Abstract
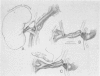
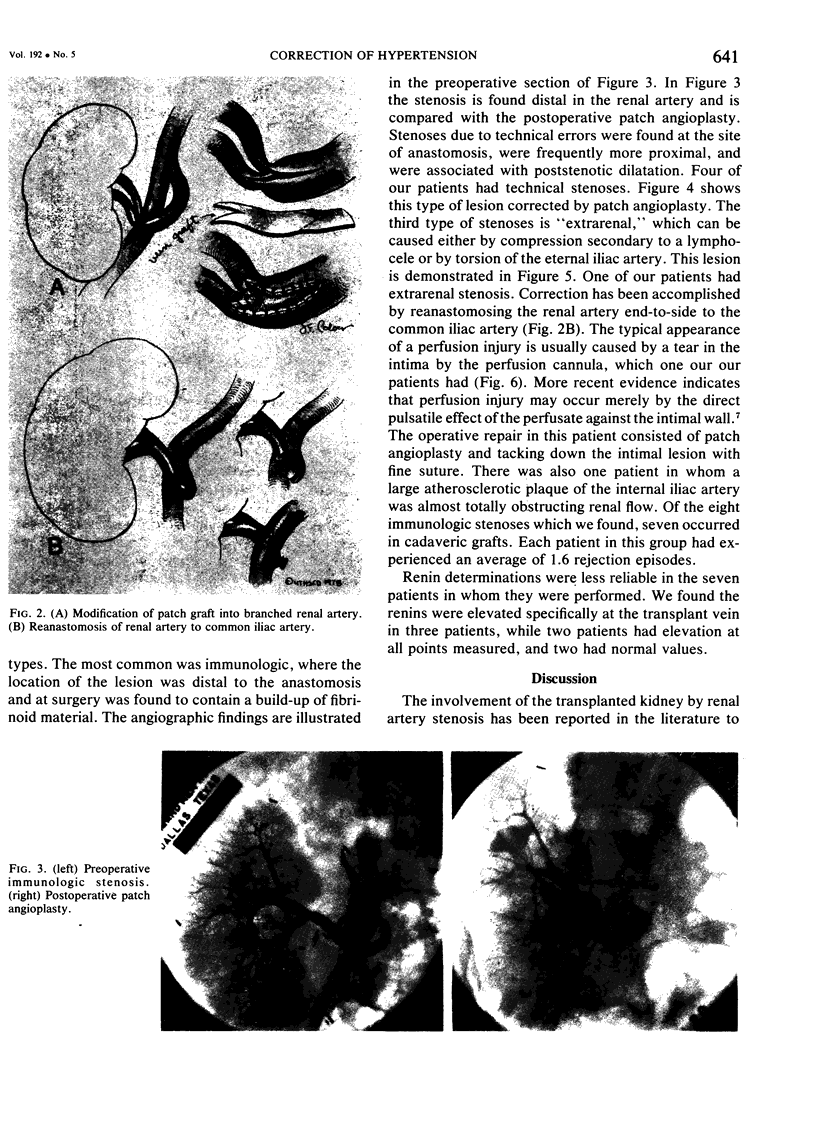
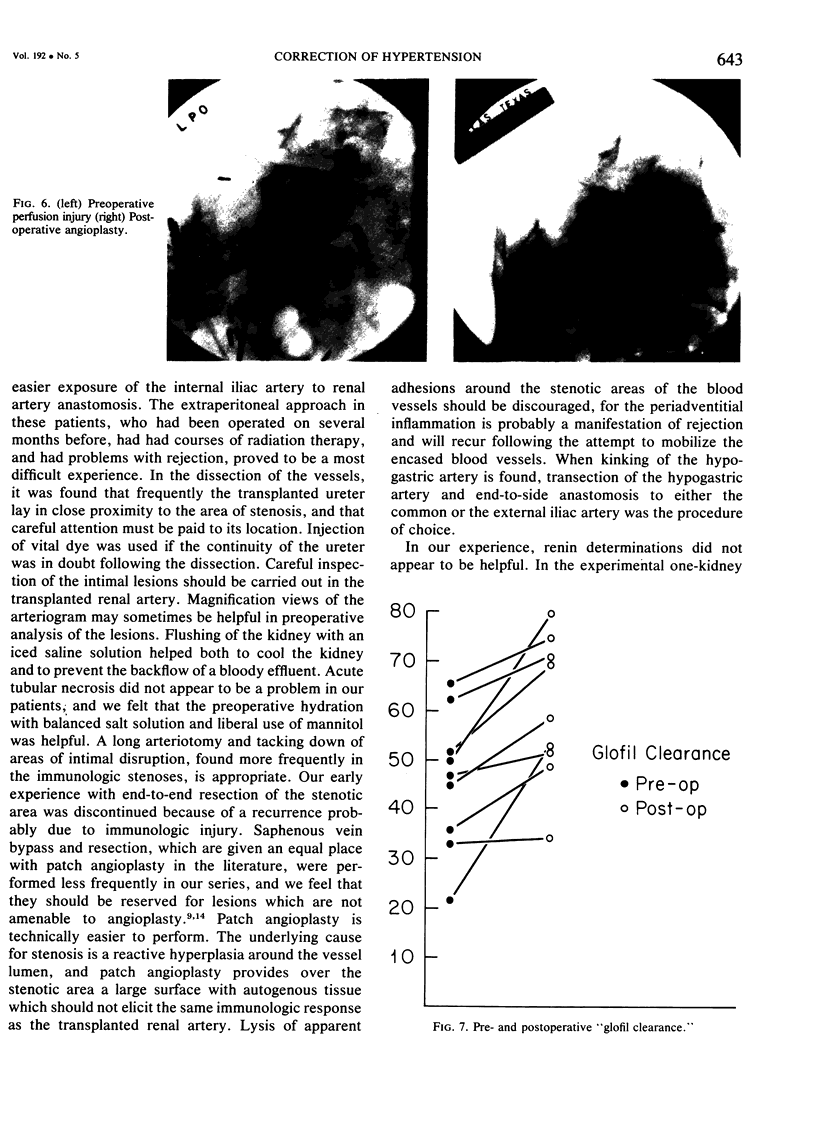
The incidence of renovascular hypertension in the transplanted kidney is reported to range between 5 and 15%. A review of 391 consecutive renal transplant patients revealed 16 patients (5.4%) with hypertension secondary to partial obstruction of renal arterial blood flow. The clinical course of this group of patients was marked by early normotension followed by progressive diastolic pressure elevation, with improving renal function and loss of accumulated excess volume. Five etiologic factors are responsible for impaired arterial flow in this group of patients. Indication for operation was based on hypertension and/or impaired renal function. Patch angioplasty using saphenous veins was the procedure of choice in most instances. The average blood pressure was 185 mmHg; systolic/125 mmHg; diastolic preoperatively, compared with 140 mmHg; systolic/90 mmHg: diastolic postoperatively. Twelve of 16 patients had good results, and improvement in renal function was observed in eight patients. Serum renin levels did not correlate well with the operative findings. The use of meticulous technique, combined with maximum use of autogenous tissue, is emphasized.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett W. M., McDonald W. J., Lawson R. K., Porter G. A. Posttransplant hypertension: studies of cortical blood flow and the renal pressor system. Kidney Int. 1974 Aug;6(2):99–108. doi: 10.1038/ki.1974.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coles G. A., Jones G. R., Crosby D. L., Jones J. H., McVeigh S. Hypertension following cadaveric renal transplantation. Postgrad Med J. 1972 Jul;48(561):399–404. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.48.561.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross F. The renin-angiotensin system and hypertension. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Nov;75(5):777–787. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-5-777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israelit A. H., Long D. L., White M. G., Hull A. R. Measurement of glomerular filtration rate utilizing a single subcutaneous injection of 125I-iothalamate. Kidney Int. 1973 Nov;4(5):346–349. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornerup H. J., Pedersen E. B. Plasma renin, plasma aldosterone and exchangeable sodium in normotensive and hypertensive kidney transplant recipients with and without transplant renal artery stenosis. Acta Med Scand. 1977;202(6):509–516. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb16873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. Arterial stenosis complicating renal allotransplantation in man: a study of 38 cases. Ann Surg. 1975 Mar;181(3):283–288. