Abstract
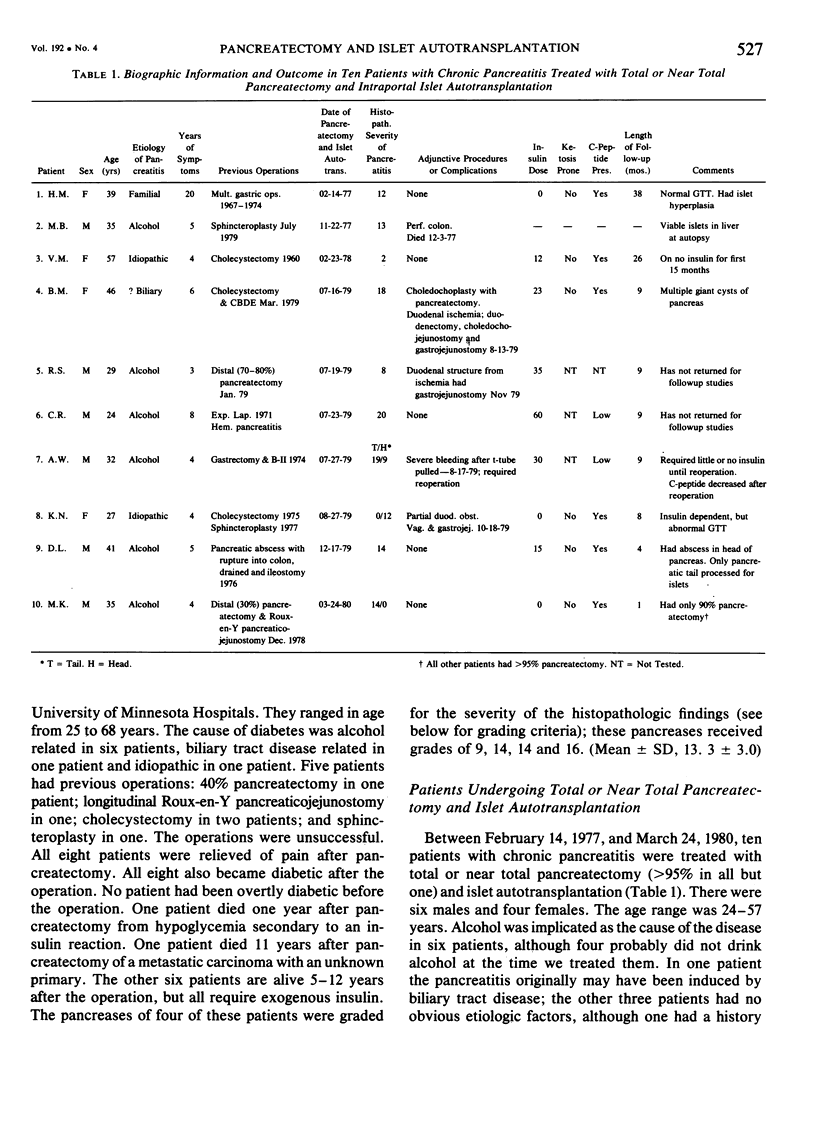
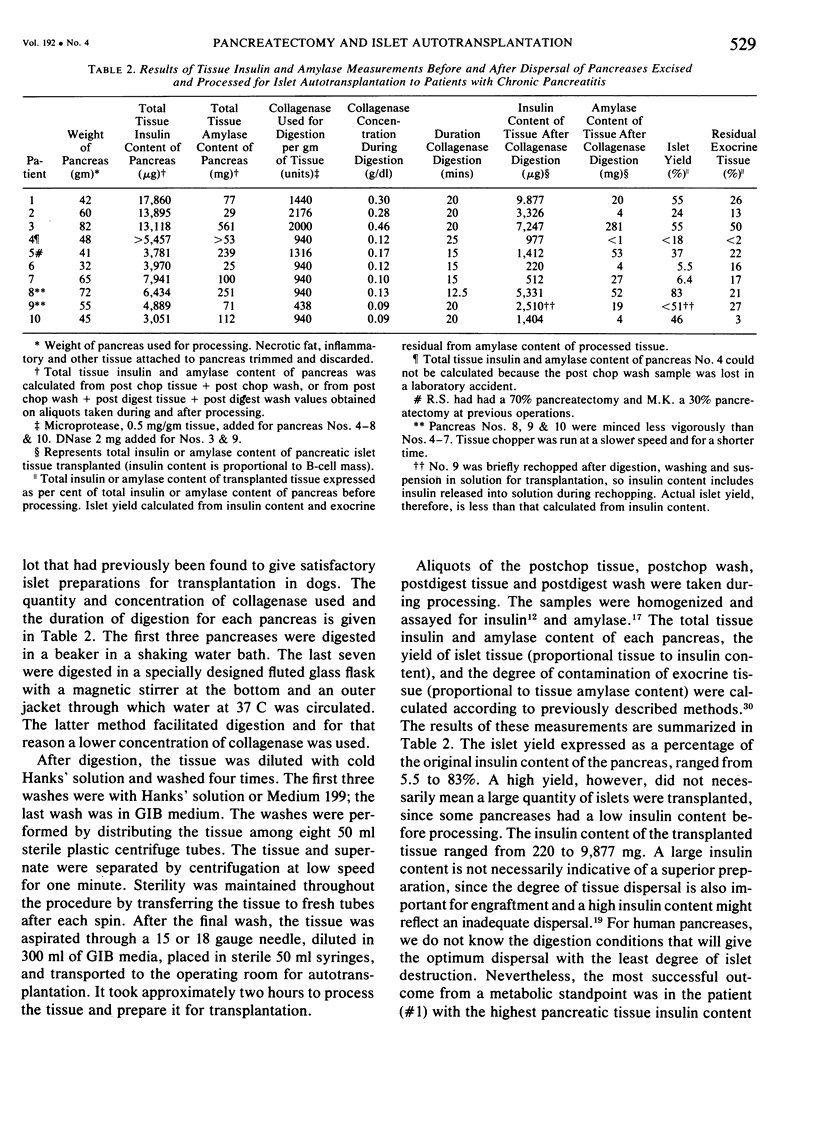
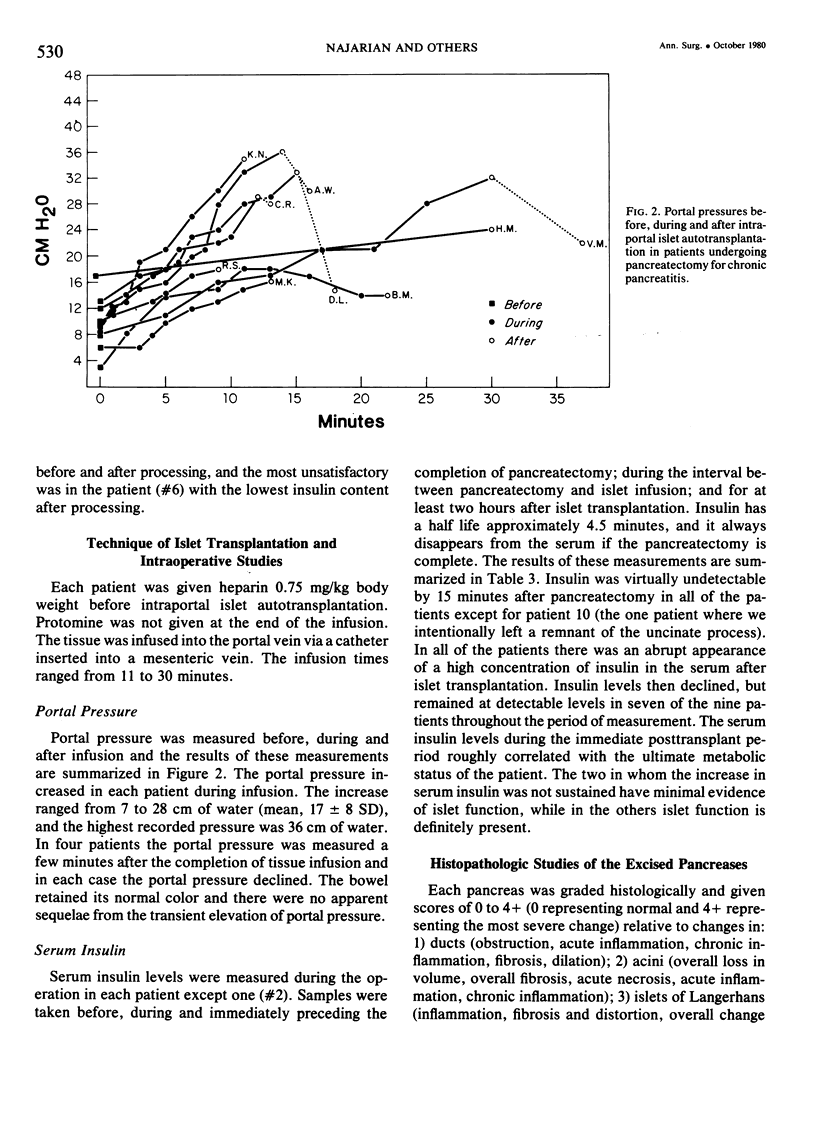
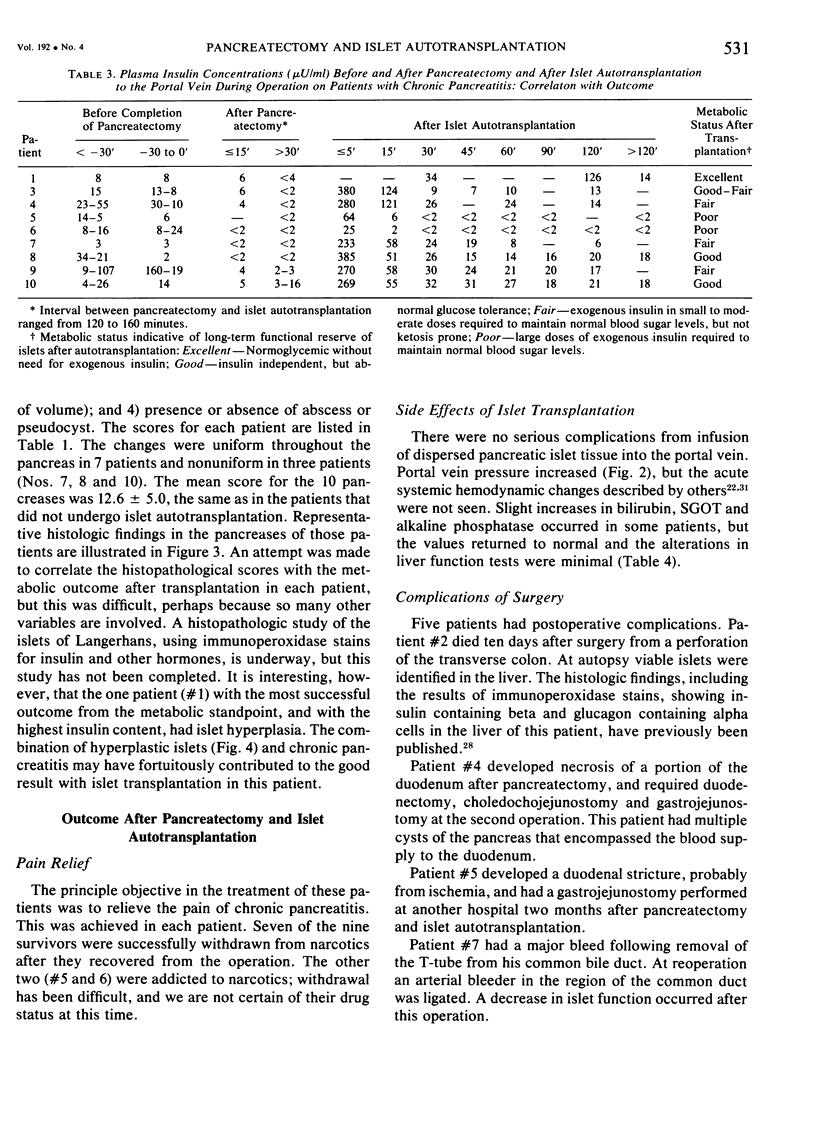
Total or near total pancreatectomy is the surest way to relieve the pain of chronic pancreatitis but is rarely applied because the metabolic consequences are so severe. For most patients drainage procedures are applicable, but pancreatectomy may be the only alternative for small duct disease or where procedures to improve duct drainage have failed. Preservation of endocrine function is a major problem in patients who require pancreatectomy. Experiments in pancreatectomized dogs have shown that intrasplenic or intraportal transplantation of unpurified pancreatic islet tissue dispersed by collagenase digestion can prevent diabetes. We have applied this technique to ten patients with chronic pancreatitis, small ducts, and intractable pain. The entire pancreas of > 95% of the pancrease was excised, minced, dispersed by collagenase digestion and infused into the portal vein < 2 1/2 hours after removal. Mean (+/- SD) rise in portal pressure was 17 +/- 8 cm of water. Liver function tests were altered minimally. All patients were relieved of pain. One patient died of a complication not related to the islet autotransplant; viable islets were identified