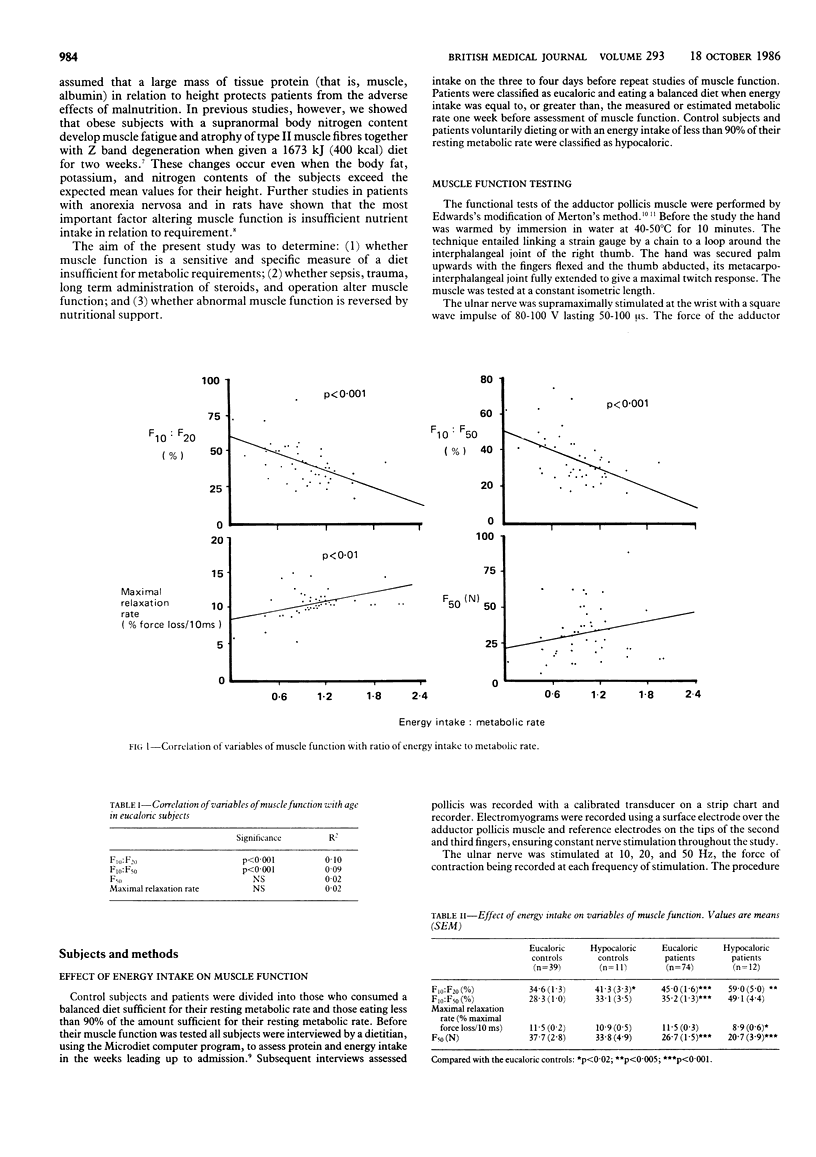
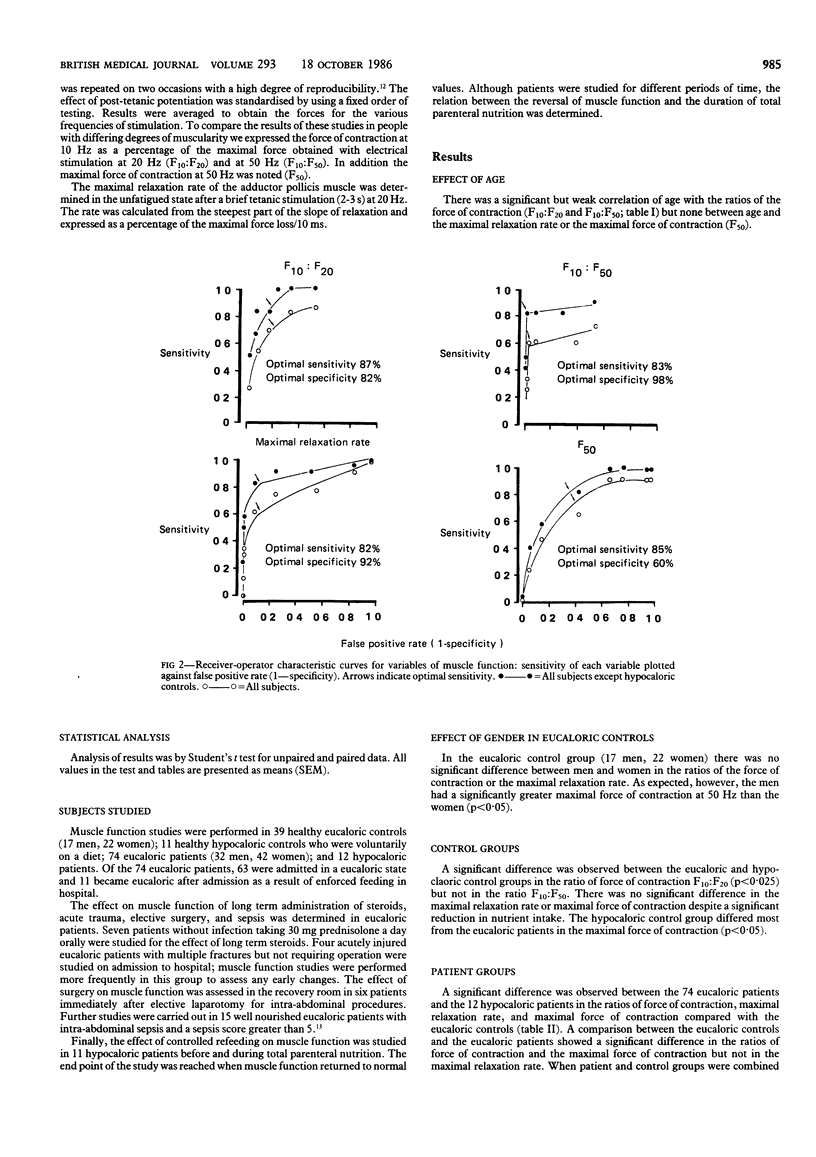
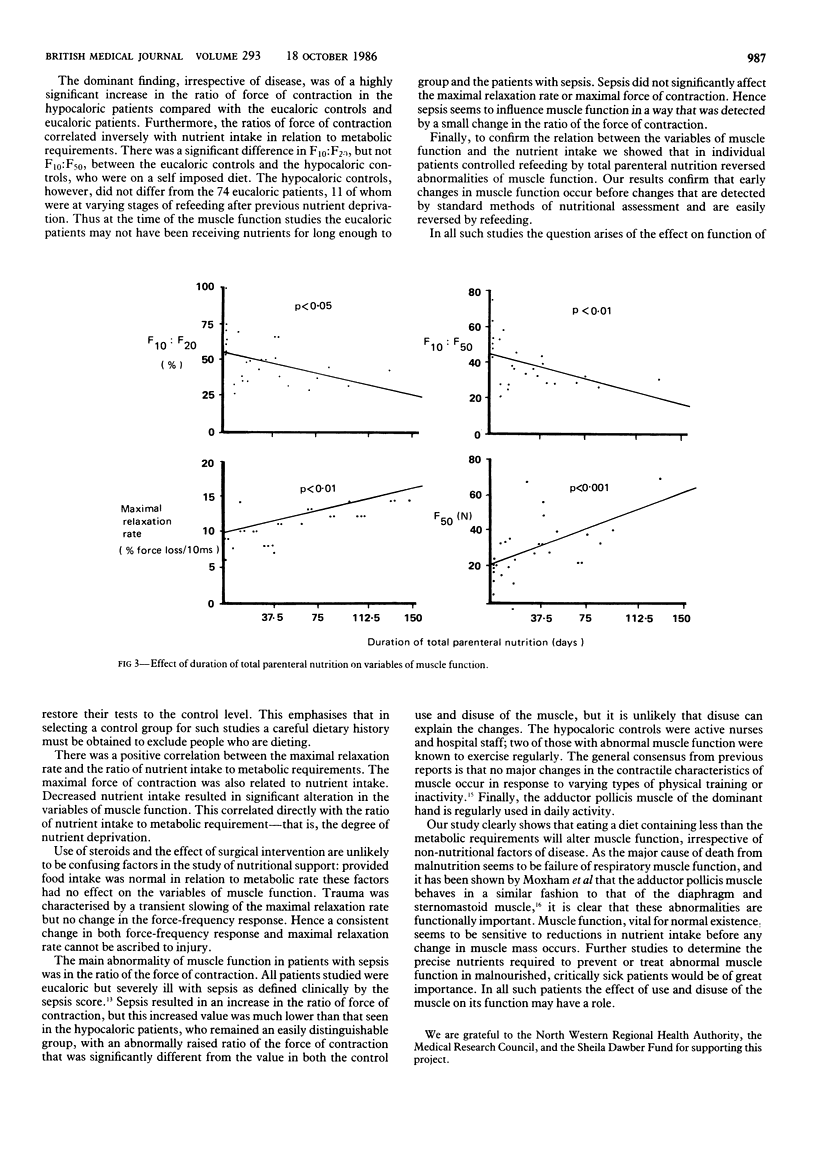
Abstract
The stimulated contraction-relaxation characteristics of the adductor pollicis muscle were used to assess nutritional state in patients and healthy controls. In both groups insufficient nutrition resulted in abnormal muscle function. The ratio of force of contraction at 10 Hz to that at 20 Hz yielded the best combination of sensitivity (87%) and specificity (82%). Sepsis resulted in abnormal muscle function, but the changes were easily distinguishable from those in subjects taking an inadequate diet. Long term administration of steroids, trauma, and surgery had no effect on muscle function. A prospective study of 11 malnourished patients with abnormal muscle function showed that all variables of muscle function returned to normal values with total parenteral nutrition. This reversal correlated significantly with the duration of parenteral nutrition and occurred before any change in anthropometric variables or plasma albumin concentration. Muscle function studies are sensitive and specific indicators of malnutrition; results depend on energy intake but are not influenced by administration of steroids, trauma, or surgery.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R., Maini B. S., Schlamm H. T., Smith M. F. Nutritional and metabolic assessment of the hospitalized patient. