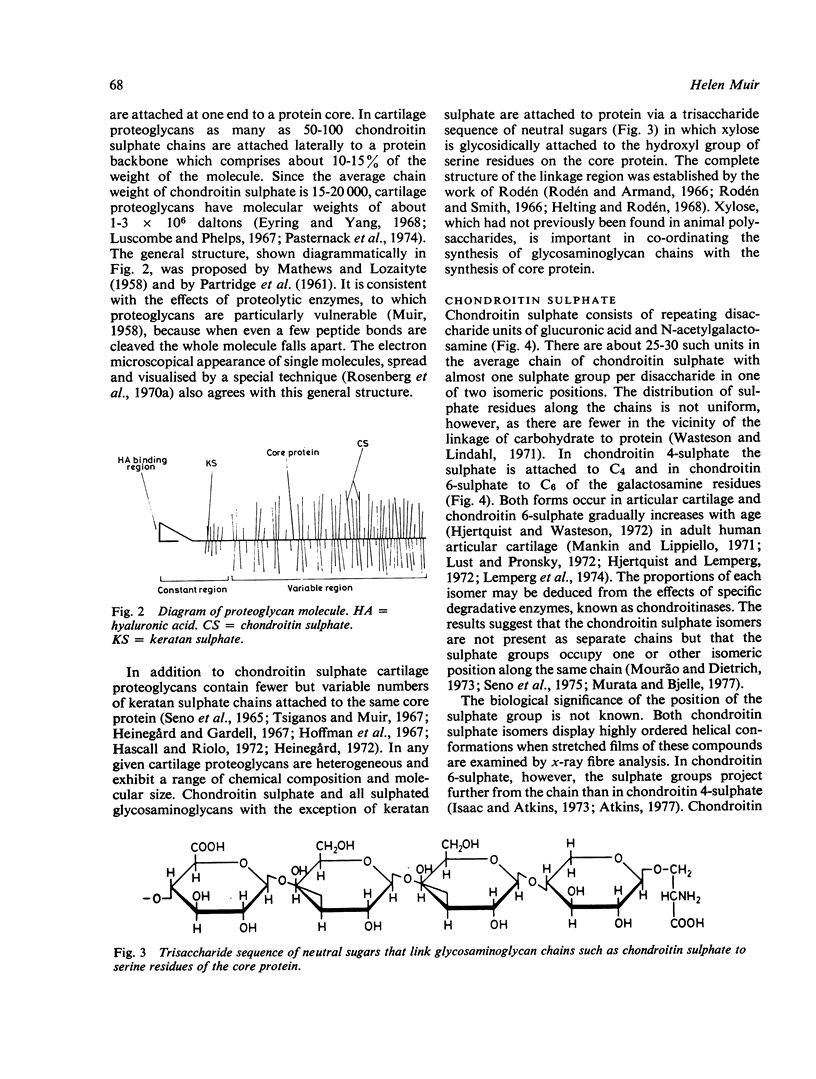
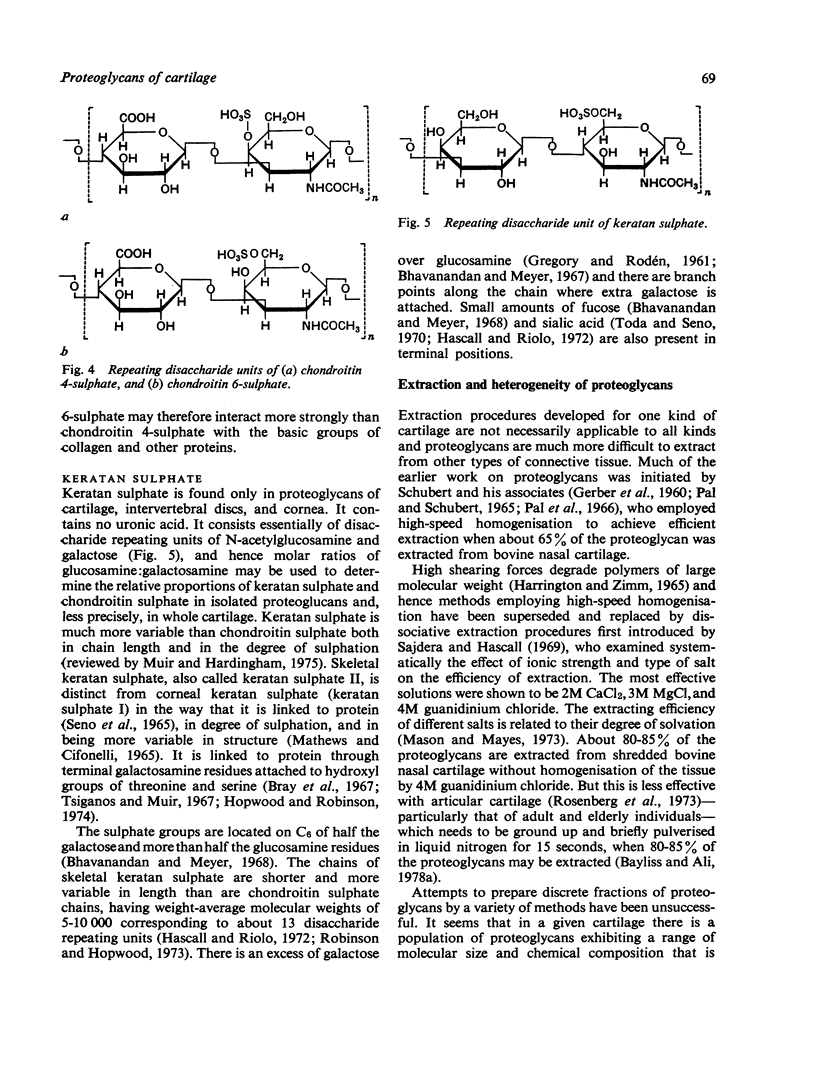
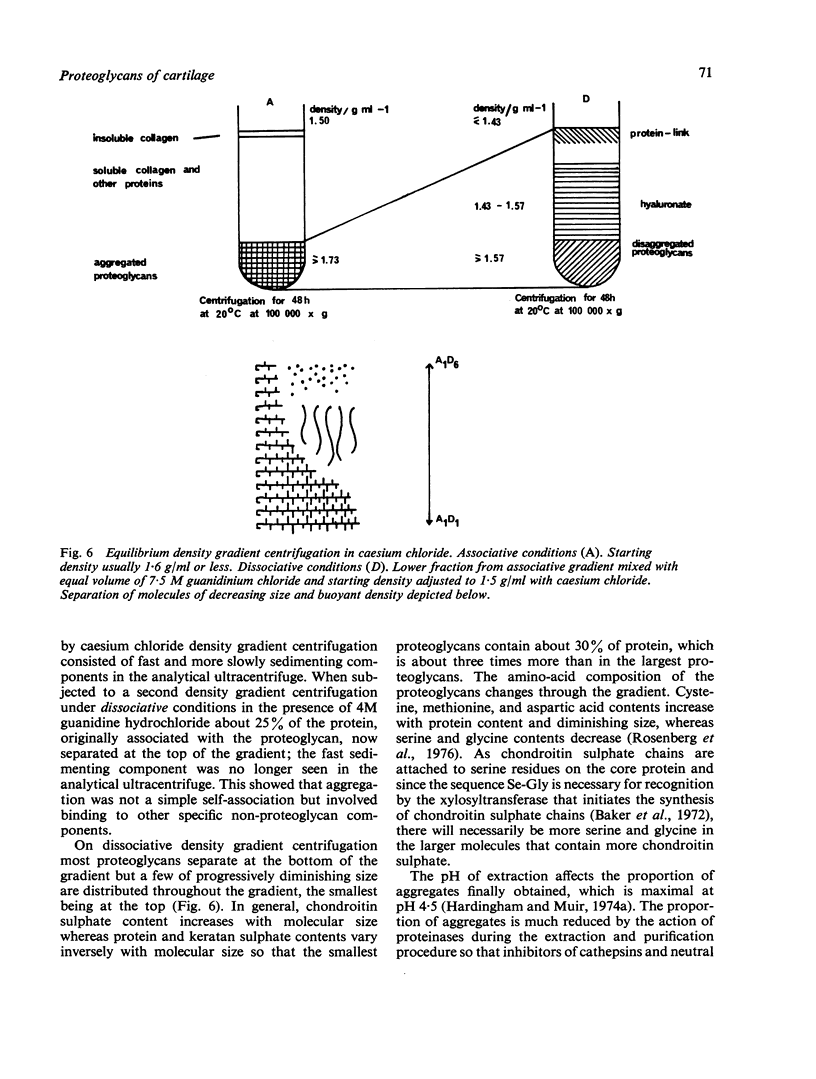
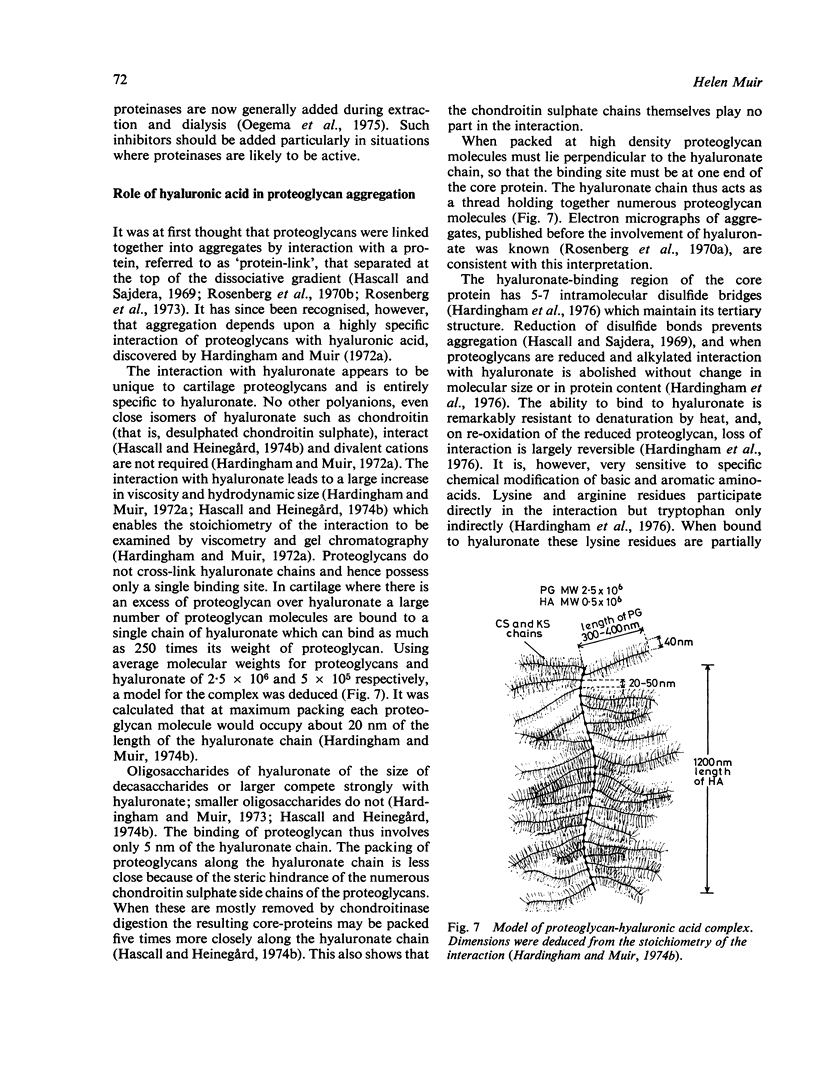
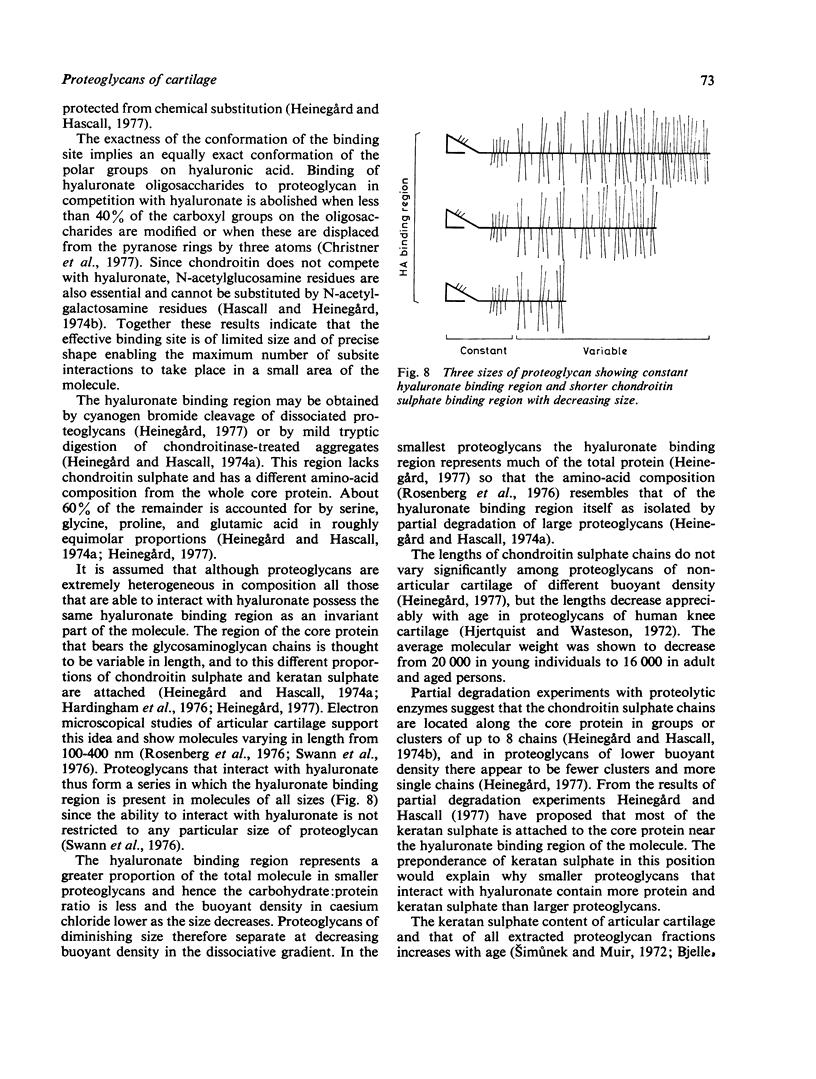
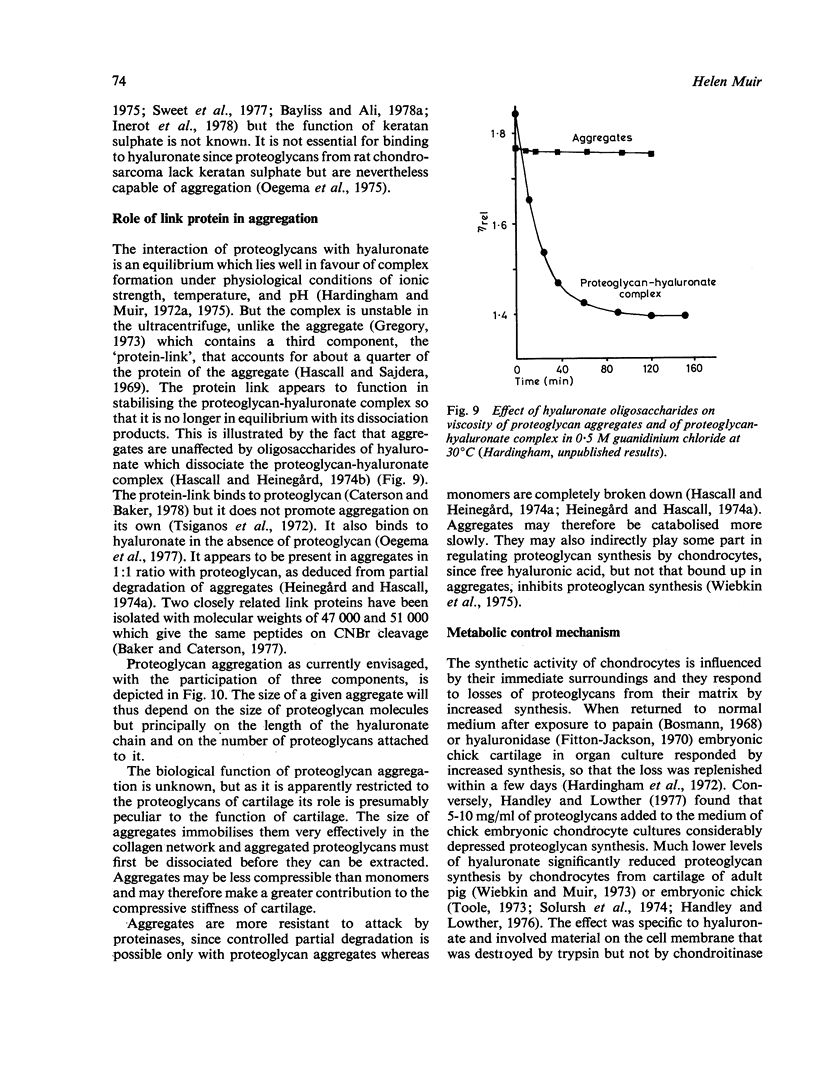
Full text
PDF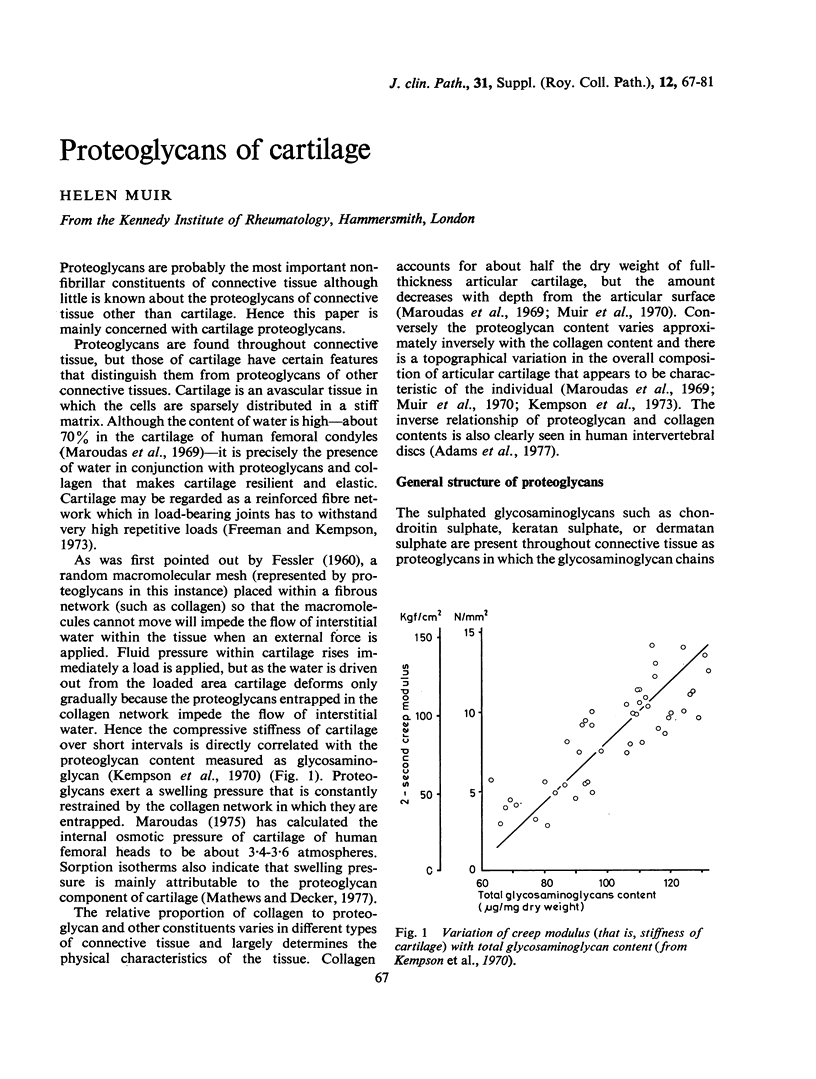








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J., Holtzer H. The loss of phenotypic traits by differentiated cells, V. The effect of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on cloned chondrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1144–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P., Eyre D. R., Muir H. Biochemical aspects of development and ageing of human lumbar intervertebral discs. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1977 Feb;16(1):22–29. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/16.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y. Analysis of matrix vesicles and their role in the calcification of epiphyseal cartilage. Fed Proc. 1976 Feb;35(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali S. Y., Evans L. Enzymic degradation of cartilage in osteoarthritis. Fed Proc. 1973 Apr;32(4):1494–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J. R., Rodén L., Stoolmiller A. C. Biosynthesis of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan. Xylosyl transfer to Smith-degraded cartilage proteoglycan and other exogenous acceptors. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3838–3847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker J., Caterson B. The purification and cyanogen bromide cleavage of the 'link proteins' from cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 11;77(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80157-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Ali S. Y. Isolation of proteoglycans from human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):123–132. doi: 10.1042/bj1690123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss M. T., Ali S. Y. Studies on cathepsin B in human articular cartilage. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):149–154. doi: 10.1042/bj1710149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Meyer K. Studies on keratosulfates. Methylation and partial acid hydrolysis of bovine corneal keratosulfate. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4352–4359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhavanandan V. P., Meyer K. Studies on keratosulfates. Methylation, desulfation, and acid hydrolysis studies on old human rib cartilage keratosulfate. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 10;243(5):1052–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjelle A. Content and composition of glycosaminoglycans in human knee joint cartilage. Variation with site and age in adults. Connect Tissue Res. 1975;3(2):141–147. doi: 10.3109/03008207509152172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosmann H. B. Cellular control of macromolecular synthesis: rates of synthesis of extracellular macromolecules during and after depletion by papain. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1968 Mar 26;169(1017):399–425. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1968.0017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D. Enhanced extractability of articular cartilage protoglycans in osteoarthrosis. Biochem J. 1974 Nov;143(2):475–478. doi: 10.1042/bj1430475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Characterization of protein-polysaccharides of articular cartilage from mature and immature pigs. Biochem J. 1969 Oct;114(4):871–876. doi: 10.1042/bj1140871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Heterogeneity of protein-polysaccharides of porcine articular cartilage. The chondroitin sulphate proteins associaterd with collagen. