Abstract
Twenty-six patients who had typical symptoms of biliary tract disease, e.g. postprandial right upper quadrant pain, nausea and vomiting, fatty food intolerance and flatulence and who had had two or more normal oral cholecystograms were subjected to cholecytokinin cholescystography. Ten patients showed a normal response to the intravenous administration of cholecystokinin, namely prompt and complete emptying of the gallbladder without producing any adverse reaction or symptoms. Sixteen patients demonstrated either no contraction or incomplete contraction of the gallbladder in response to cholecystokinin; several patients had moderate contraction of the gallbladder accompanied by symptoms of biliary colic. This latter group underwent cholecystectomy and operative cholangiography. Fifteen of the 16 patients are asymptomatic or improved, and only one patient continues to have symptoms. All removed gallbladders had histologic evidence of chronic cholecystitis. It is concluded that in some individuals with continuing symptoms suggesting gallbladder disease but normal oral cholecystograms, cholecystokinin cholecystography may be helpful in identifying physiologic dysfunction of the gallbladder.
Full text
PDF

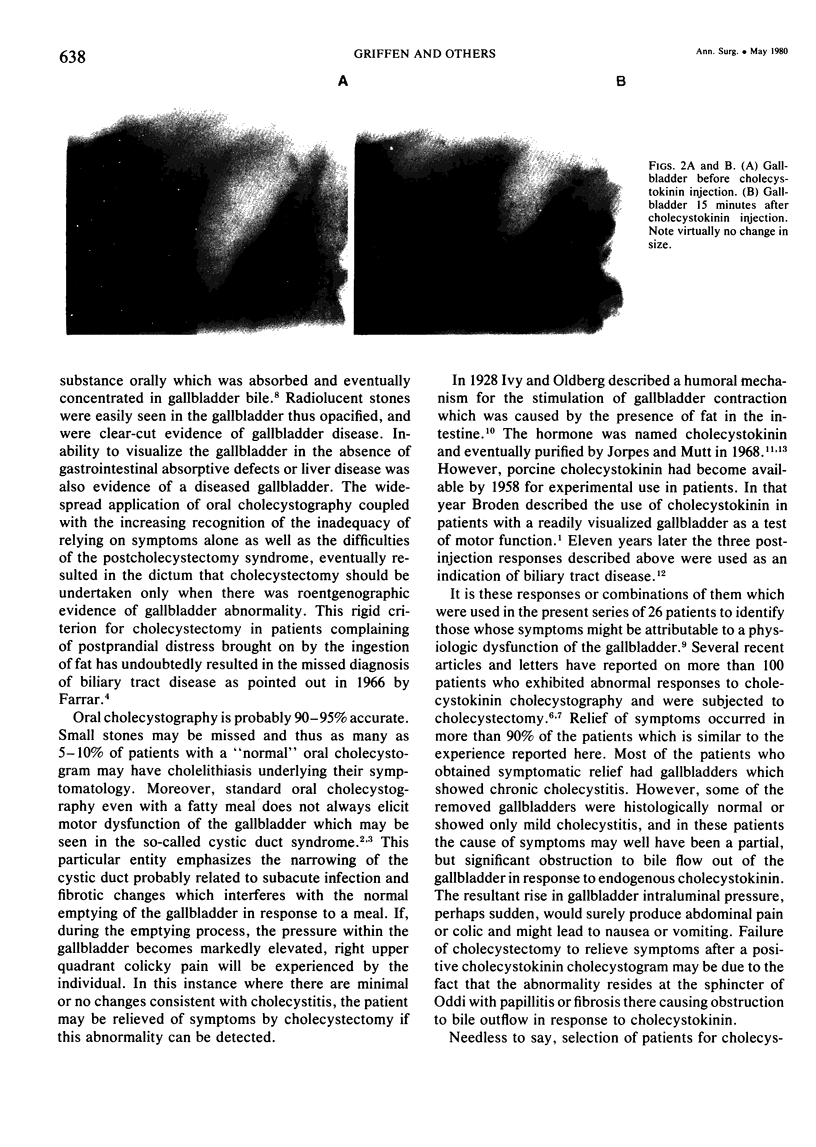

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODEN B. Experiments with cholecystokinin in cholecystography. Acta radiol. 1958 Jan;49(1):25–30. doi: 10.3109/00016925809170975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COZZOLINO H. J., GOLDSTEIN F., GREENING R. R., WIRTS C. W. THE CYSTIC DUCT SYNDROME. JAMA. 1963 Sep 21;185:920–924. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03060120030017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. T. Underdiagnosis of biliary tract disorders? Gastroenterology. 1966 Dec;51(6):1074–1075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiegenschuh W. H., Loughry C. W. The false-normal oral cholecystogram. Surgery. 1977 Feb;81(2):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman J. B., Cohen W. N., DenBesten L. Cholecystokinin cholangiography and analysis of duodenal bile in the investigation of pain in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen without gallstones. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1975 Mar;140(3):371–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffen W. O., Jr Editorials: The concept of physiologic dysfunction of the gallbladder. Arch Surg. 1975 Apr;110(4):369–370. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360100011001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorpes J. E. The isolation and chemistry of secretin and cholecystokinin. Gastroenterology. 1968 Aug;55(2):157–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland J. O., Currin J. Cholecystokinin and the cystic duct syndrome. Clinical experience in a community hospital. Am J Gastroenterol. 1969 Dec;52(6):515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutt V., Jorpes J. E. Structure of porcine cholecystokinin-pancreozymin. 1. Cleavage with thrombin and with trypsin. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Oct 17;6(1):156–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent E. N., Meyers H. I., Hubsher J. Cholecystokinetic cholecystography: efficacy and tolerance study of sincalide. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976 Aug;127(2):267–271. doi: 10.2214/ajr.127.2.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber K., DeMarco S. J., 3rd Use of duodenal drainage in diagnosis of cholecystitis. Am Surg. 1973 Oct;39(10):568–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