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1977;1(1):11–22. doi: 10.1177/014860717700100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozzetti F., Pagnoni A. M., Del Vecchio M. Excessive caloric expenditure as a cause of malnutrition in patients with cancer. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1980 Feb;150(2):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzby G. P., Mullen J. L., Matthews D. C., Hobbs C. L., Rosato E. F. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. Am J Surg. 1980 Jan;139(1):160–167. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90246-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detsky A. S., Baker J. P., Mendelson R. A., Wolman S. L., Wesson D. E., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Evaluating the accuracy of nutritional assessment techniques applied to hospitalized patients: methodology and comparisons. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1984 Mar-Apr;8(2):153–159. doi: 10.1177/0148607184008002153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. H., Young A., Hosking G. P., Jones D. A. Human skeletal muscle function: description of tests and normal values. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977 Mar;52(3):283–290. doi: 10.1042/cs0520283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elebute E. A., Stoner H. B. The grading of sepsis. Br J Surg. 1983 Jan;70(1):29–31. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800700111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes J., Russell D. M., Whitwell J., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Skeletal muscle function in malnutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982 Oct;36(4):602–610. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/36.4.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERTON P. A. Voluntary strength and fatigue. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):553–564. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham J., Morris A. J., Spiro S. G., Edwards R. H., Green M. Contractile properties and fatigue of the diaphragm in man. Thorax. 1981 Mar;36(3):164–168. doi: 10.1136/thx.36.3.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Prendergast P. J., Darby P. L., Garfinkel P. E., Whitwell J., Jeejeebhoy K. N. A comparison between muscle function and body composition in anorexia nervosa: the effect of refeeding. Am J Clin Nutr. 1983 Aug;38(2):229–237. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/38.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. M., Walker P. M., Leiter L. A., Sima A. A., Tanner W. K., Mickle D. A., Whitwell J., Marliss E. B., Jeejeebhoy K. N. Metabolic and structural changes in skeletal muscle during hypocaloric dieting. Am J Clin Nutr. 1984 Apr;39(4):503–513. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/39.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


