Abstract
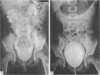
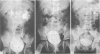
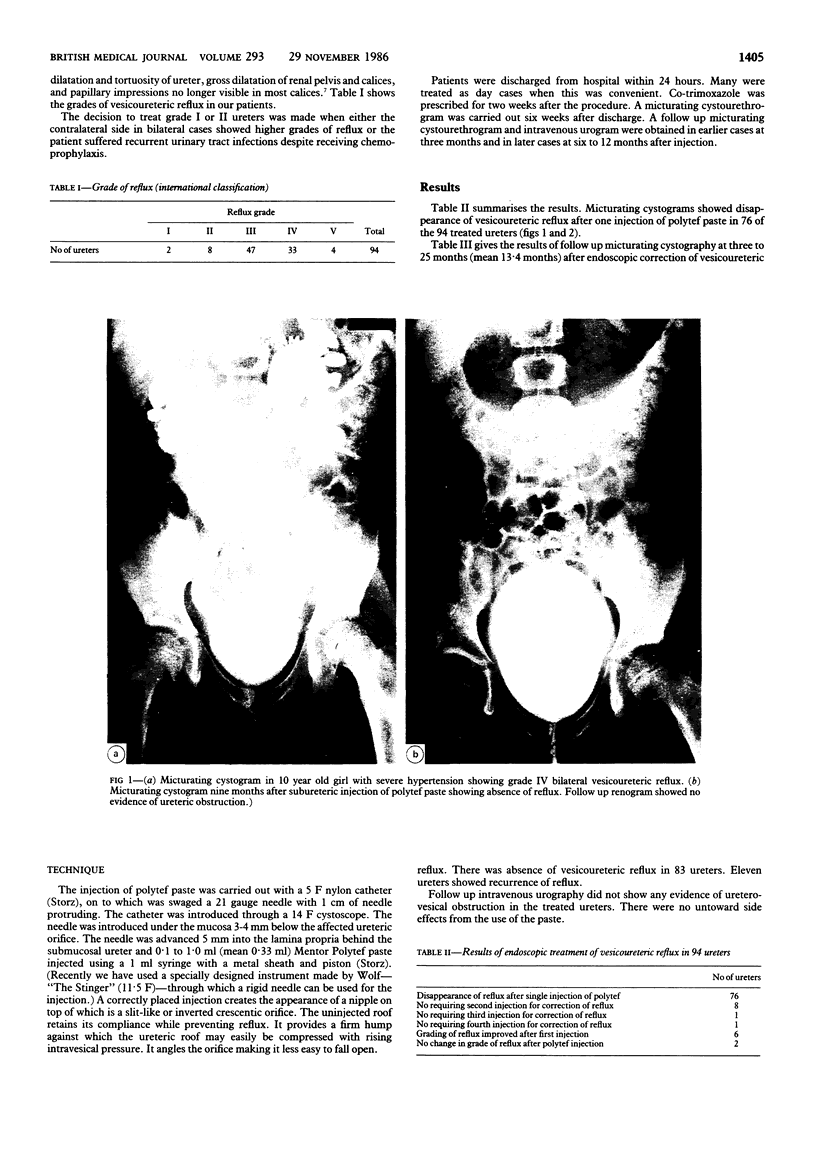
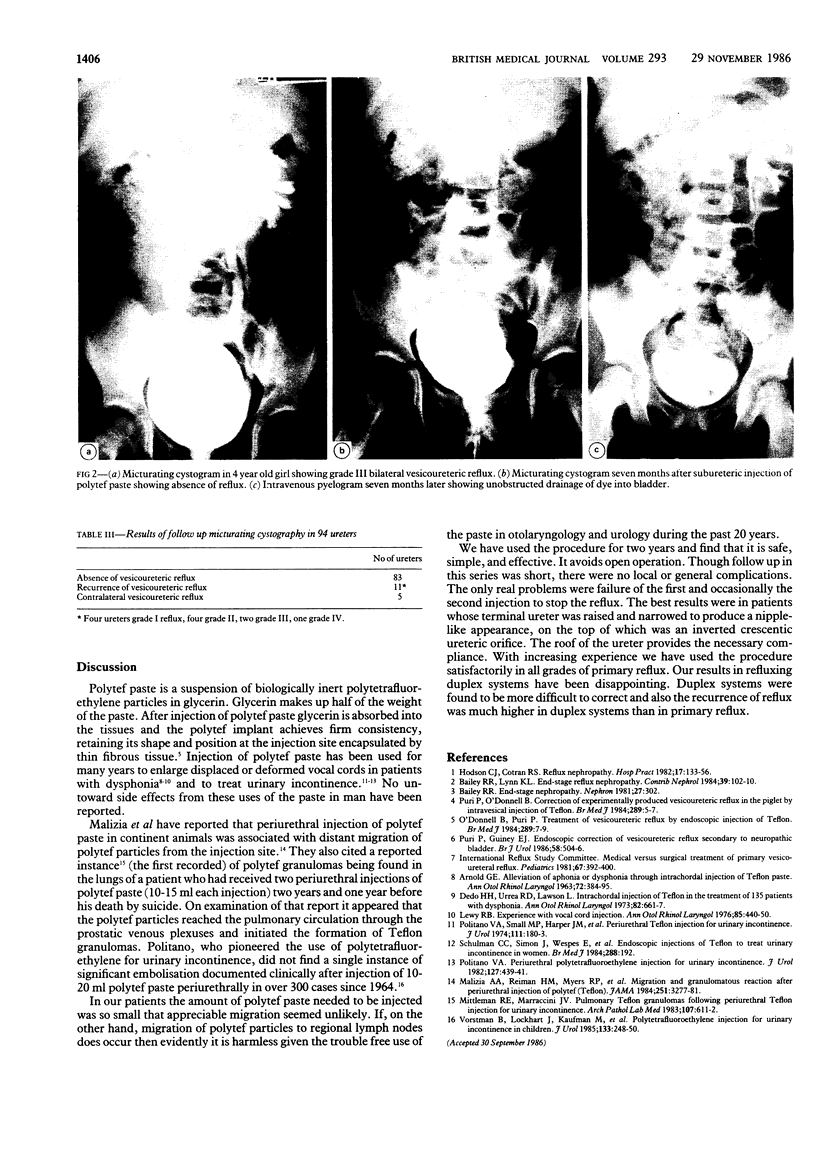
Sixty one patients with primary vesicoureteric reflux were treated by endoscopic injection of Mentor Polytef paste. Seventy six of the 94 treated ureters showed complete disappearance of vesicoureteric reflux after one injection. Eight refluxing ureters required a second injection, one required a third, and one a fourth. Six ureters showed improvement in the grade of reflux after the first injection. Two ureters did not show any change in the grade of reflux after endoscopic injection. The amount of paste injected to correct reflux in the 94 ureters varied from 0.1 to 1.0 ml (mean 0.33 ml). Patients were followed up for three to 25 months (mean 13.4 months). Follow up micturating cystograms in the 94 ureters showed absence of reflux in 83. Eleven ureters showed recurrence of reflux. Recurrence of reflux was attributed to early technical difficulties and to insufficient amounts of polytef paste used in some cases. Follow up urograms did not show evidence of ureteric obstruction in the treated ureters. Endoscopic injection of polytef paste is a safe, simple, and effective procedure for primary vesicoureteric reflux and averts the need for open operation.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey R. R. End-stage reflux nephropathy. Nephron. 1981;27(6):302–306. doi: 10.1159/000182075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey R. R., Lynn K. L. End-stage reflux nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 1984;39:102–110. doi: 10.1159/000409239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedo H. H., Urrea R. D., Lawson L. Intracordal injection of Teflon in the treatment of 135 patients with dysphonia. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1973 Sep-Oct;82(5):661–667. doi: 10.1177/000348947308200509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodson C. J., Cotran R. S. Reflux nephropathy. Hosp Pract (Hosp Ed) 1982 Apr;17(4):133-5, 138-41, 148-56. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1982.11698062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewy R. B. Experience with vocal cord injection. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1976 Jul-Aug;85(4 Pt 1):440–450. doi: 10.1177/000348947608500404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malizia A. A., Jr, Reiman H. M., Myers R. P., Sande J. R., Barham S. S., Benson R. C., Jr, Dewanjee M. K., Utz W. J. Migration and granulomatous reaction after periurethral injection of polytef (Teflon). JAMA. 1984 Jun 22;251(24):3277–3281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politano V. A., Small M. P., Harper J. M., Lynne C. M. Periurethral teflon injection for urinary incontinence. J Urol. 1974 Feb;111(2):180–183. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59921-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri P., Guiney E. J. Endoscopic correction of vesicoureteric reflux secondary to neuropathic bladder. Br J Urol. 1986 Oct;58(5):504–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1986.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri P., O'Donnell B. Correction of experimentally produced vesicoureteric reflux in the piglet by intravesical injection of Teflon. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984 Jul 7;289(6436):5–7. doi: 10.1136/bmj.289.6436.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]