Abstract
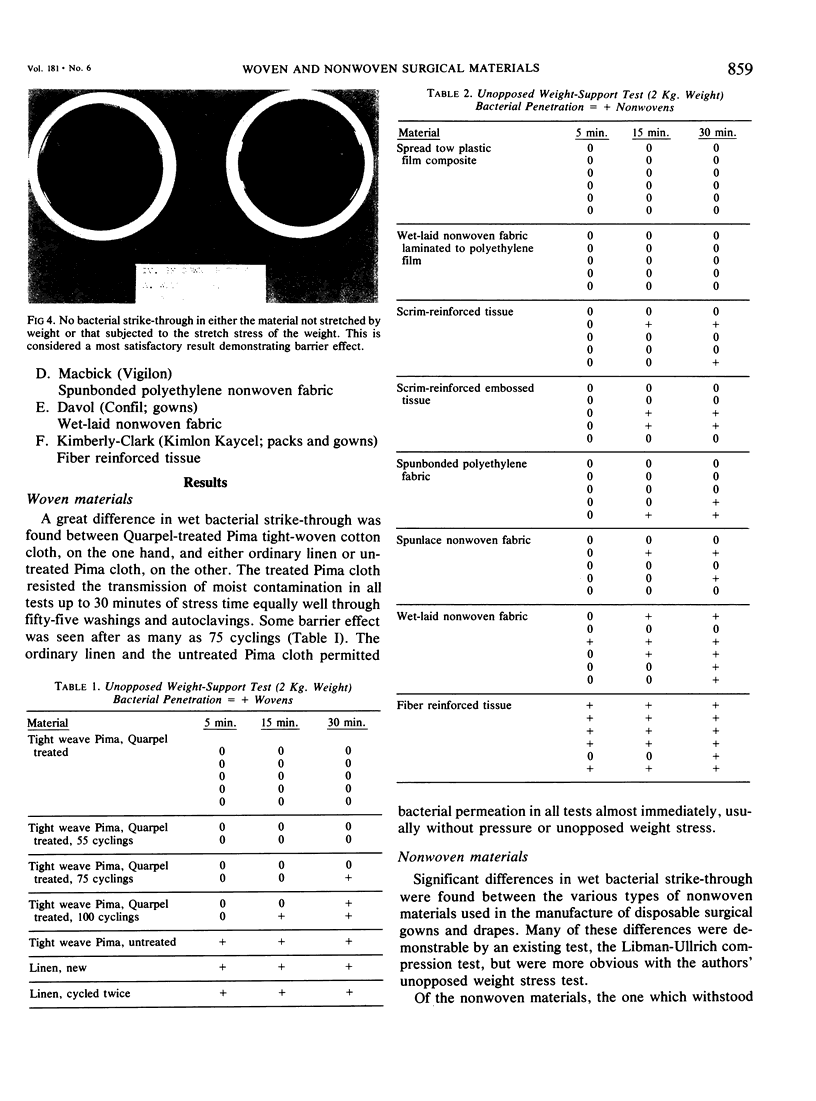
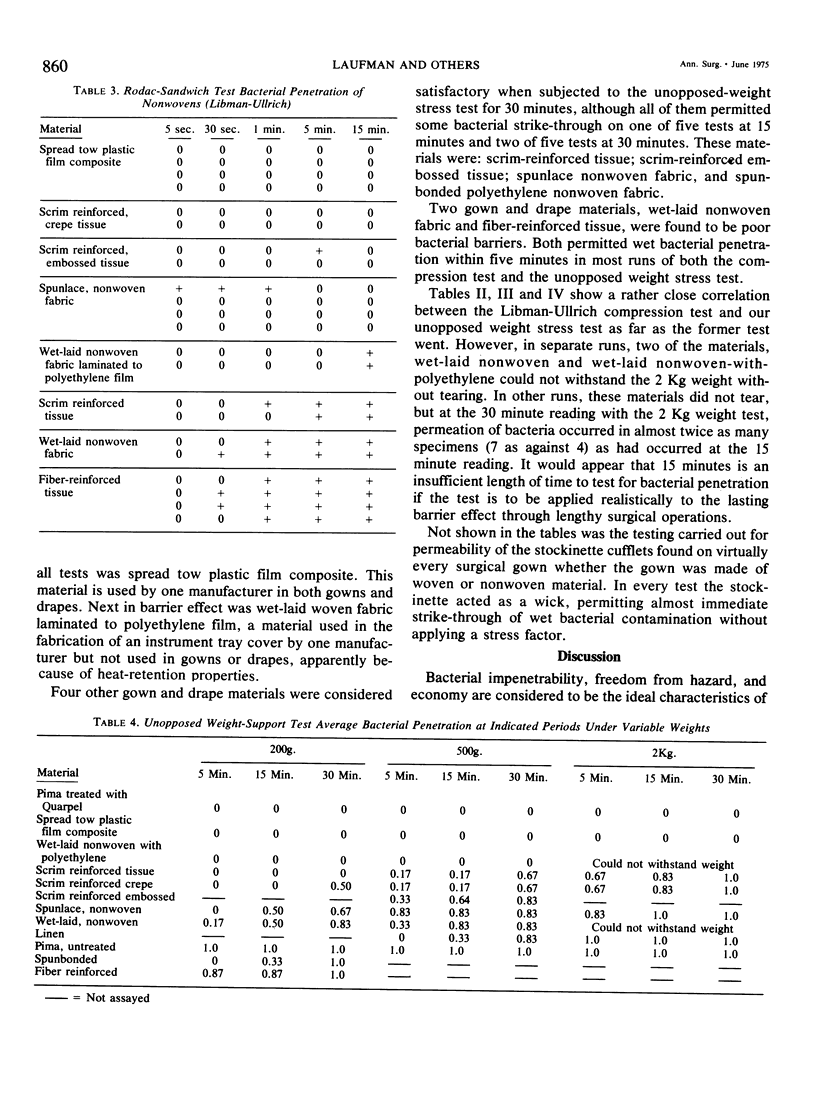
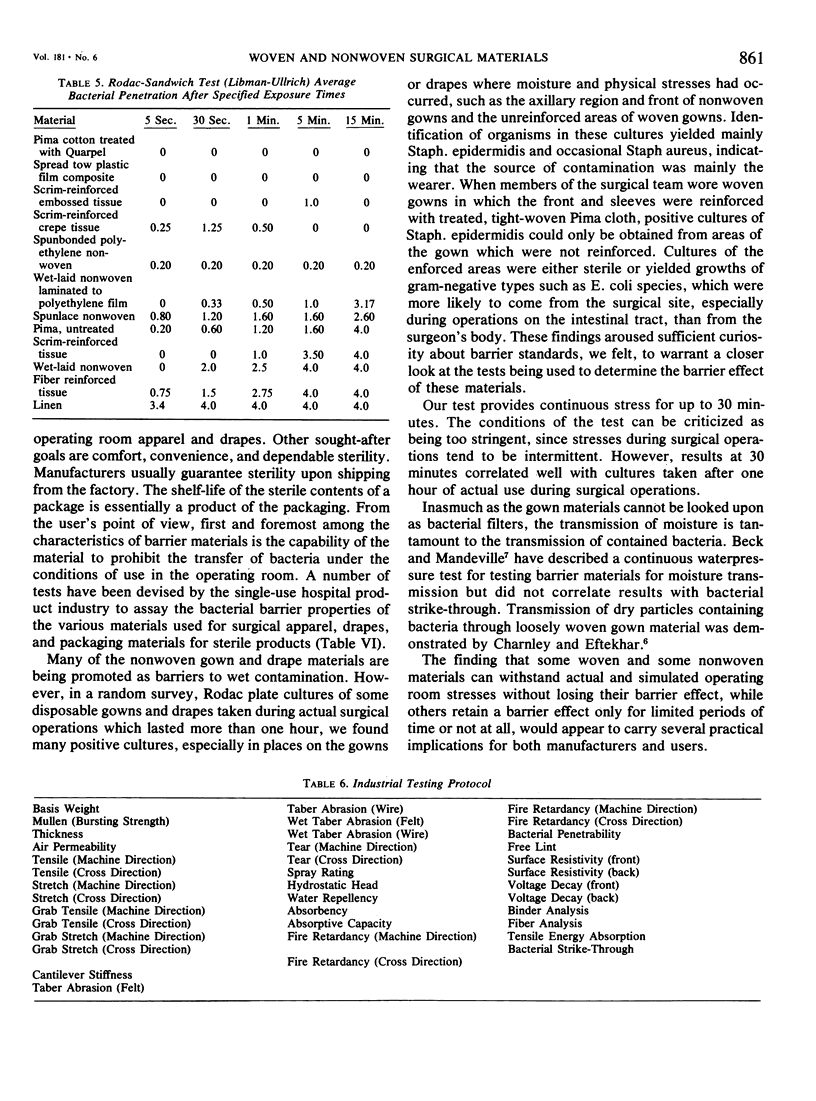
A test is described which correlates the stress of stretching surgical gown and drape material with moist bacterial strike-through. By application of this test to a number of woven and nonwoven surgical gown and drape materials, it was found that not all of these materials, either woven or nonwoven, are impermeable to moist contamination for equal periods of time. Nonwoven disposable materials now in use range from those which remain impermeable to moist bacterial permeation through all tests while some remain impermeable for limited periods of time, and others almost immediately permeable to moist bacterial penetration. The same situation holds for woven materials. Under conditions of our test, Quarpel treated Pima tight-woven cotton cloth was impermeable to moist bacterial strike-through, through up to 75 washing and sterilizing cyclings, while ordinary linen and untreated Pima cloth permitted bacterial permeation almost immediately. These results have significance in lengthy wet surgical operations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charnley J., Eftekhar N. Penetration of gown material by organisms from the surgeon's body. Lancet. 1969 Jan 25;1(7587):172–173. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dineen P. Penetration of surgical draping material by bacteria. Hospitals. 1969 Oct 1;43(19):82–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standard P. G., Mallison G. F., Mackel D. C. Microbial penetration through three types of double wrappers for sterile packs. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jul;26(1):59–62. doi: 10.1128/am.26.1.59-62.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]