Abstract
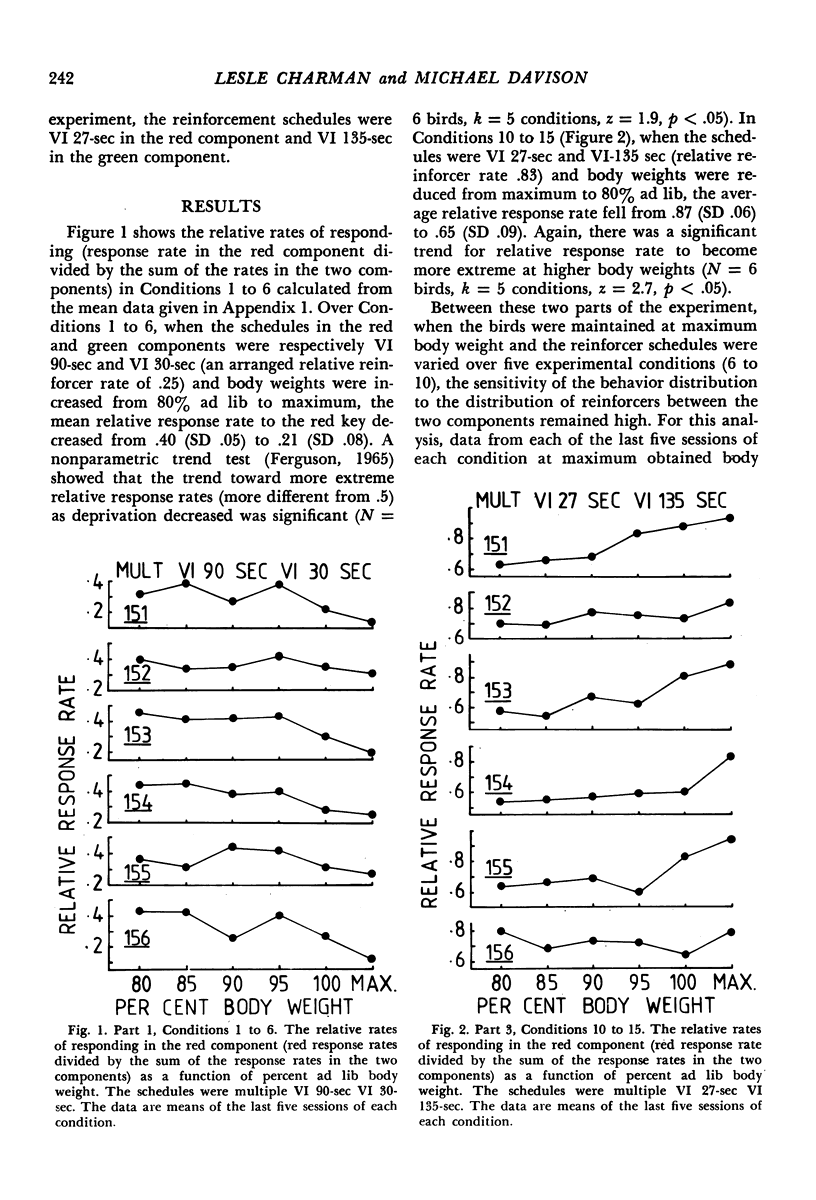
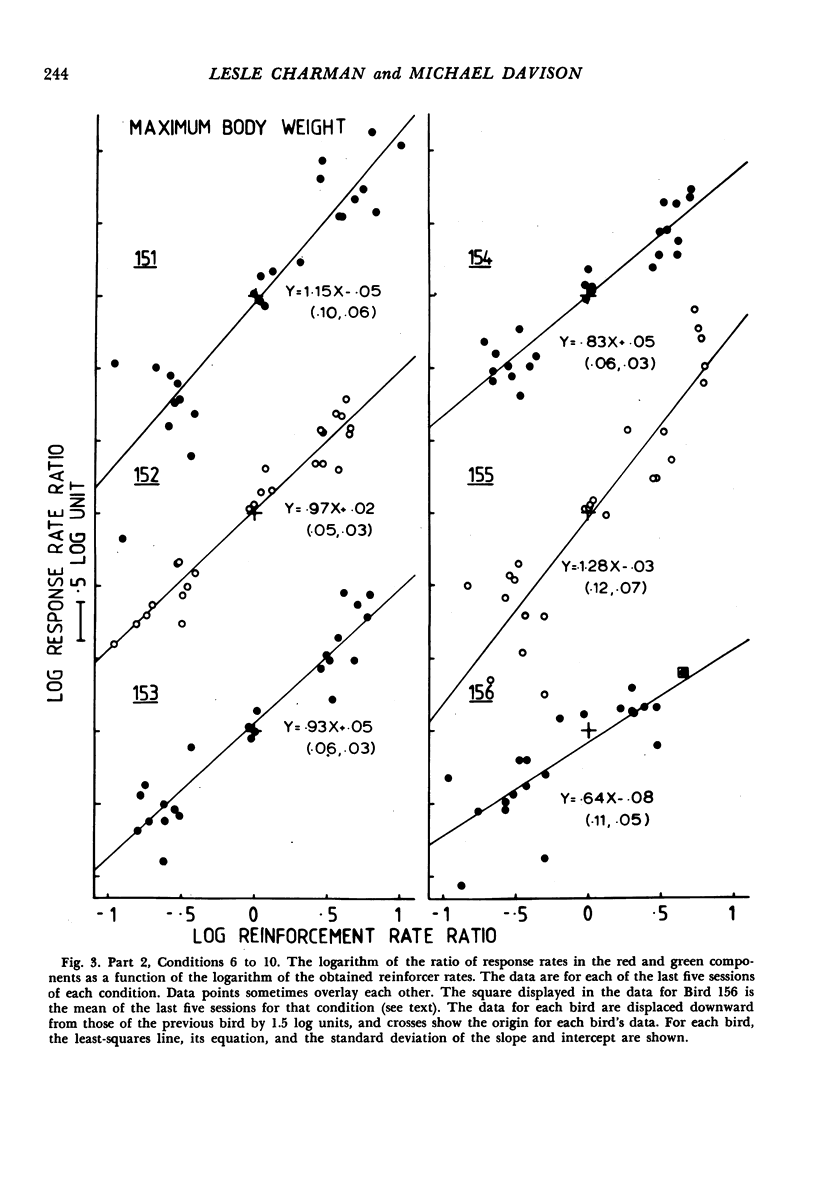
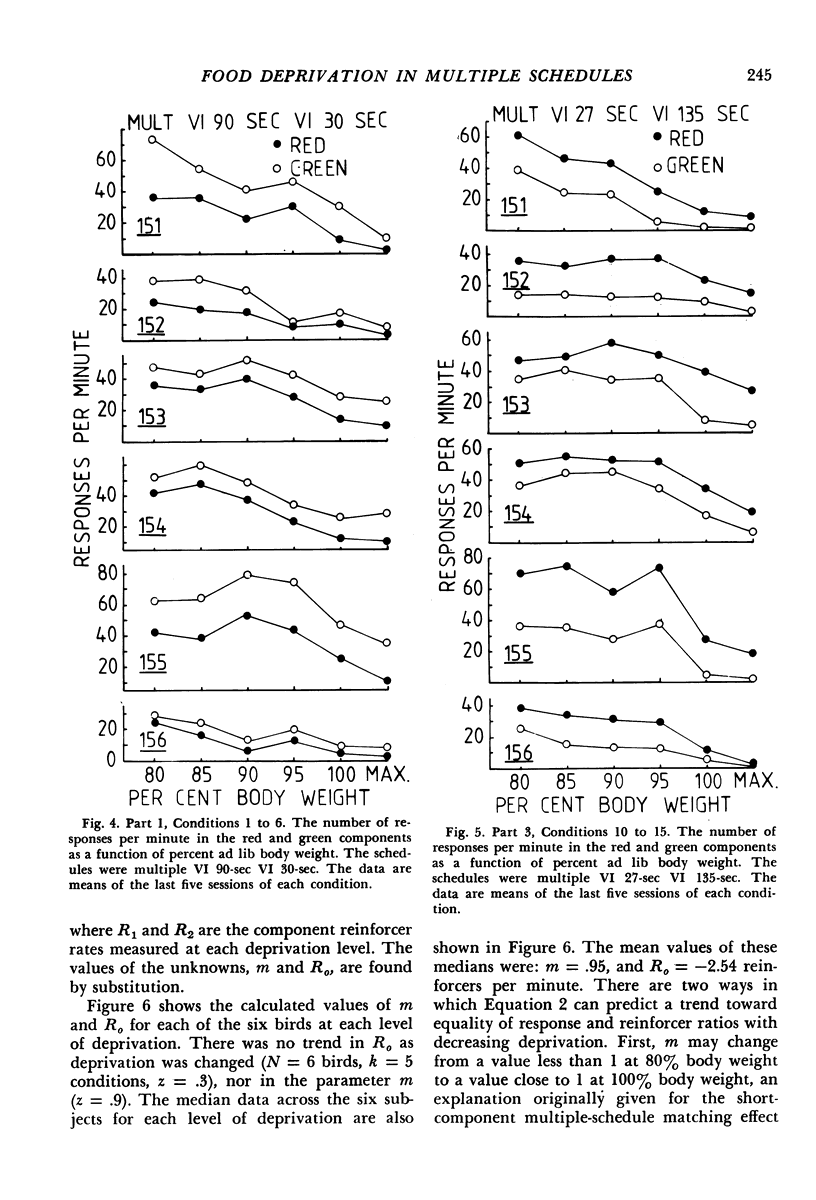
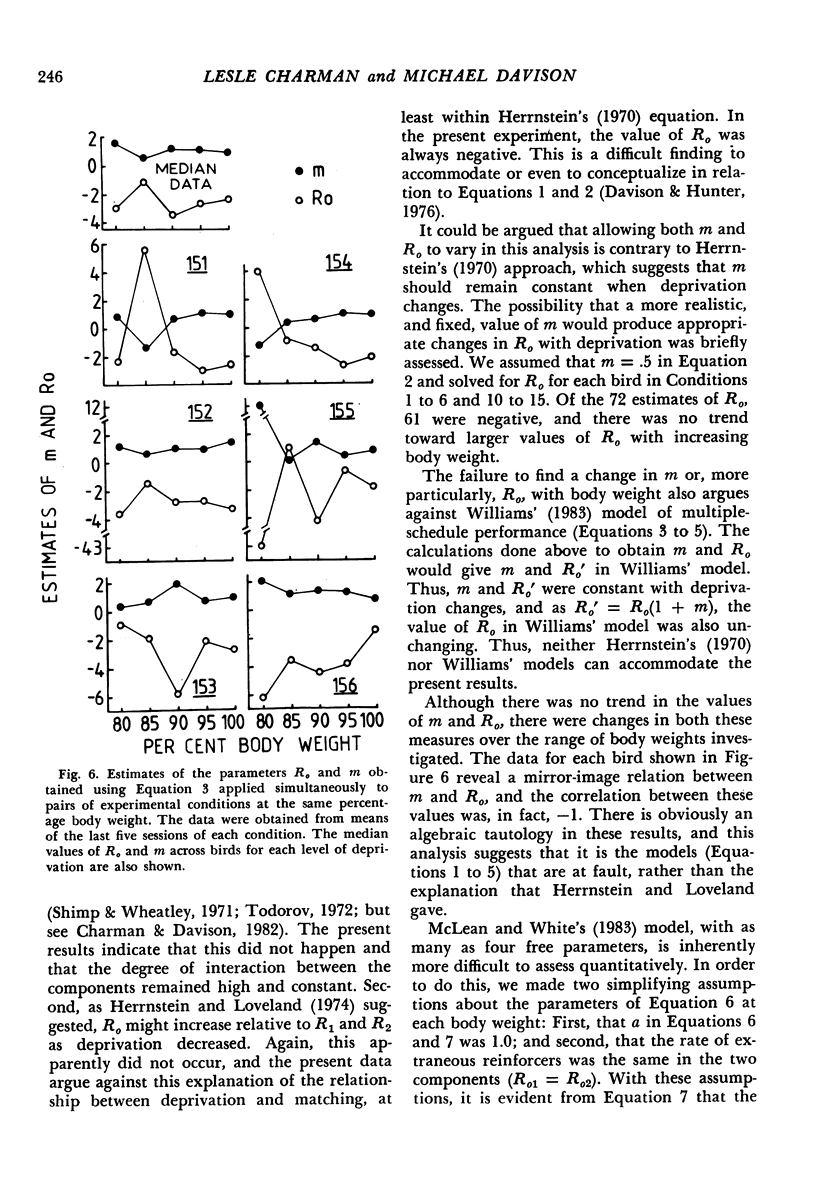
Six pigeons were used to investigate the effects of varying body weight and component reinforcer rates in two-component multiple variable-interval variable-interval schedules. In Parts 1 and 3 of the experiment, unequal component reinforcer rates were arranged, and body weights were respectively increased and decreased. At 80% ad lib weight, response-rate ratios were closer to unity than reinforcer-rate ratios, but at 100% or more of ad lib weight, response-rate ratios generally equaled reinforcer-rate ratios. In Part 2, component reinforcer-rate ratios were varied over five conditions with the subjects maintained at 100% or more of their ad lib weights, and response-rate ratios matched reinforcer-rate ratios. The data thus support the empirical finding that response allocation in multiple schedules is a function of deprivation. Although this qualitative result is predicted by three models of multiple-schedule performance, only a model that assumes no direct component interaction adequately describes the data.
