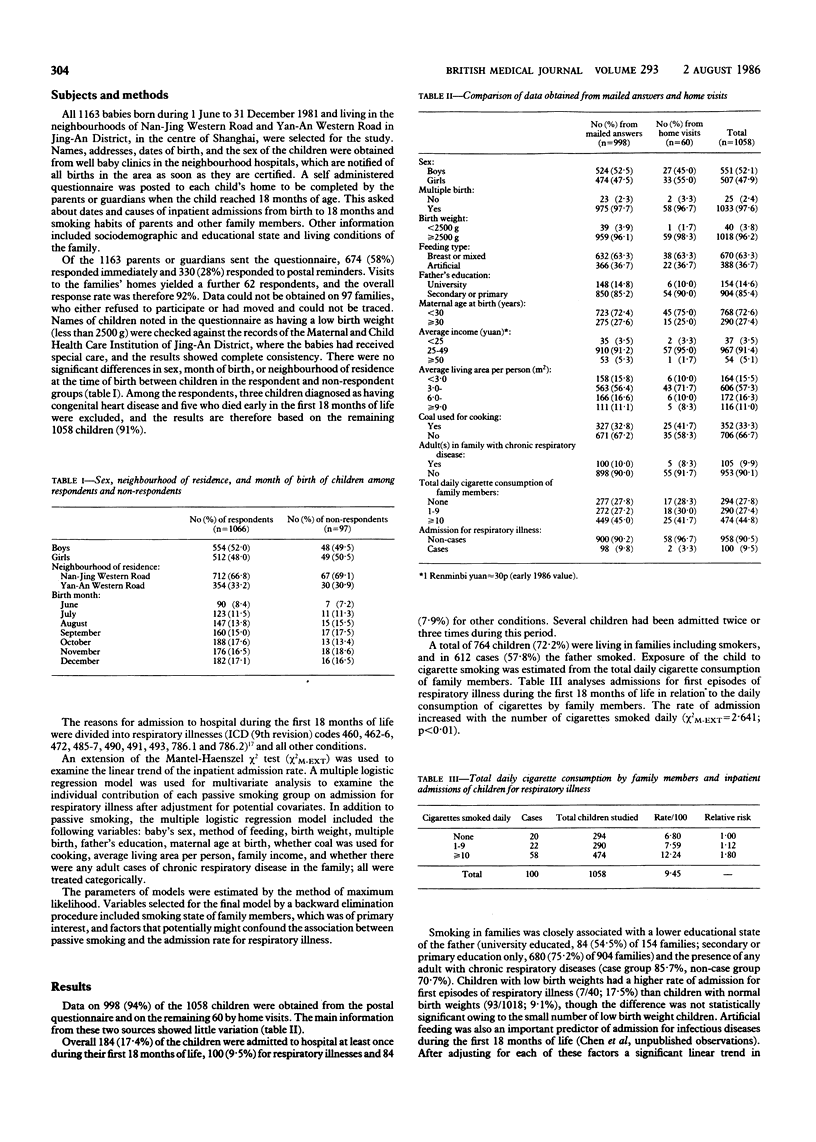
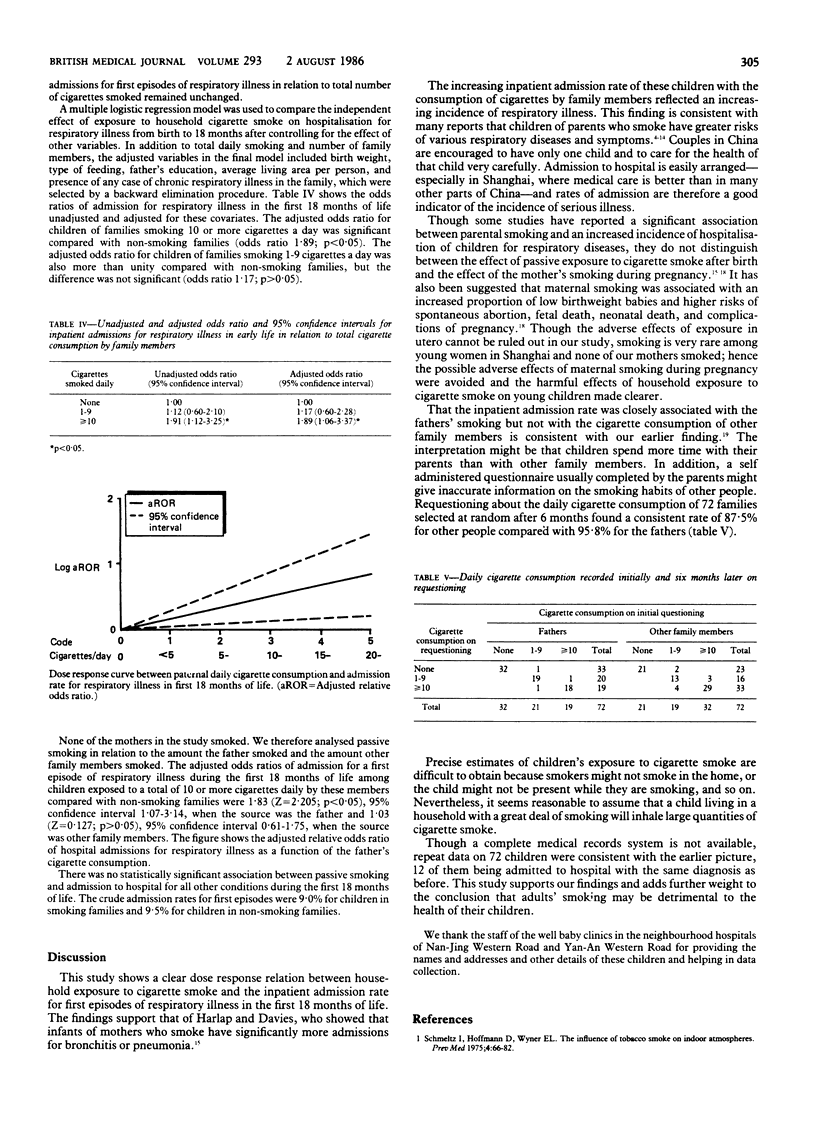
Abstract
An association was sought between passive smoking and inpatient admissions for respiratory illness in 1058 children born between 1 June and 31 December 1981 and living in the neighborhoods of Nan-Jing Western Road and Yan-An Western Road in Jing-An District, Shanghai. The admission rate for first episodes of respiratory illness was positively correlated with the total daily cigarette consumption of family members during the children's first 18 months of life. The relative risk of developing a first episode of respiratory illness was 1.80 for children living in families including people who smoked 10 or more cigarettes a day compared with those living in non-smoking families. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the effect of passive smoking on inpatient admission for respiratory illness was independent of the child's birth weight, type of feeding, father's education, size of the home, and chronic respiratory disease among adults in the family. The adjusted odds ratios compared with the non-smoking group were 1.17 in families smoking 1.9 cigarettes daily and 1.89 in families smoking 10 or more cigarettes daily. These data suggest that exposure to household cigarette smoke of children in early life increases the risk of severe respiratory illness.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Binder R. E., Mitchell C. A., Hosein H. R., Bouhuys A. Importance of the indoor environment in air pollution exposure. Arch Environ Health. 1976 Nov-Dec;31(6):277–279. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1976.10667235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley J. R. Respiratory symptoms in children and parental smoking and phlegm production. Br Med J. 1974 Apr 27;2(5912):201–204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5912.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fergusson D. M., Horwood L. J., Shannon F. T., Taylor B. Parental smoking and lower respiratory illness in the first three years of life. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1981 Sep;35(3):180–184. doi: 10.1136/jech.35.3.