Abstract
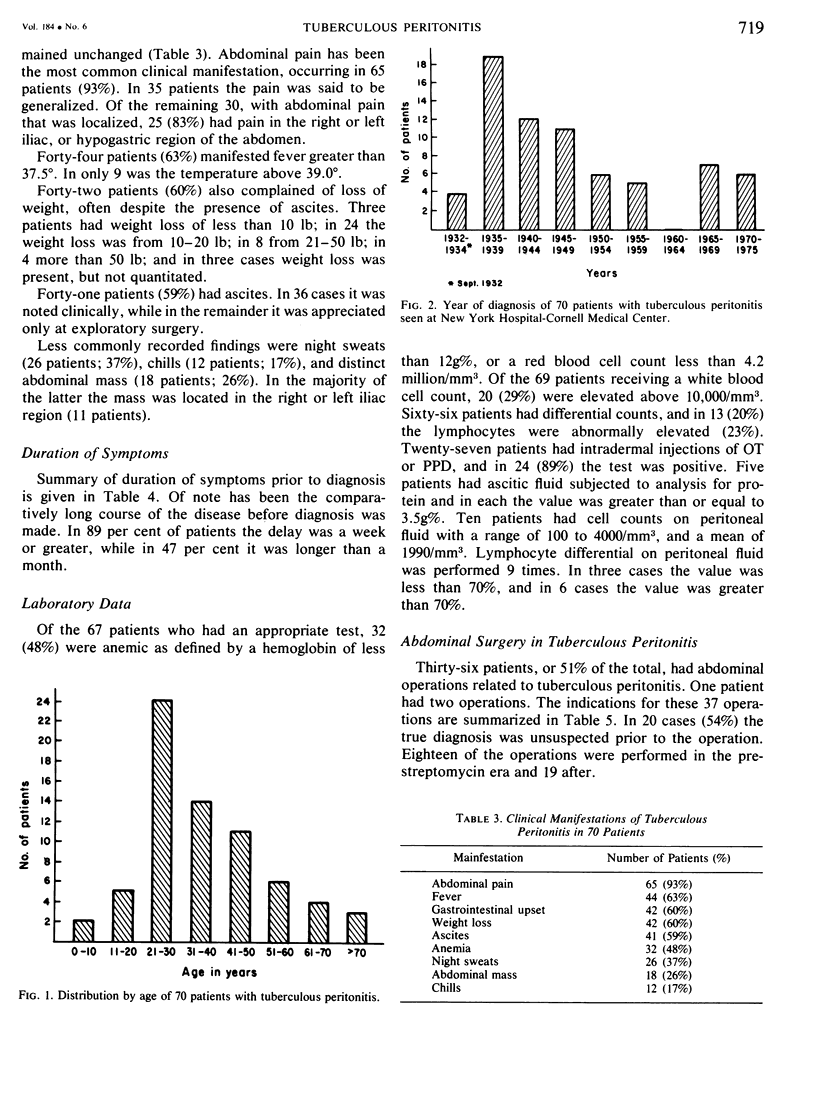
The clinical course of 70 patients with tuberculous peritonitis seen over a 43 year period has been reviewed. Thirty-seven patients were diagnosed prior to the advent of anti-tuberculous chemotherapy and 33 after. Clinical manifestations remained unchanged over the period of study. Abdominal pain (93%), fever (63%), gastrointestinal upset (60%), weight loss (60%), and ascites (59%) continue to be the most common findings. Females outnumbered males 2:1. In 89% of patients the duration of symptoms prior to diagnosis was a week or longer, and in 47% it was longer than a month. Diagnosis was confirmed by histologic examination of intra-abdominal tissue in 44% of cases, by clinical suspicion with an extraperitoneal site of tuberculosis in 29%, by bacteriology of peritoneal fluid in 24%, and by autopsy alone in 3%. An extraperitoneal site of tuberculsis was present in 83% of patients. The importance of obtaining a definitive diagnosis, and of instituting immediate antimicrobial therapy is emphasized by the mortality of 49% in the pre-antibiotic era, and of 7% in patients receiving anti-microbial therapy. The conclusions from this review are that: 1) with suggestive clinical manifestations and bacteriologic proof of active tuberculosis anywhere in the patient, operation is not mandated; 2) in the presence of the above clinical manifestations, and in the absence of definitive bacteriologic proof, exploratory laparotomy is indicated for diagnostic purposes; 3) antituberculous chemotherapy is highly effective, and is the treatment of choice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borhanmanesh F., Hekmat K., Vaezzadeh K., Rezai H. R. Tuberculous peritonitis. Prospective study of 32 cases in Iran. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Apr;76(4):567–572. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-4-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES H. J., CARR D. T., GERACI J. E. Tuberculous peritonitis: a review of 34 cases with emphasis on the diagnostic aspects. Dis Chest. 1960 Jul;38:42–50. doi: 10.1378/chest.38.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homan W., Harman E., Braun N. M., Felton C. P., King T. K., Smith J. P. Miliary tuberculosis presenting as acute respiratory failure: treatment by membrane oxygenator and ventricle pump. Chest. 1975 Mar;67(3):366–369. doi: 10.1378/chest.67.3.366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHRS T. Tuberculous peritonitis; a follow-up study of 169 cases. Tubercle. 1952 May;33(5):132–138. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(52)80081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUGHEED J. C., SAPORTA J., HOLMES J. TREATMENT AND CURRENT STATUS OF TUBERCULOUS PERITONITIS. Am Surg. 1963 Dec;29:850–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh J. W. Rifampin in treatment of advanced pulmonary tuberculosis. Report of a VA cooperative pilot study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1972 Mar;105(3):397–409. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1972.105.3.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh M. M., Bhargava A. N., Jain K. P. Tuberculous peritonitis. An evaluation of pathogenetic mechanisms, diagnostic procedures and therapeutic measures. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 13;281(20):1091–1094. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911132812003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sochocky S. Tuberculous peritonitis. A review of 100 cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Mar;95(3):398–401. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.3.398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolinsky E. New drug regimens in the treatment of tuberculosis. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1975 Oct;51(9):1096–1102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


