Abstract
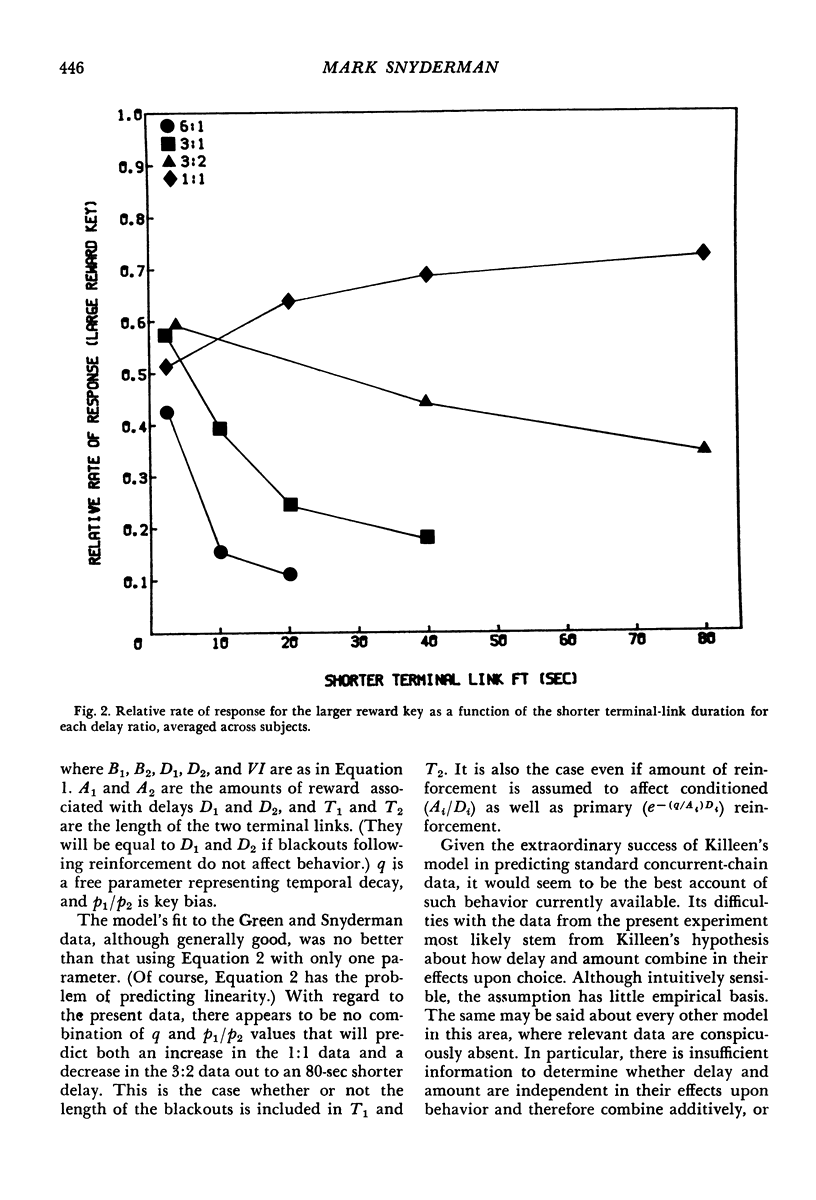
Eight pigeons responded under a concurrent-chain schedule for rewards differing in both delay and amount, the larger reward being associated with the longer delay. Preference was examined as the absolute durations of the terminal-link delays were increased at four different delay ratios. Difficulties with other experiments of this type were controlled for by the use of (a) a single-tape initial link to equalize terminal-link entries, (b) a blackout following the more immediate reward to equalize terminal-link length, and (c) a photocell to measure reinforcer duration more accurately. Preference for the larger reward changed systematically as delays increased in all conditions, decreasing for the 6:1, 3:1, and 3:2 ratios, and increasing for the 1:1 ratio. These results were similar to, but significantly different from, those of previous investigations. The implications of these results for various models of concurrent-chain behavior are discussed.
Keywords: concurrent chain, delay of reinforcement, self-control, pigeons
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainslie G. W. Impulse control in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):485–489. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainslie G. Specious reward: a behavioral theory of impulsiveness and impulse control. Psychol Bull. 1975 Jul;82(4):463–496. doi: 10.1037/h0076860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantino E. Choice and rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Sep;12(5):723–730. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry G. D., Marr M. J. Choice and reinforcement delay. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Jan;33(1):27–37. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.33-27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Snyderman M. Choice between rewards differing in amount and delay: Toward a choice model of self control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):135–147. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosch J., Neuringer A. Self-control in pigeons under the Mischel paradigm. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Jan;35(1):3–21. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Asaki K. Choice behavior of rats in a concurrent-chains schedule: Amount and delay of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 May;37(3):383–392. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOGAN F. A. DECISION MAKING BY RATS: DELAY VERSUS AMOUNT OF REWARD. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1965 Feb;59:1–12. doi: 10.1037/h0021633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macewen D. The effects of terminal-link fixed-interval and variable-interval schedules on responding under concurrent chained schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Sep;18(2):253–261. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazur J. E., Logue A. W. Choice in a "self-control" paradigm: effects of a fading procedure. J Exp Anal Behav. 1978 Jul;30(1):11–17. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1978.30-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachlin H., Green L. Commitment, choice and self-control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):15–22. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs D. A., Pliskoff S. S. Concurrent responding with fixed relative rate of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Nov;12(6):887–895. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