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;123(5):747–755. doi: 10.1042/bj1230747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Muir H. Heterogeneity of protein-polysaccharides of porcine articular cartilage. The sequential extraction of chondroitin sulphate-proteins with iso-osmotic neutral sodium acetate. Biochem J. 1971 Jan;121(2):261–270. doi: 10.1042/bj1210261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt K. D., Palmoski M. J., Perricone E. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II Evidence for the presence of a hyaluronate-binding region on proteoglycans from osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Nov-Dec;19(6):1308–1314. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray B. A., Lieberman R., Meyer K. Structure of human skeletal keratosulfate. The linkage region. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 25;242(14):3373–3380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. D., Contepomi C. A., Farkas T. A. A post mortem study of the hip joint. Including the prevalence of the features of the right side. Ann Rheum Dis. 1970 Jan;29(1):15–31. doi: 10.1136/ard.29.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caterson B., Baker J. The interaction of link proteins with proteoglycan monomers in the absence of hyaluronic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91596-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christner J. E., Brown M. L., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Interaction of cartilage proteoglycans with hyaluronic acid. The role of the hyaluronic acid carboxyl groups. Biochem J. 1977 Dec 1;167(3):711–716. doi: 10.1042/bj1670711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuervo L. A., Pita J. C., Howell D. S. Inhibition of calcium phosphate mineral growth by proteoglycan aggregate fractions in a synthetic lymph. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973;13(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF02015390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Luca S., Heinegård D., Hascall V. C., Kimura J. H., Caplan A. I. Chemical and physical changes in proteoglycans during development of chick limb bud chondrocytes grown in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6600–6608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingle J. T., Barrett A. J., Poole A. R., Stovin P. Inhibition by pepstatin of human cartilage degradation. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):443–444. doi: 10.1042/bj1270443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dondi P., Muir H. Collagen synthesis and deposition in cartilage during disrupted proteoglycan production. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):117–120. doi: 10.1042/bj1600117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyring E. J., Yang J. T. Conformation of protein-polysaccharide complex from bovine nasal septum. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1306–1311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FESSLER J. H. A structural function of mucopolysaccharide in connective tissue. Biochem J. 1960 Jul;76:124–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0760124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell H. B., Barratt M. E. The role of soft connective tissue in the breakdown of pig articular cartilage cultivated in the presence of complement-sufficient antiserum to pig erythrocytes. I. Histological changes. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(3):441–468. doi: 10.1159/000230951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell H. B., Jubb R. W. The effect of synovial tissue on the breakdown of articular cartilage in organ culture. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Sep-Oct;20(7):1359–1371. