Abstract
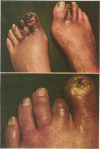
Thirty-five patients with gangrene or pregangrene of the feed associated with palpable peripheral pulses have been treated with the platelet suppressive drugs aspirin and dipyridamole. Sulphinpyrazone was substituted for two patients who could not tolerate aspirin. Complete reversal of the signs and symptoms occurred in more than 50% of the treated patients. Recurrence of pain occurred in the five patients in whom antiplatelet therapy was discontinued. Reversal of symptoms was again achieved by reintroduction of the drugs. An increased incidence of spontaneous platelet aggregation and hypersensitive platelets was observed in those patients who responded to platelet suppressive therapy. These results indicate that platelet suppressive therapy is of therapeutic value in selected patients with peripheral gangrene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenowitz J. B., Edwards W. S. The management of atheromatous emboli to the lower extremities. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Dec;143(6):941–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns T. S., Saunders R. N. Quantitation of in vivo platelet aggregation by the platelet aggregate ratio method. Thromb Res. 1977 Apr;10(4):629–633. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane C. Atherothrombotic embolism of lower extremities in arteriosclerosis. Arch Surg. 1967 Jan;94(1):96–101. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330070098020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOYE S. J., TEITELBAUM S., GORE I., WARREN R. Atheromatous embolization; a factor in peripheral gangrene. N Engl J Med. 1959 Jul 16;261(3):128–131. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195907162610305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlam C. A., Moore S., Bolton A. E., Pepper D. S., Cash J. D. The release of a human platelet specific protein measured by a radioimmunoassay. Thromb Res. 1975 Jun;6(6):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(75)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley C. B., Ward J. D., Timperley W. R., Porter N. R., Preston F. E. Platelet abnormalities in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Lancet. 1975 Dec 27;2(7948):1274–1276. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston F. E., Emmanuel I. G., Winfield D. A., Malia R. G. Essential thrombocythaemia and peripheral gangrene. Br Med J. 1974 Aug 31;3(5930):548–552. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5930.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaney G. Dead digits and patent pulses. S Afr J Surg. 1974 Sep;12(3):137–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walden R., Adar R., Mozes M. Gangrene of toes with normal peripheral pulses. Ann Surg. 1977 Mar;185(3):269–272. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197703000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. S., Porter N., Preston F. E., Morris-Jones W. Platelet aggregation in patients with peripheral vascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Jan;29(1):63–68. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Hoak J. C. A new method for the quantitative detection of platelet aggregates in patients with arterial insufficiency. Lancet. 1974 Oct 19;2(7886):924–926. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]