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197503000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindfors O., Laasonen L., Fyhrquist F., Kock B., Lindström B. Renal artery stenosis in hypertensive renal transplant recipients. J Urol. 1977 Aug;118(2):240–243. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)57956-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsey E. S., Garbus S. B., Golladay E. S., McDonald J. C. Hypertension due to renal artery stenosis in transplanted kidneys. Ann Surg. 1975 May;181(5):604–610. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197505000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margules R. M., Belzer F. O., Kountz S. L. Surgical correction of renovascular hypertension following renal allotransplantation. Arch Surg. 1973 Jan;106(1):13–16. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1973.01350130017003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matas A. J., Simmons R. L., Kjellstrand C. M., Najarian J. S. Pseudorejection: factors mimicking rejection in renal allograft recipients. Ann Surg. 1977 Jul;186(1):51–59. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197707000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris P. J., Yadav R. V., Kincaid-Smith P., Anderton J., Hare W. S., Johnson N., Johnson W., Marshall V. C. Renal artey stenosis in renal transplantation. Med J Aust. 1971 Jun 12;1(24):1255–1257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricotta J. J., Schaff H. V., Williams G. M., Rolley R. T., Whelton P. K., Harrington D. M. Renal artery stenosis following transplantation: etiology, diagnosis, and prevention. Surgery. 1978 Nov;84(5):595–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacht R. A., Martin D. G., Karalakulasingam R., Wheeler C. S., Lansing A. M. Renal artery stenosis after renal transplantation. Am J Surg. 1976 Jun;131(6):653–657. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie W. A., Vinik M., Hume D. M. Angiographic investigation of hypertension complicating human renal transplantation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 May;128(5):963–968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. B., Cosimi A. B., Lordon R., Thompson A. L., Ehrlich R. M. Diagnosis and management of arterial stenosis causing hypertension after successful renal transplantation. J Urol. 1976 Jun;115(6):639–642. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59318-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spees E. K., Jr, Oakes D. D., McAllister H. A. Renal artery stenosis after machine preservation and transplantation of cadaver kidneys. Surgery. 1979 Dec;86(6):907–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobian L., Coffee K., McCrea P. Contrasting exchangeable sodium in rats with different types of Goldblatt hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1969 Aug;217(2):458–460. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.217.2.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]