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franek M. D., Dunstone J. R. Density-gradient centrifugation in the isolation of polysaccharide-protein complexes from aortic tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Sep 26;127(1):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90491-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERBER B. R., FRANKLIN E. C., SCHUBERT M. Ultracentrifugal fractionation of bovine nasal chondromucoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1960 Oct;235:2870–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory J. D. Multiple aggregation factors in cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):383–386. doi: 10.1042/bj1330383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Extracellular matrix metabolism by chondrocytes. III. Modulation of proteoglycan synthesis by extracellular levels of proteoglycan in cartilage cells in culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 7;500(1):132–139. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handley C. J., Lowther D. A. Inhibition of proteoglycan biosynthesis by hyaluronic acid in chondrocytes in cell culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 24;444(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Ewins R. J., Muir H. Cartilage proteoglycans. Structure and heterogeneity of the protein core and the effects of specific protein modifications on the binding to hyaluronate. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):127–143. doi: 10.1042/bj1570127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Fitton-Jackson S., Muir H. Replacement of proteoglycans in embryonic chick cartilage in organ culture after treatment with testicular hyaluronidase. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):101–112. doi: 10.1042/bj1290101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Binding of oligosaccharides of hyaluronic acid to proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):905–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1350905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Biosynthesis of proteoglycans in cartilage slices. Fractionation by gel chromatography and equilibrium density-gradient centrifugation. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):791–803. doi: 10.1042/bj1260791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Hyaluronic acid in cartilage and proteoglycan aggregation. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):565–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1390565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardingham T. E., Muir H. The specific interaction of hyaluronic acid with cartillage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 15;279(2):401–405. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. I. The role of hyaluronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4232–4241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Heinegård D. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. II. Oligosaccharide competitors of the proteoglycan-hyaluronic acid interaction. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4242–4249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Riolo R. L. Characteristics of the protein-keratan sulfate core and of keratan sulfate prepared from bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4529–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hascall V. C., Sajdera S. W. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. The function of glycoprotein in the formation of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 10;244(9):2384–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Gardell S. Studies on protein-polysaccharide complex (proteoglycan) from human nucleus pulposus. I. Isolation and preliminary characterisation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):164–171. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. 3. Characteristics of the proteins isolated from trypsin digests of aggregates. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4250–4256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D., Hascall V. C. Characterization of chondroitin sulfate isolated from trypsin-chymotrypsin digests of cartilage proteoglycans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):427–441. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Hyaluronidase digestion and alkaline treatment of bovine tracheal cartilage proteoglycans. Isolation and characterisation of different keratan sulfate proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Nov 28;285(1):193–207. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90191-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinegård D. Polydispersity of cartilage proteoglycans. Structural variations with size and buoyant density of the molecules. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1980–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helting T., Rodén L. The carbohydrate-protein linkage region of chondroitin 6-sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertquist S. O., Lemperg R. Identification and concentration of the glycosaminoglycans of human articular cartilage in relation to age and osteoarthritis. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;10(3):223–237. doi: 10.1007/BF02012552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjertquist S. O., Wasteson A. The molecular weight of chondroitin sulphate from human articular cartilage. Effect of age and of osteoarthritis. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;10(1):31–37. doi: 10.1007/BF02012533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P., Mashburn T. A., Jr, Meyer K. Proteinpolysaccharide of bovine cartilage. II. The relation of keratan sulfate and chondroitin sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1967 Sep 10;242(17):3805–3809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood J. J., Robinson H. C. The structure and composition of cartilage keratan sulphate. Biochem J. 1974 Aug;141(2):517–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1410517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell D. S., Muniz O., Pita J. C., Enis J. E. Pyrophosphate release by osteoarthritis cartilage incubates. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 May-Jun;19 (Suppl 3):488–494. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197605/06)19:3+<488::aid-art1780190724>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inerot S., Heinegård D., Audell L., Olsson S. E. Articular-cartilage proteoglycans in aging and osteoarthritis. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):143–156. doi: 10.1042/bj1690143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac D. H., Atkins E. D. Molecular conformations of chondroitin-4-sulphate. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 22;244(138):252–253. doi: 10.1038/newbio244252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. F. Environmental control of macromolecular synthesis in cartilage and bone: morphogenetic response to hyaluronidase. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Sep 29;175(1041):405–453. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1970.0029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keiser H., Greenwald R. A., Feinstein G., Janoff A. Degradation of cartilage proteoglycan by human leukocyte granule neutral proteases--a model of joint injury. II. Degradation of isolated bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycan. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):625–632. doi: 10.1172/JCI108318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Muir H., Pollard C., Tuke M. The tensile properties of the cartilage of human femoral condyles related to the content of collagen and glycosaminoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 28;297(2):456–472. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempson G. E., Muir H., Swanson S. A., Freeman M. A. Correlations between stiffness and the chemical constituents of cartilage on the human femoral head. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 21;215(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettner K. E., Croxen R. L., Eisenstein R., Sorgente N. Proteinase inhibitor activity in connective tissues. Experientia. 1974 Jun 15;30(6):595–597. doi: 10.1007/BF01921492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuettner K. E., Hiti J., Eisenstein R., Harper E. Collagenase inhibition by cationic proteins derived from cartilage and aorta. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Sep 7;72(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90957-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemperg R., Larsson S. E., Hjertquist S. O. The glycosaminoglycans of bovine articular cartilage. I. Concentration and distribution in different layers in relation to age. Calcif Tissue Res. 1974;15(3):237–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02059060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander S., Hjerpe A. Proteoglycans of mineralizing rib and epiphyseal cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 8;404(1):93–109. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90151-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander S. Proteoglycans of guinea-pig coastal cartilage. Fractionation and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Sep 15;57(2):549–559. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmander S. Turnover of proteoglycans in guinea pig costal cartilage. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Apr 15;180(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe M., Phelps C. F. The composition and physicochemical properties of bovine nasal-septa protein-polysaccharide complex. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):110–119. doi: 10.1042/bj1020110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lust G., Pronsky W. Glycosaminoglycan contents of normal and degenerative articular cartilage from dogs. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Jul;39(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEWS M. B., LOZAITYTE I. Sodium chondroitin sulfate-protein complexes of cartilage. I. Molecular weight and shape. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Mar;74(1):158–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90210-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUIR H. The nature of the link between protein and carbohydrate of a chondroitin sulphate complex from hyaline cartilage. Biochem J. 1958 Jun;69(2):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj0690195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malemud C. J., Janoff A. Identification of neutral proteases in human neutrophil granules that degrade articular cartilage proteoglycan. Arthritis Rheum. 1975 Jul-Aug;18(4):361–368. doi: 10.1002/art.1780180413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Dorfman H., Lippiello L., Zarins A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Apr;53(3):523–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Lippiello L. The glycosaminoglycans of normal and arthritic cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1971 Aug;50(8):1712–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI106660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A. Biophysical chemistry of cartilaginous tissues with special reference to solute and fluid transport. Biorheology. 1975 Jun;12(3-4):233–248. doi: 10.3233/bir-1975-123-416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A., Muir H., Wingham J. The correlation of fixed negative charge with glycosaminoglycan content of human articular cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):492–500. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90311-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. M., Mayes R. W. Extraction of cartilage protein-polysaccharides with inorganic salt solutions. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):535–540. doi: 10.1042/bj1310535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Cifonelli J. A. Comparative biochemistry of keratosulfates. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4140–4145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Decker L. Comparative studies of water sorption of hyaline cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 29;497(1):151–159. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes R. W., Mason R. M., Griffin D. C. The composition of cartilage proteoglycans. An investigation using high- and low-inonic-strength extraction procedures. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):541–553. doi: 10.1042/bj1310541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt C. A., Muir H. Biochemical changes in the cartilage of the knee in experimental and natural osteoarthritis in the dog. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1976 Feb;58(1):94–101. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.58B1.131804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt C., Gilbertson E., Muir H. An experimental model of osteoarthritis; early morphological and biochemical changes. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977 Feb;59(1):24–35. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.59B1.576611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison R. I., Barrett A. J., Dingle J. T., Prior D. Cathepsins BI and D. Action on human cartilage proteoglycans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 12;302(2):411–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourão P. A., Dietrich C. P. Differences in the content of chondroitin sulfate C and chondroitin sulfate A in the epiphysial growth cartilages of human vertebrae and long bones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):210–213. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir H., Bullough P., Maroudas A. The distribution of collagen in human articular cartilage with some of its physiological implications. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970 Aug;52(3):554–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir H. Heberden Oration, 1976. Molecular approach to the understanding of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Jun;36(3):199–208. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.3.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata K., Bjelle A. O. Constitutional heterogeneity of the glycosaminoglycans in articular cartilage proteoglycans. Connect Tissue Res. 1977;5(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/03008207709152237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Brown M., Dziewiatkowski D. D. The link protein in proteoglycan aggregates from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6470–6477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oegema T. R., Jr, Hascall V. C., Dziewiatkowski D. D. Isolation and characterization of proteoglycans from the swarm rat chondrosarcoma. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6151–6159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAL S., SCHUBERT M. THE ACTION OF HYDROXYLAMINE ON THE PROTEINPOLYSACCHARIDES OF CARTILAGE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3245–3248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARTRIDGE S. M., DAVIS H. F., ADAIR G. S. The chemistry of connective tissues. 6. The constitution of the chondroitin sulphate-protein complex in cartilage. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:15–26. doi: 10.1042/bj0790015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pal S., Doganges P. T., Schubert M. The separation of new forms of the proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nasal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1966 Sep 25;241(18):4261–4266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmoski M., Brandt K. Hyaluronate-binding by proteoglycans. Comparison of mildly and severely osteoarthritic regions of human femoral cartilage. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Jul 1;70(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternack S. G., Veis A., Breen M. Solvent-dependent changes in proteoglycan subunit conformation in aqueous guanidine hydrochloride solutions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2206–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J. P., Mason R. M. The stability of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycans during isolation and storage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 23;498(1):176–188. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Barratt M. E., Fell H. B. The role of soft connective tissue in the breakdown of pig articular cartilage cultivated in the presence of complement-sufficient antiserum to pig erythrocytes. II. Distribution of immunoglobulin G (IgG). Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;44(3):469–488. doi: 10.1159/000230952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Hembry R. M., Dingle J. T. Cathepsin D in cartilage: the immunohistochemical demonstration of extracellular enzyme in normal and pathological conditions. J Cell Sci. 1974 Jan;14(1):139–161. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. C., Hopwood J. J. The alkaline cleavage and borohydride reduction of cartilage proteoglycan. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):457–470. doi: 10.1042/bj1330457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodén L., Armand G. Structure of the chondroitin 4-sulfate-protein linkage region. Isolation and characterization of the disaccharide 3-O-beta-D-glucuronosyl-D-galactose. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 10;241(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodén L., Smith R. Structure of the neutral trisaccharide of the chondroitin 4-sulfate-protein linkage region. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5949–5954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. C., Pal S., Beale R. J. Proteoglycans from bovine proximal humeral articular cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3681–3690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Hellmann W., Kleinschmidt A. K. Macromolecular models of proteinpolysaccharides from bovine nasal cartilage based on electron microscopic studies. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4123–4130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Pal S., Beale R., Schubert M. A comparison of proteinpolysaccharides of bovine nasal cartilage isolated and fractionated by different methods. J Biol Chem. 1970 Aug 25;245(16):4112–4122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L., Wolfenstein-Todel C., Margolis R., Pal S., Strider W. Proteoglycans from bovine proximal humeral articular cartilage. Structural basis for the polydispersity of proteoglycan subunit. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6439–6444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Mason R. M. The electrophoretic heterogeneity of bovine nasal cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):357–367. doi: 10.1042/bj1570357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roughley P. J., Murphy G., Barrett A. J. Proteinase inhibitors of bovine nasal cartilage. Biochem J. 1978 Mar 1;169(3):721–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1690721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SENO N., MEYER K., ANDERSON B., HOFFMAN P. VARIATIONS IN KERATOSULFATES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1005–1010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajdera S. W., Hascall V. C. Proteinpolysaccharide complex from bovine nasal cartilage. A comparison of low and high shear extraction procedures. