Abstract
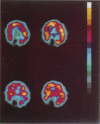
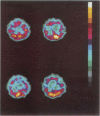
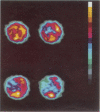
Tc-HMPAO isotope brain scans were performed in three patients who received hyperbaric oxygen treatment following carbon monoxide poisoning. Cerebral perfusion imaging provides an index of severity of the initial cerebral damage which correlated with outcome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broome J. R., Skrine H., Pearson R. R. Carbon monoxide poisoning: forgotten not gone! Br J Hosp Med. 1988 Apr;39(4):298-300, 302, 304-5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi I. S., Kim S. K., Lee S. S., Choi Y. C. Evaluation of outcome of delayed neurologic sequelae after carbon monoxide poisoning by technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime brain single photon emission computed tomography. Eur Neurol. 1995;35(3):137–142. doi: 10.1159/000117109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denays R., Makhoul E., Dachy B., Tondeur M., Noel P., Ham H. R., Mols P. Electroencephalographic mapping and 99mTc HMPAO single-photon emission computed tomography in carbon monoxide poisoning. Ann Emerg Med. 1994 Nov;24(5):947–952. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70212-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbaum L. R., Orellano T., Dergal E. Mechanism of the toxic action of carbon monoxide. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1976 Jul-Aug;6(4):372–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman D. F., Clayton D., Gilligan J. E., Webb R. K. A longitudinal study of 100 consecutive admissions for carbon monoxide poisoning to the Royal Adelaide Hospital. Anaesth Intensive Care. 1992 Aug;20(3):311–316. doi: 10.1177/0310057X9202000306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. A., Snyder S. K., Emhoff T. A. Subacute sequelae of carbon monoxide poisoning. Ann Emerg Med. 1985 Dec;14(12):1163–1167. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(85)81022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norkool D. M., Kirkpatrick J. N. Treatment of acute carbon monoxide poisoning with hyperbaric oxygen: a review of 115 cases. Ann Emerg Med. 1985 Dec;14(12):1168–1171. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(85)81023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pracyk J. B., Stolp B. W., Fife C. E., Gray L., Piantadosi C. A. Brain computerized tomography after hyperbaric oxygen therapy for carbon monoxide poisoning. Undersea Hyperb Med. 1995 Mar;22(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Takahashi M., Ohashi N., Fusamoto H., Maemura K., Kobayashi H., Yoshioka T., Sugimoto T. Computerised tomography as an indication of long-term outcome after acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Lancet. 1980 Apr 12;1(8172):783–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Brandon S. Morbidity from acute carbon monoxide poisoning at three-year follow-up. Br Med J. 1973 Feb 10;1(5849):318–321. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5849.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbles P. M., Perrotta P. L. Treatment of carbon monoxide poisoning: a critical review of human outcome studies comparing normobaric oxygen with hyperbaric oxygen. Ann Emerg Med. 1994 Aug;24(2):269–276. doi: 10.1016/s0196-0644(94)70141-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]