in the liver at autopsy. Of the remaining nine patients, three have been insulin independent for 1, 9, and 38 months. One patient was insulin indpendent for 15 months and now takes 12 units of insulin daily. Three have nonketosis prone diabetes (tested by insulin withdrawal) and take 15--30 units of insulin per day. C-peptide studies in these patients show that functioning islets are present. Two patients are diabetic and require 35 and 60 units of insulin per day. In eight of nine patients tested serum insulin concentrations fell to undetectable levels during the interval between pancreatectomy and islet transplantation. Serum insulin levels during the first few hours after islet transplantation predicted success. In the insulin independent or in the patients with mild diabetes, insulin levels were persistently greater than or equal to 6 microU/ml. In the other two patients, the increase in insulin concentration was not sustained. Islet tissue preparation from a diseased pancreas is difficult. The surgeon and the patient must still be willing to accept diabetes for relief of pain when performing this operation. In some patients, however, islet autotransplantation can prevent or partially ameliorate diabetes after pancreatectomy, and preservation of endocrine function is worthwhile.
Full text
PDF

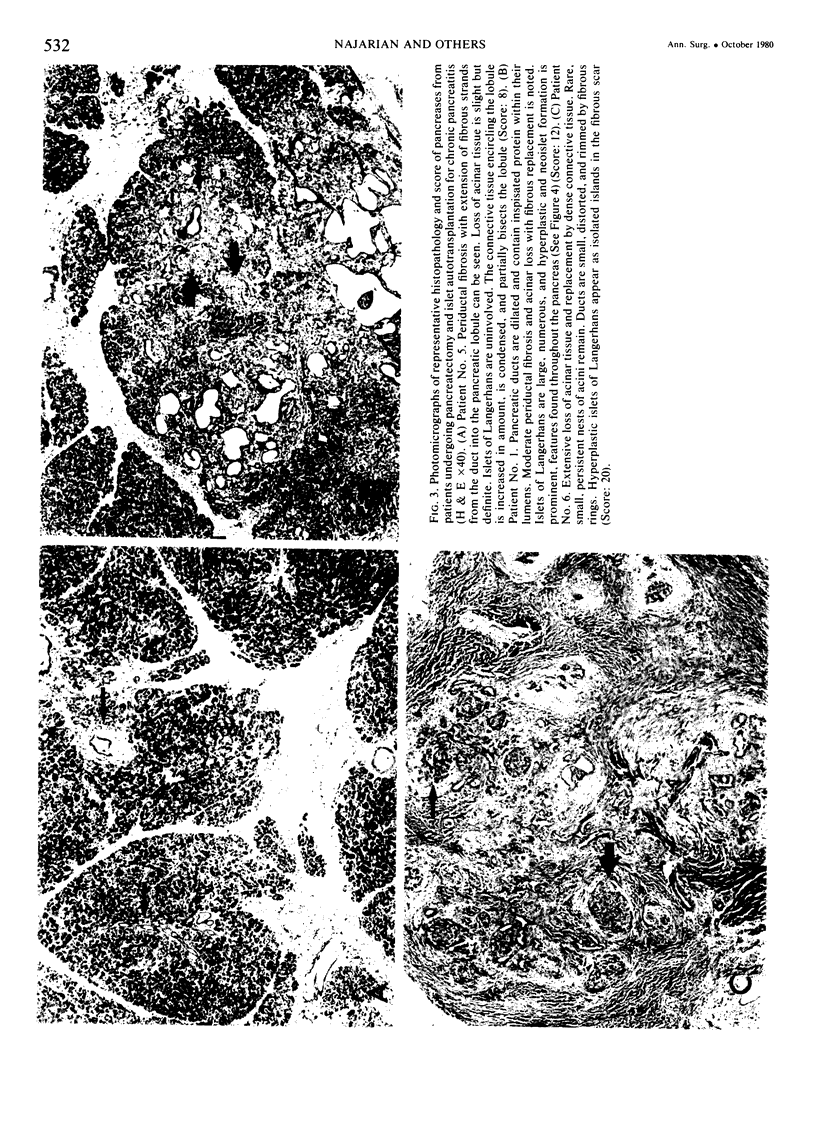

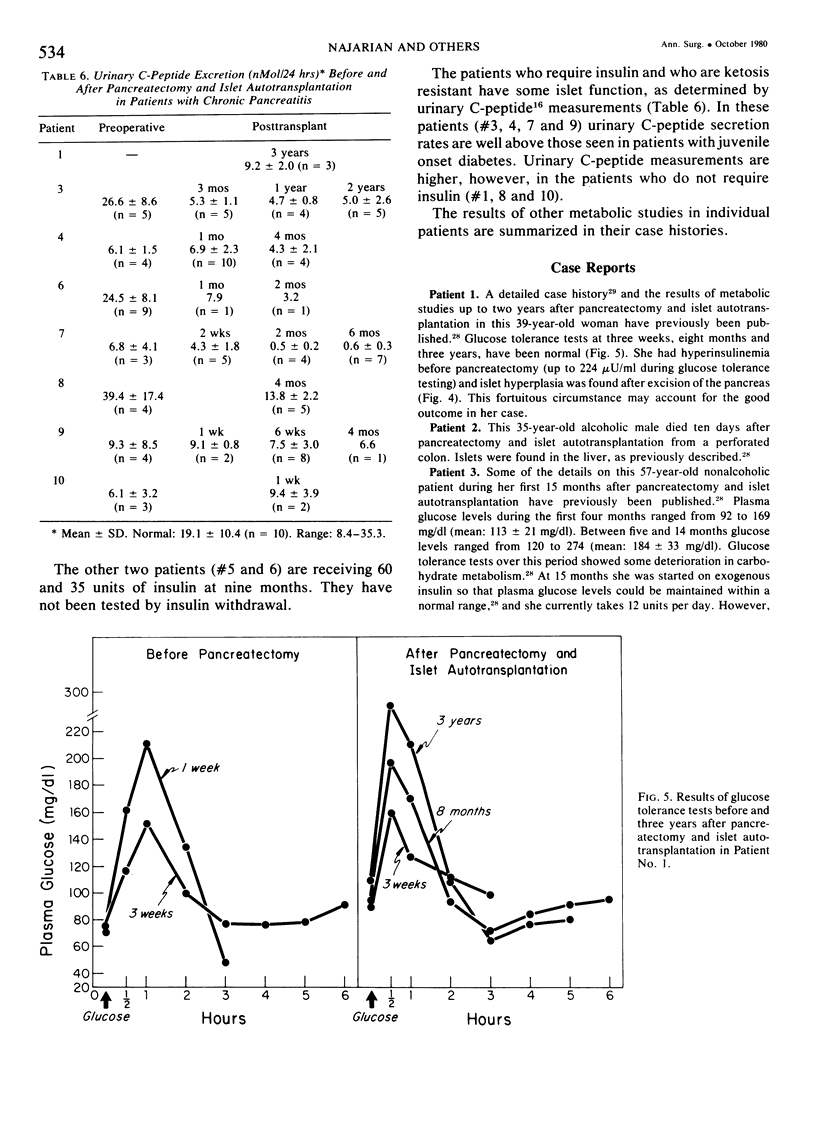
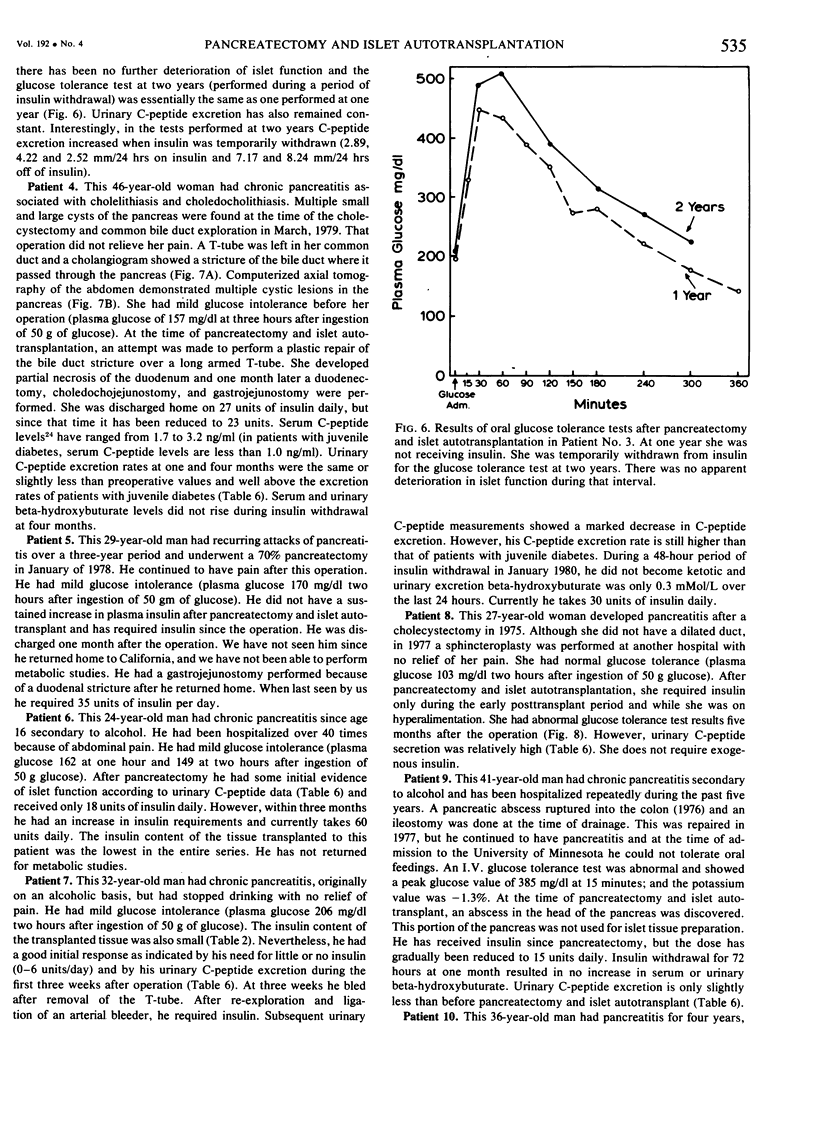

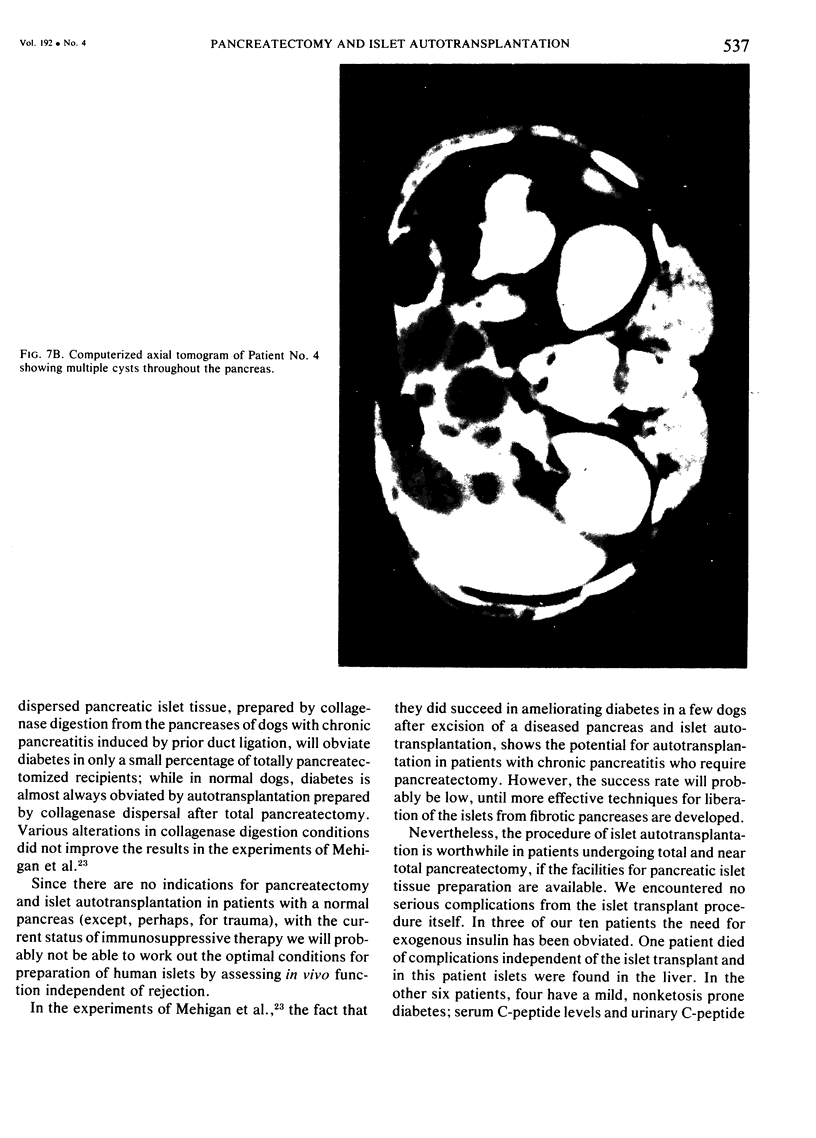

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRETT O., Jr, BOWERS W. F. Total pancreatectomy for chronic relapsing pancreatitis and calcinosis of the pancreas. U S Armed Forces Med J. 1957 Jul;8(7):1037–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes A. J., Bloom S. R., Goerge K., Alberti G. M., Smythe P., Alford F. P., Chisholm D. J. Ketoacidosis in pancreatectomized man. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 2;296(22):1250–1253. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706022962202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braasch J. W., Vito L., Nugent F. W. Total pancreatectomy of end-stage chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1978 Sep;188(3):317–322. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197809000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Child C. G., 3rd, Frey C. F., Fry W. J. A reappraisal of removal of ninety-five per cent of the distal portion of the pancreas. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1969 Jul;129(1):49–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOYLE A. P., BALCERZAK S. P., JEFFREY W. L. FATAL DIABETIC GLOMERULOSCLEROSIS AFTER TOTAL PANCREATECTOMY. N Engl J Med. 1964 Mar 19;270:623–624. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196403192701207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobroschke J., Schwemmle K., Langhoff G., Laube H., Bretzel R. G., Federlin K. Autotransplantation von Langerhansschen Inseln nach totaler Duodenopankreatektomie bie einem Patienten met chronischer Pankreatitis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1978 Dec 1;103(48):1905-6, 1909-10. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1129365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. F., Child C. G., Fry W. Pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1976 Oct;184(4):403–413. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197610000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey C. F. The operative treatment of pancreatitis. Arch Surg. 1969 Apr;98(4):406–417. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1969.01340100038003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry W. J., Child C. G., 3rd Ninety-five per cent distal pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1965 Oct;162(4):543–549. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196510000-00001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOETZ F. C., GREENBERG B. Z., ELLS J., MEINERT C. A SIMPLE IMMUNOASSAY FOR INSULIN: APPLICATION TO HUMAN AND DOG PLASMA. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Dec;23:1237–1246. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-12-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsinsky C. Surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis. A review after a ten-year experience. Arch Surg. 1980 Apr;115(4):545–551. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380040167030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle H. H., Recemtsma K. Pancreatic autotransplantation following resection. Surgery. 1978 Mar;83(3):359–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H., Katz A. I. Quantitation of human pancreatic beta-cell function by immunoassay of C-peptide in urine. Diabetes. 1977 Jan;26(1):30–35. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson A. D., Pruitt K. M., Caldwell R. C. An improved amylase assay. J Dent Res. 1969 May-Jun;48(3):483–483. doi: 10.1177/00220345690480032701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer G. J., Sutherland D. E., Matas A. J., Cain T. L., Najarian J. S. Autotransplantation of pancreatic islets without separation of exocrine and endocrine tissue in totally pancreatectomized dogs. Surgery. 