Abstract
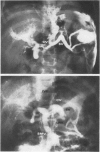
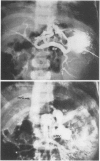
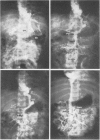
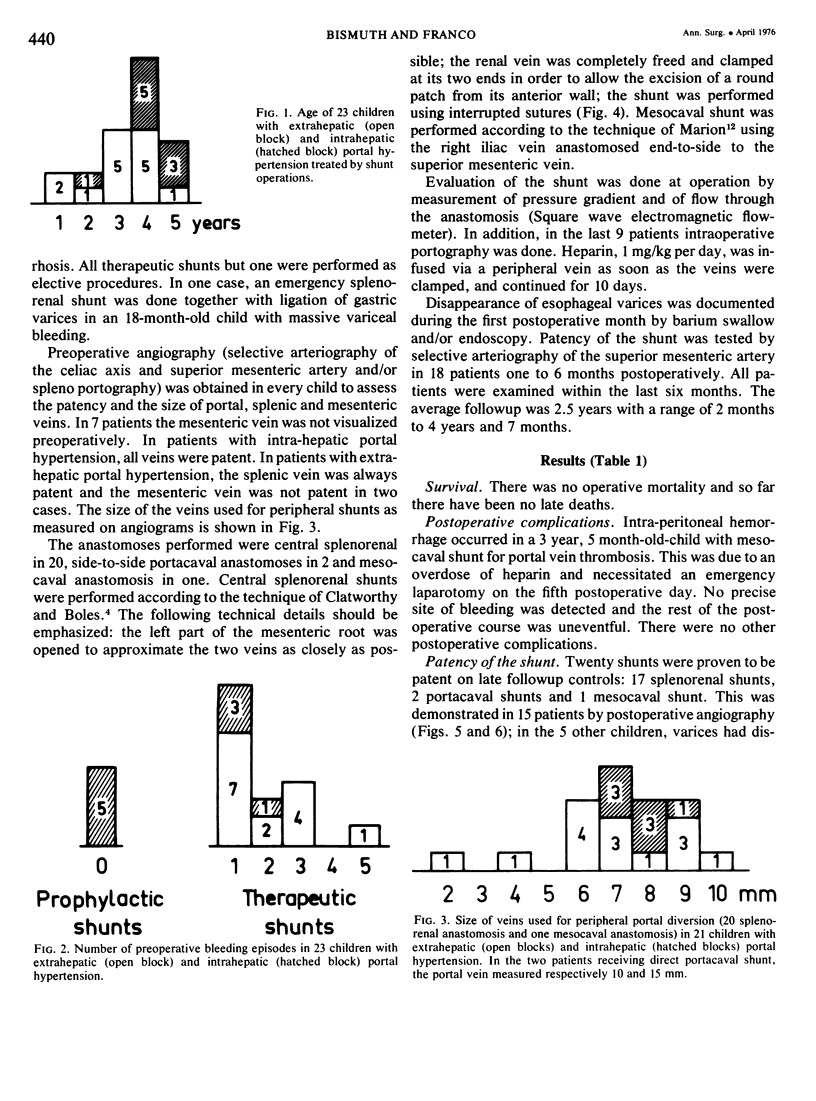
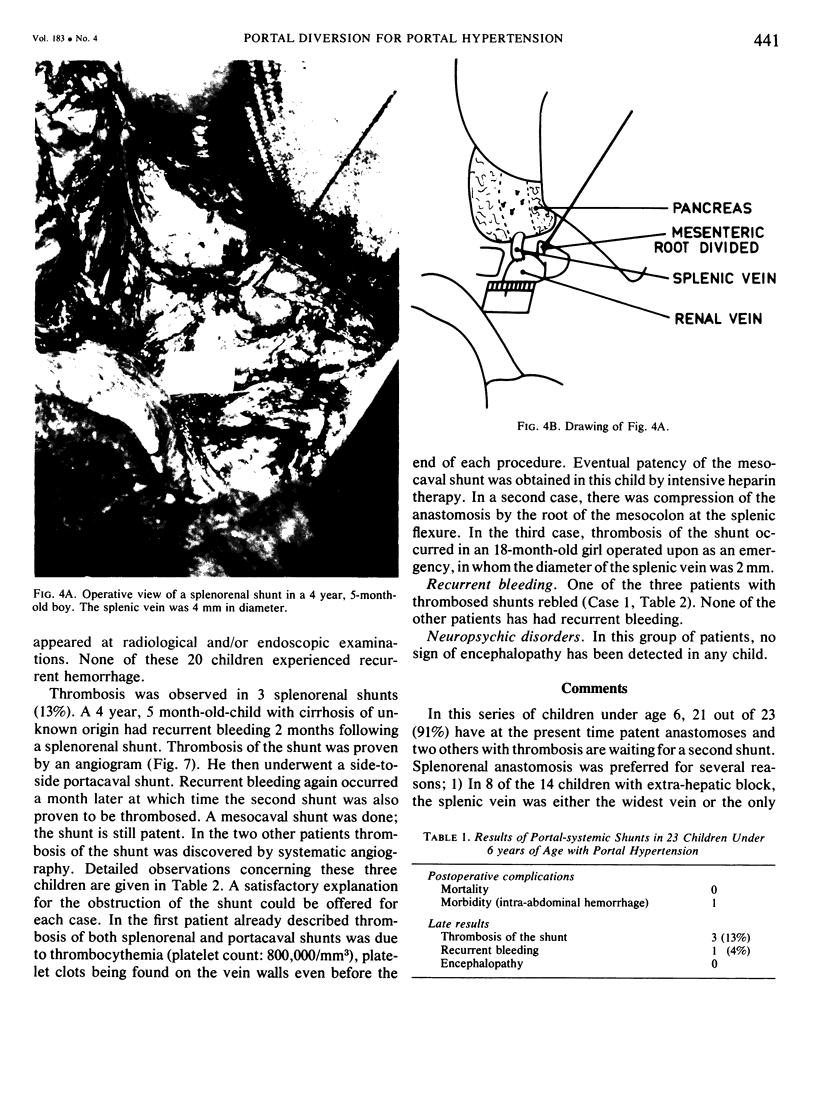
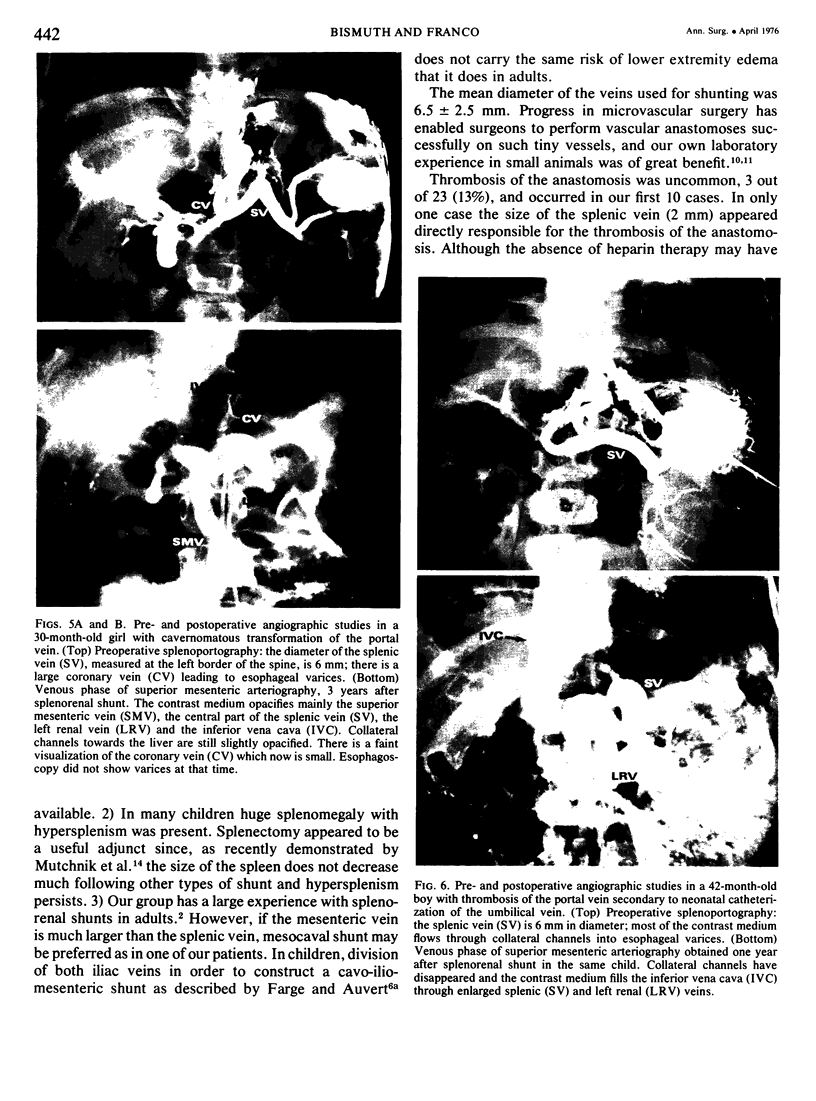
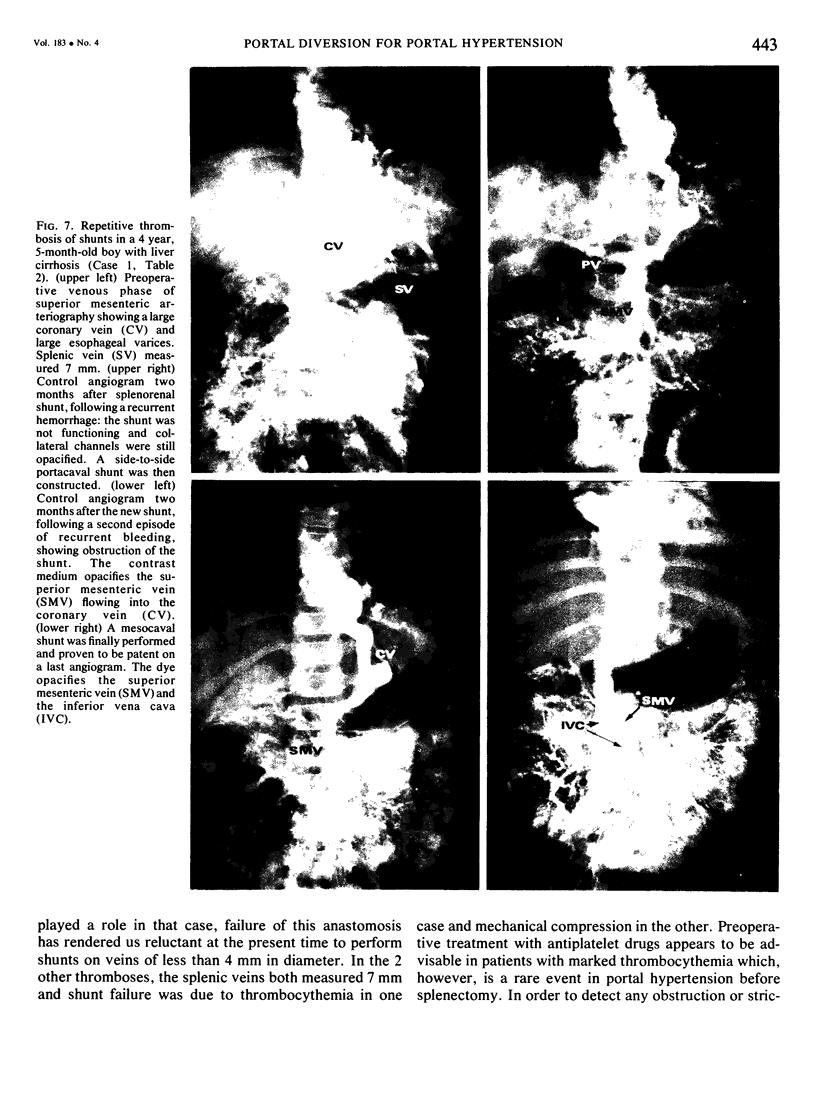
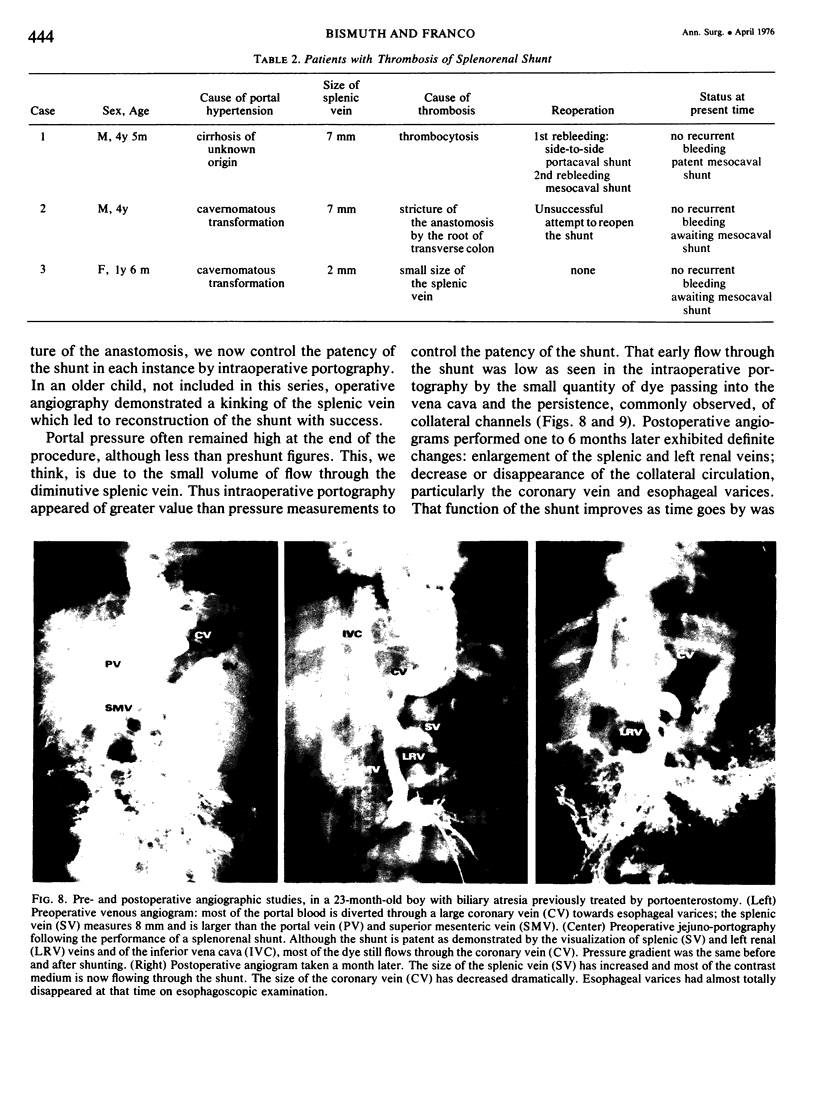
Twenty-three children under 6 years of age with portal hypertention were treated by portal diversion. Fourteen had cavernomatous transformation of the portal vein and 9 had an intrahepatic block due to cirrhosis (8) or congenital hepatic fibrosis (1). Portal-systemic shunts were central splenorenal in 20 patients, side-to-side portacaval in 2 and mesocaval in one. In 20 of the 21 peripheral shunts, the veins used for the anastomosis were less than 10 mm in diameter. There was no operative mortality. Thrombosis of the shunt occurred in 3 children (13%) and was responsible for recurrent bleeding in one who was treated later with success by a mesocaval shunt. The two other children with a thrombosed shunt are waiting, at the present time, for a mesocaval anastomosis. The volume of blood flowing through the shunt was small initially and the fall in pressure gradient was slight: therefore