Keywords: multiple schedules, variable-interval schedules, sensitivity to reinforcement, food deprivation, pigeons
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baum W. M. On two types of deviation from the matching law: bias and undermatching. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jul;22(1):231–242. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charman L., Davison M. On the effects of component durations and component reinforcement rates in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 May;37(3):417–439. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison M. C., Hunter I. W. Performance on variable-interval schedules arranged singly and concurrently. J Exp Anal Behav. 1976 May;25(3):335–345. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1976.25-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J., Loveland D. H. Hunger and contrast in a multiple schedule. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 May;21(3):511–517. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein R. J. On the law of effect. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Mar;13(2):243–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.13-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson J. M., Staddon J. E. Behavioral competition: a mechanism for schedule interactions. Science. 1978 Oct 27;202(4366):432–434. doi: 10.1126/science.705334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. P., White K. G. Temporal constraint on choice: Sensitivity and bias in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 May;39(3):405–426. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimp C. P., Wheatley K. L. Matching to relative reinforcement frequency in multiple schedules with a short component duration. J Exp Anal Behav. 1971 Mar;15(2):205–210. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1971.15-205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov J. C. Component duration and relative response rates in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jan;17(1):45–49. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.17-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILKINSON G. N. Statistical estimations in enzyme kinetics. Biochem J. 1961 Aug;80:324–332. doi: 10.1042/bj0800324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. Another look at contrast in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Mar;39(2):345–384. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