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 10;244(1):77–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky A. I., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Neutral proteases and cathepsin D in human articular cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1044–1053. doi: 10.1172/JCI107641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky A. I., Keiser H., Howell D. S., Woessner J. F., Jr Metalloproteases of human articular cartilage that digest cartilage proteoglycan at neutral and acid pH. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):1030–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI108526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seno N., Anno K., Yaegashi Y., Okuyama T. Microheterogeneity of chondroitin sulfates from various cartilages. Connect Tissue Res. 1975;3(1):87–96. doi: 10.3109/03008207509152345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simůnek Z., Muir H. Changes in the protein-polysaccharides of pig articular cartilage during prenatal life, development and old age. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(3):515–523. doi: 10.1042/bj1260515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Peters T. J., Serafini-Fracassini A. Observations on the distribution of the proteinpolysaccharide complex and collagen in bovine articular cartilage. J Cell Sci. 1967 Mar;2(1):129–136. doi: 10.1242/jcs.2.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solursh M., Vaerewyck S. A., Reiter R. S. Depression by hyaluronic acid of glycosaminoglycan synthesis by cultured chick embryo chondrocytes. Dev Biol. 1974 Dec;41(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90302-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swann D. A., Powell S., Broadhurst J., Sordillo E., Sotman S. The formation of a stable complex between dissociated proteoglycan and hyaluronic acid in the absence of a link protein. Biochem J. 1976 Aug 1;157(2):503–506. doi: 10.1042/bj1570503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet M. B., Thonar E. J., Immelman A. R., Solomon L. Biochemical changes in progressive osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1977 Oct;36(5):387–398. doi: 10.1136/ard.36.5.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda N., Seno N. Sialic acid in the keratan sulfate fraction from whale cartilage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 12;208(2):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiganos C. P., Hardingham T. E., Muir H. Aggregation of cartilage proteoglycans. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(4):121P–121P. doi: 10.1042/bj1280121p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiganos C. P., Muir H. Studies on protein-polysaccharides from pig laryngeal cartilage. Heterogeneity, fractionation and characterization. Biochem J. 1969 Aug;113(5):885–894. doi: 10.1042/bj1130885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasteson A., Lindahl U. The distribution of sulphate residues in the chondroitin sulphate chain. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):903–908. doi: 10.1042/bj1250903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebkin O. W., Muir H. Influence of the cells on the pericellular environment. The effect of hyaluronic acid on proteoglycan synthesis and secretion by chondrocytes of adult cartilage. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jul 17;271(912):283–291. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebkin O. W., Muir H. The inhibition of sulphate incorporation in isolated adult chondrocytes by hyaluronic acid. FEBS Lett. 1973 Nov 15;37(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80422-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. M., Wusteman F. S., Curtis C. G. The degradation of intravenously injected chondroitin 4-sulphate in the rat. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1009–1013. doi: 10.1042/bj1341009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