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gortmaker S. L., Walker D. K., Jacobs F. H., Ruch-Ross H. Parental smoking and the risk of childhood asthma. Am J Public Health. 1982 Jun;72(6):574–579. doi: 10.2105/ajph.72.6.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz M. D., Burrows B. Respiratory symptoms related to smoking habits of family adults. Chest. 1976 Jan;69(1):48–50. doi: 10.1378/chest.69.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullan C. R., Hey E. N. Wheezing, asthma, and pulmonary dysfunction 10 years after infection with respiratory syncytial virus in infancy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jun 5;284(6330):1665–1669. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6330.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said G., Zalokar J., Lellouch J., Patois E. Parental smoking related to adenoidectomy and tonsillectomy in children. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1978 Jun;32(2):97–101. doi: 10.1136/jech.32.2.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling R. S., Letai A. D., Hui S. L., Beck G. J., Schoenberg J. B., Bouhuys A. Lung function, respiratory disease, and smoking in families. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Oct;106(4):274–283. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speizer F. E., Ferris B., Jr, Bishop Y. M., Spengler J. Respiratory disease rates and pulmonary function in children associated with NO2 exposure. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Jan;121(1):3–10. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.121.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stedman R. L. The chemical composition of tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chem Rev. 1968 Apr;68(2):153–207. doi: 10.1021/cr60252a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. T., Tager I. B., Speizer F. E., Rosner B. Persistent wheeze. Its relation to respiratory illness, cigarette smoking, and level of pulmonary function in a population sample of children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980 Nov;122(5):697–707. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1980.122.5.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