1977 Jul;82(1):74–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer G. J., Sutherland D. R., Matas A. J., Payne W. D., Najarian J. S. Autotransplantation of pancreatic fragments to the portal vein and spleen of totally pancreatectomized dogs: a comparative evaluation. Ann Surg. 1978 Jan;187(1):79–86. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197801000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matas A. J., Sutherland D. E., Steffes M. W., Najarian J. S. Islet transplantation. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1977 Nov;145(5):757–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matas A. J., Sutherland D. E., Steffes M. W., Najarian J. S. Short-term culture of adult pancreatic fragments for purification and transplantation of islets of Langerhans. Surgery. 1976 Aug;80(2):183–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehigan D. G., Bell W. R., Zuidema G. D., Eggleston J. C., Cameron J. L. Disseminated intravascular coagulation and portal hypertension following pancreatic islet autotransplantation. Ann Surg. 1980 Mar;191(3):287–293. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198003000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehigan D. G., Zuidema G. D., Eggleston J. C., Cameron J. L. Pancreatic islet autotransplantation: results in dogs with chronic duct ligation. Am J Surg. 1980 Feb;139(2):170–174. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90248-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melani F., Rubenstein A. H., Oyer P. E., Steiner D. F. Identification of proinsulin and C-peptide in human serum by a specific immunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):148–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch V., Campiche M. Successful intrasplenic autotransplantation of pancreatic tissue in totally pancreatectomised dogs. Transplantation. 1976 Mar;21(3):265–269. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197603000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian J. S., Sutherland D. E., Matas A. J., Goetz F. C. Human islet autotransplantation following pancreatectomy. Transplant Proc. 1979 Mar;11(1):336–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjövall S., Hoevels J., Sundqvist K. Fatal outcome from emergency embolization of an intrahepatic aneurysm: a case report. Surgery. 1980 Mar;87(3):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Matas A. J., Goetz F. C., Najarian J. S. Transplantation of dispersed pancreatic islet tissue in humans: autografts and allografts. Diabetes. 1980;29 (Suppl 1):31–44. doi: 10.2337/diab.29.1.s31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Matas A. J., Najarian J. S. Pancreatic islet cell transplantation. Surg Clin North Am. 1978 Apr;58(2):365–382. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E., Matas A. J., Steffes M. W., Najarian J. S. Infant human pancreas. A potential source of islet tissue for transplantation. Diabetes. 1976 Dec;25(12):1123–1128. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.12.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITFIELD A. G., CRANE C. W., FRENCH J. M., BAYLEY T. J. LIFE WITHOUT A PANCREAS. Lancet. 1965 Mar 27;1(7387):675–677. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(65)91829-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. W. Surgical management of chronic relapsing pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1969 Jan;117(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. D., Leite C. A., Baumeister F., Poucher R. L., Kalser M. H. Clinical and metabolic response to radical distal pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1967 Jan;113(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(67)90260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiland D. E., Kuntz D. J., Kimball H. W. Subtotal pancreatectomy for chronic pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1969 Dec;118(6):973–975. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(69)90269-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]