Abstract
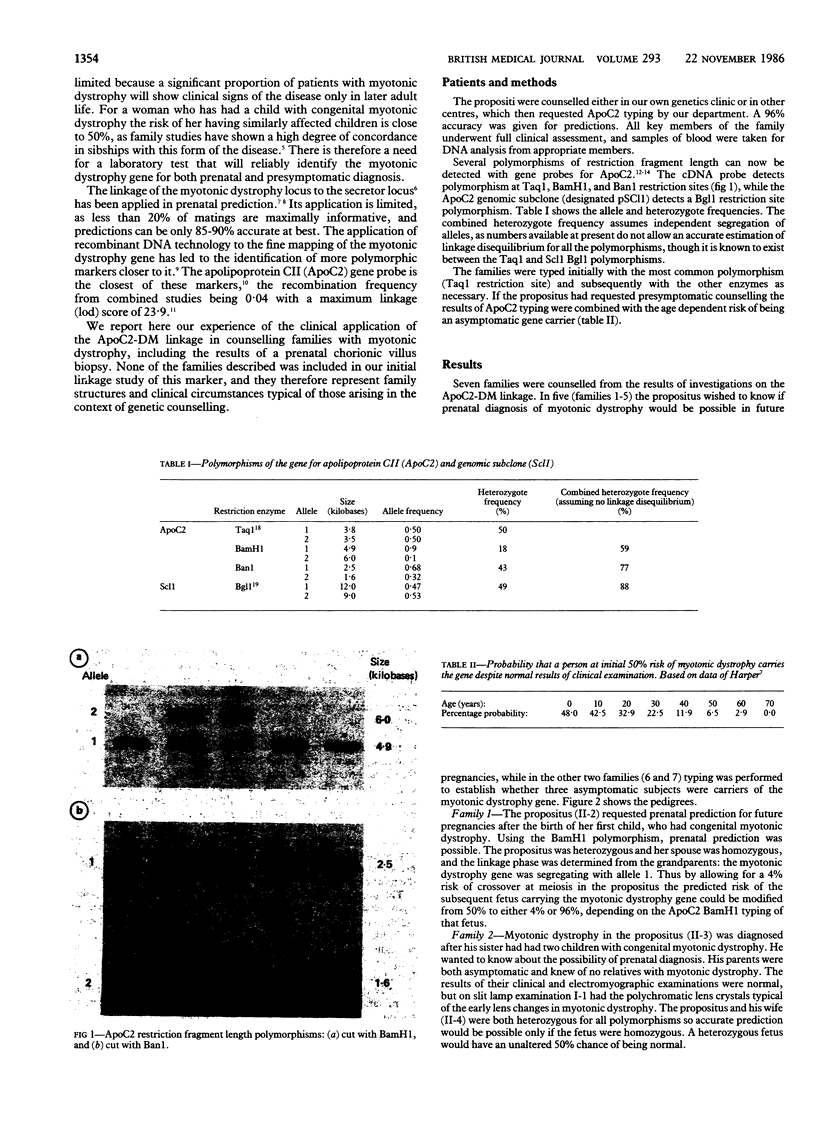
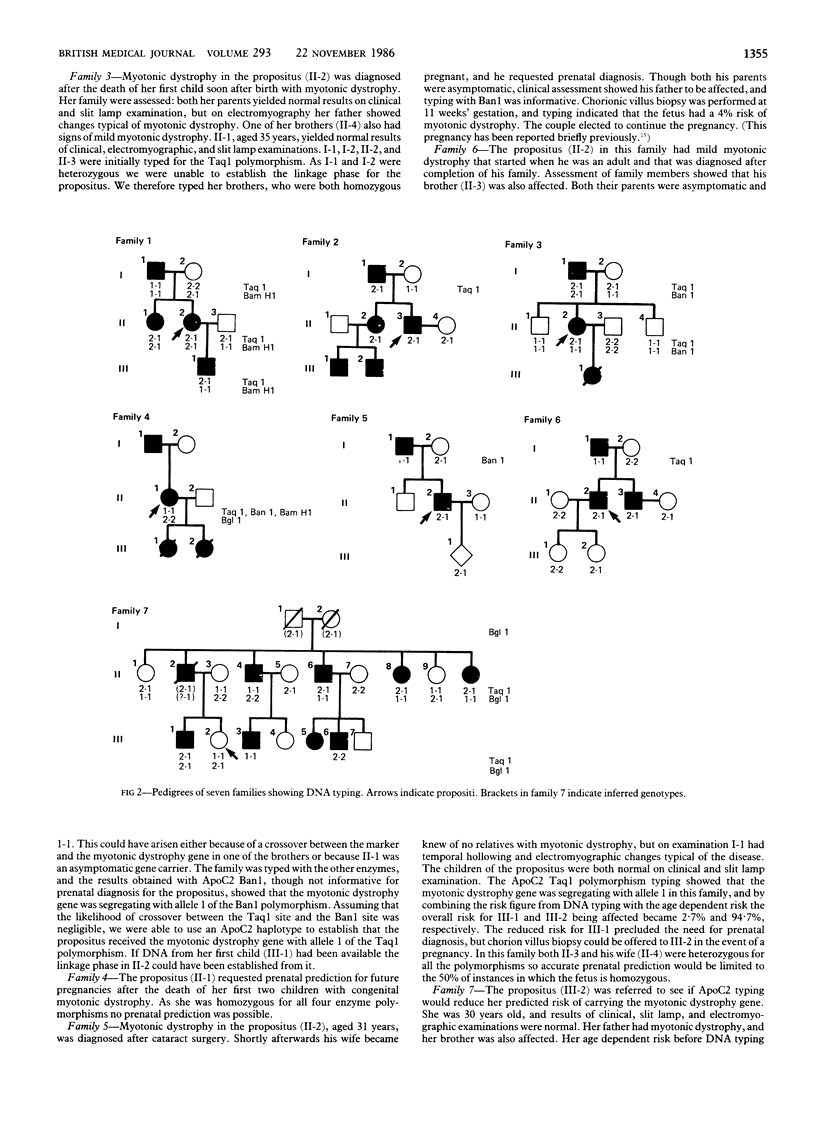
The close genetic linkage between the loci for apolipoprotein CII (ApoC2) and myotonic dystrophy makes ApoC2 the closest fully validated marker for prediction of myotonic dystrophy. Application to genetic counselling and presymptomatic and prenatal prediction is reported in seven families with myotonic dystrophy, including one case in which the disorder was excluded prenatally. Only one of the families did not have members with ApoC2 genotypes that allowed prediction, but careful clinical study of older family members was found to be an important factor. ApoC2 typing of families with myotonic dystrophy should be of practical help both in prediction for asymptomatic relatives and for prenatal diagnosis in pregnancies of an affected parent.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bundey S., Carter C. O., Soothill J. F. Early recognition of heterozygotes for the gene for dystrophia myotonica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Jun;33(3):279–293. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper P. S., Rivas M. L., Bias W. B., Hutchinson J. R., Dyken P. R., McKusick V. A. Genetic linkage confirmed between the locus for myotonic dystrophy and the ABH-secretion and Lutheran blood group loci. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 May;24(3):310–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M., Julier C., Ott J. Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombination. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):482–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naylor S., Lalouel J. M., Shaw D. J. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of Chromosomes 17, 18 and 19. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;40(1-4):242–267. doi: 10.1159/000132176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polgar J. G., Bradley W. G., Upton A. R., Anderson J., Howat J. M., Petito F., Roberts D. F., Scopa J. The early detection of dystrophia myotonica. Brain. 1972;95(4):761–766. doi: 10.1093/brain/95.4.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roses A. D., Pericak-Vance M. A., Ross D. A., Yamaoka L., Bartlett R. J. RFLPs at the D19S19 locus of human chromosome 19 linked to myotonic dystrophy (DM). Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5569–5569. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. J., Meredith A. L., Sarfarazi M., Huson S. M., Brook J. D., Myklebost O., Harper P. S. The apolipoprotein CII gene: subchromosomal localisation and linkage to the myotonic dystrophy locus. Hum Genet. 1985;70(3):271–273. doi: 10.1007/BF00273455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis S. C., Donald J. A., Forrest L. A., Williamson R., Humphries S. E. The isolation of a genomic clone containing the apolipoprotein CII gene and the detection of linkage disequilibrium between two common DNA polymorphisms around the gene. Hum Genet. 1984;68(4):286–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00292585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]