intraoperative angiography appeared to be a better way to assess the patency of shunts done at an early age than pressure or flow measurements. The figures recently reported by Clatworthy, with a mortality rate of 12% directly or indirectly related to repeated hemorrhage, are for us a forceful argument for early adequate management of portal hypertension in children. Until now, portal-systemic shunts have been complicated by a high frequency of thrombosis and have given discouraging results. Our results suggest that it is possible to perform portal diversion successfully on diminutive veins (down to 4 mm). From this experience early portal diversion appears to represent the treatment of choice for portal hypertension in childhood.
Full text
PDF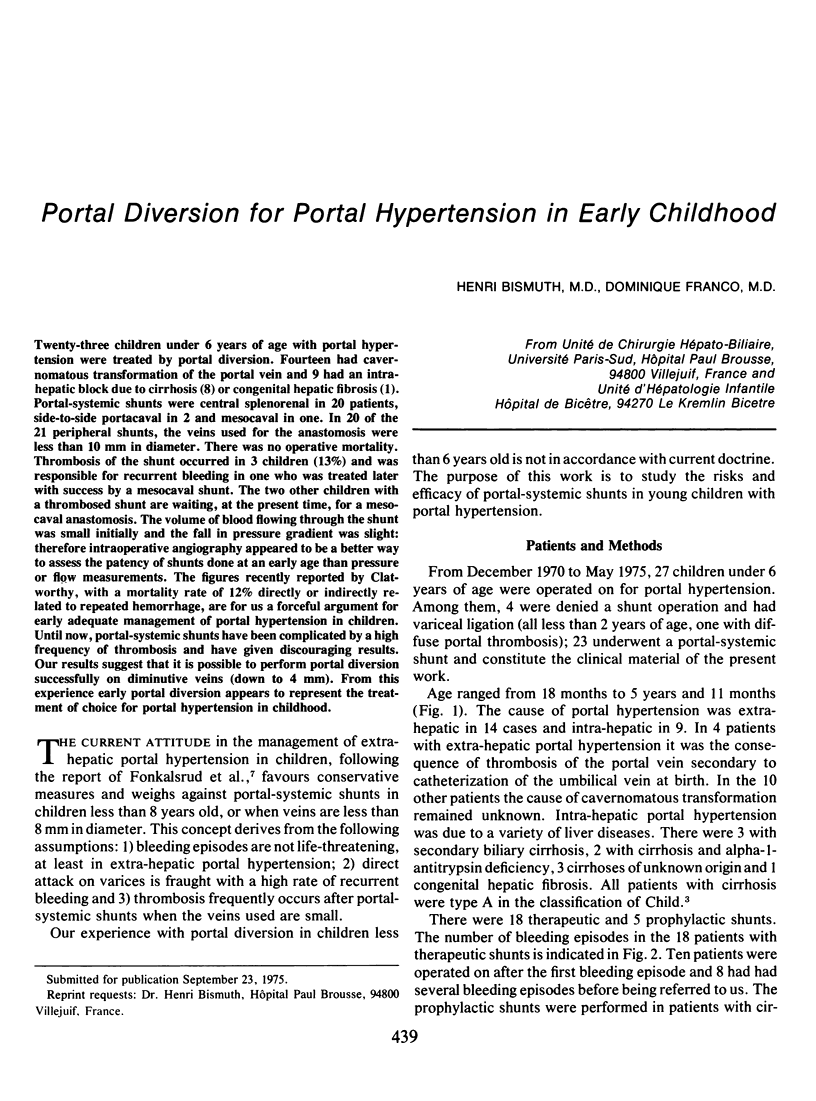


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCARI F. A., LYNN H. B. Bleeding esophageal varices in children. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1961 Jan;112:101–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth H., Franco D., Hepp J. Portal-systemic shunt in hepatic cirrhosis: does the type of shunt decisively influence the clinical result? Ann Surg. 1974 Feb;179(2):209–218. