Abstract
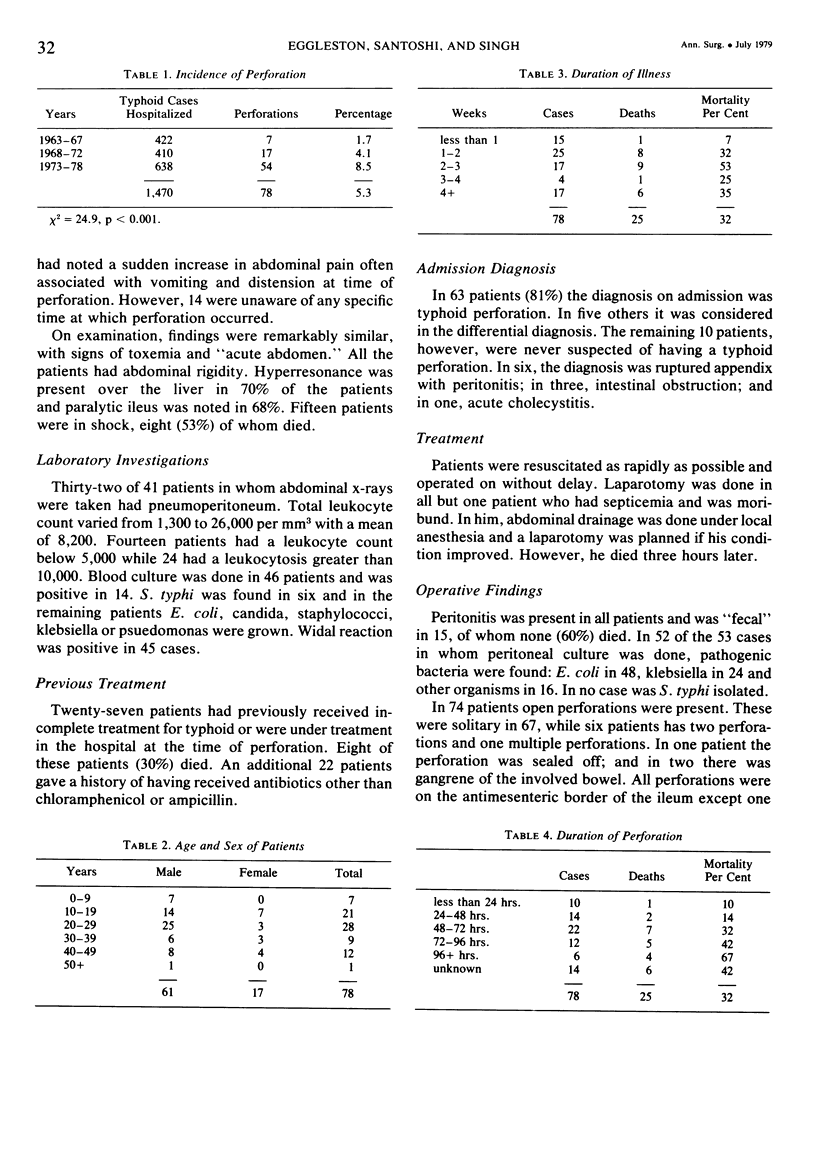
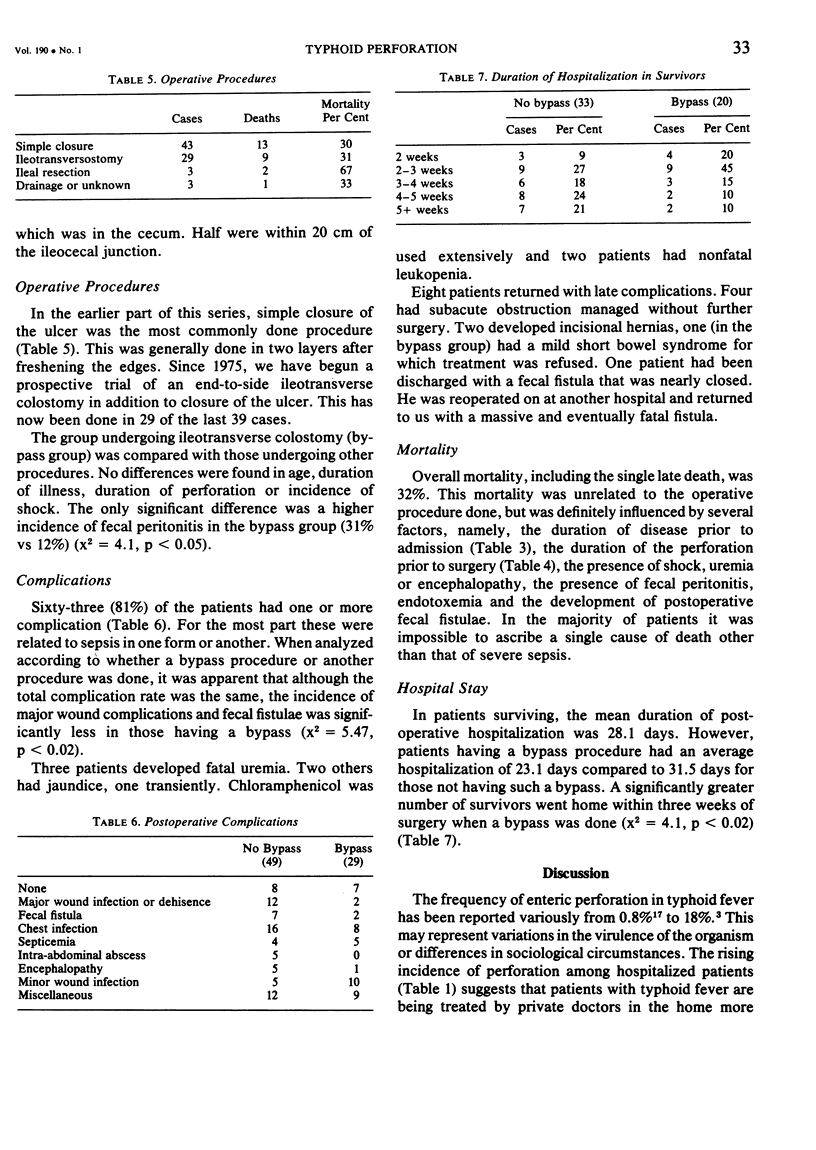
Seventy-eight patients ranging from four to 65 years of age were treated for typhoid perforation of the bowel. Sixty-one patients (78%) were males. The average time from perforation to admission was 56 hours. The mortality rate was 32% and was adversely influenced by the duration of illness, duration of perforation, shock, uremia, encephalopathy and fecal peritonitis. Forty-nine patients were treated by closure of the perforation, resection or miscellaneous procedures; the other 29 by closure of the perforation combined with an end-to-end ileotransverse colostomy. Although mortality was the same in both groups, those undergoing bypass had a significantly smoother postoperative course.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-meneim R. I. Surgical management of perforated thyphoid ulcer. Int Surg. 1969 Nov;52(5):405–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archampong E. Q. Operative treatment of typhoid perforation of the bowel. Br Med J. 1969 Aug 2;3(5665):273–276. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5665.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archampong E. Q. Typhoid ileal perforations: why such mortalities? Br J Surg. 1976 Apr;63(4):317–321. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONROY J. V. Acute ileitis with ulceration and perforation due to paratyphoid fever; report of eighty-five cases. Mil Med. 1957 Feb;120(2):79–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICKSON J. A., COLE G. J. PERFORATION OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM. A REVIEW OF 38 CASES. Br J Surg. 1964 Dec;51:893–897. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800511207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson J. H. Surgical management of typhoid perforation of the ileum. Am Surg. 1970 Oct;36(10):620–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKSTEP R. L. Recent advances in the surgery of typhoid fever. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1960 Apr;26:207–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaul B. K. Operative management of typhoid perforation in children. Int Surg. 1975 Aug;60(8):407–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Oh S. K., Jarrett F. Management of ileal perforation due to typhoid fever. Ann Surg. 1975 Jan;181(1):88–91. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197501000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan T. O. The treatment of typhoid perforation of the ileum. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1972 Nov;17(6):364–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olurin E. O., Ajayi O. O., Bohrer S. P. Typhoid perforations. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1972 Nov;17(6):353–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad P. B., Choudhury D. K., Prakash O. Typhoid perforation treated by closure and proximal side to side ileotransverse colostomy. J Indian Med Assoc. 1975 Dec 1;65(11):297–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWLAND H. A. The complications of typhoid fever. J Trop Med Hyg. 1961 Jun;64:143–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samantray S. K., Johnson S. C., Chakrabarti A. K. Enteric fever: an analysis of 500 cases. Practitioner. 1977 Mar;218(1305):400–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spay G., Ejazy M. M., Rahimi N. A propos de 31 cas de perforation typhique. (Place de la résection-iléostomie temporaire. J Chir (Paris) 1973 Oct;106(4):341–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. P., Martin N. C. Surgical treatment of typhoid perforation. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1078–1080. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91840-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