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197402000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLATWORTHY H. W., Jr, BOLES E. T., Jr Extrahepatic portal bed block in children: pathogenesis and treatment. Ann Surg. 1959 Sep;150:371–383. doi: 10.1097/00000658-195909000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLATWORTHY H. W., Jr, DELORIMER A. A. PORTAL DECOMPRESSION PROCEDURES IN CHILDREN. Am J Surg. 1964 Mar;107:447–451. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(64)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARGE C., AUVERT J. [IIio-mesenteric anastomosis, a process improving cavo-mesenteric vein anastomosis for portal hypertension]. Presse Med. 1962 Nov 3;70:2217–2218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. H., HOLCOMB G. W., KIRTLEY J. A. Results of surgical treatment of portal hypertension in children. Ann Surg. 1963 Jun;157:868–880. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196306000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonkalsrud E. W., Myers N. A., Robinson M. J. Management of extrahepatic portal hypertension in children. Ann Surg. 1974 Oct;180(4):487–493. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197410000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudicelli J. F., Witchitz S., Larno S., Boissier J. R. Experimental evaluation of antiarrhythmic drugs in the guinea pig. Biomedicine. 1973 Jul 20;19(7):308–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOOP C. E., KAVIANIAN A. REAPPRAISAL OF COLONIC REPLACEMENT OF DISTAL ESOPHAGUS AND PROXIMAL STOMACH IN THE MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING VARICES IN CHILDREN. Surgery. 1965 Mar;57:454–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecompte Y., Franco D., Martin E. D., Bismuth H. Liver arterialization with portacaval shunt in the cirrhotic rat. Surgery. 1974 Feb;75(2):161–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARION P. Les obstructions portales. Sem Hop. 1953 Sep 26;29(57):2781–2790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen W. P. Extrahepatic portal hypertension in children. Am J Surg. 1966 Mar;111(3):333–340. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(66)80008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton J. A., Holcomb G. W., Jr, Foster J. H. Portal hypertension in childhood. Ann Surg. 1972 Jun;175(6):870–886. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197206010-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffensperger J. G., Shkolnik A. A., Boggs J. D., Swenson O. Portal hypertension in children. Arch Surg. 1972 Aug;105(2):249–254. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1972.04180080101017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOORHEES A. B., Jr, HARRIS R. C., BRITTON R. C., PRICE J. B., SANTULLI T. V. PORTAL HYPERTENSION IN CHILDREN: 98 CASES. Surgery. 1965 Sep;58:540–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees A. B., Jr, Chaitman E., Schneider S., Nicholson J. F., Kornfeld S., Price J. B., Jr Portal-systemic encephalopathy in the noncirrhotic patient. Effect of portal-systemic shunting. Arch Surg. 1973 Nov;107(5):659–663. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1973.01350230017005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees A. B., Jr, Price J. B., Jr Extrahepatic portal hypertension. A retrospective analysis of 127 cases and associated clinical implications. Arch Surg. 1974 Mar;108(3):338–341. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01350270068012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER R. M. Treatment of portal hypertension in children. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Sep;55:770–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]