Abstract
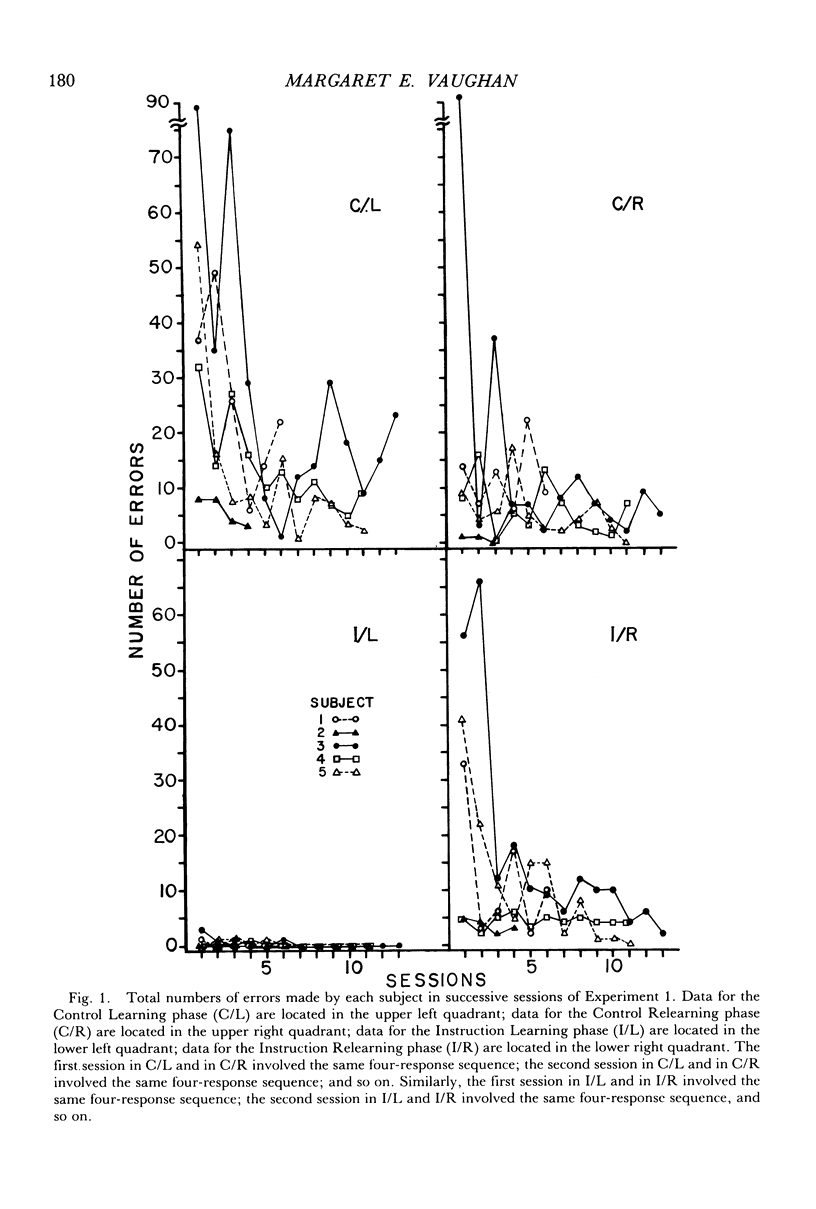
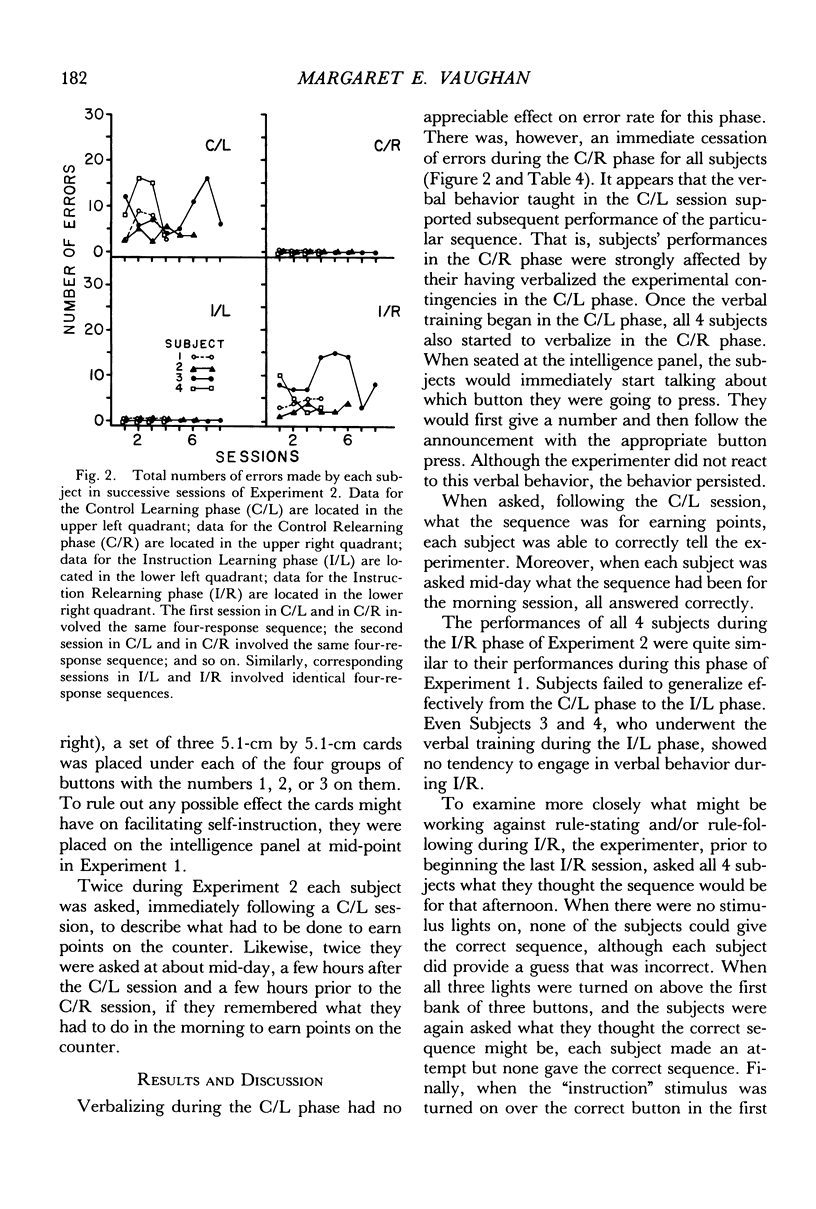
Five children, ranging in age from 3½ years to 5½ years, were taught various four-response chains using conditioned reinforcement. Experiment 1 investigated the effects of presenting “instruction” stimuli—a sequence of lights over the correct response buttons—to assess their role in facilitating the acquisition of a chain of responses. Without the “instruction” stimuli, children made many errors before responses were brought under the control of the programmed contingencies. When confronted with the same contingencies later in the day, these subjects made fewer errors. In contrast, in the presence of the “instruction” stimuli, subjects made virtually no errors. However, when the “instruction” stimuli were discontinued in the subsequent session, all 5 subjects made errors. In Experiment 2, the subjects were taught to verbalize the contingencies during the phase without the “instruction” stimuli. This resulted in errorless performance during the subsequent exposure to the same procedure, but errors nevertheless occurred again during reexposure to the procedure with the “instruction” stimuli discontinued.
Keywords: rule-governed behavior, self-instruction, repeated acquisition, children
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bem S. L. Verbal self-control: the establishment of effective self-instruction. J Exp Psychol. 1967 Aug;74(4):485–491. doi: 10.1037/h0024822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boren J. J., Devine D. D. The repeated acquisition of behavioral chains. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):651–660. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P. H., Quevillon R. P. The effects of a self-instructional package on overactive preschool boys. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Summer;9(2):179–188. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catania A. C., Matthews B. A., Shimoff E. Instructed versus shaped human verbal behavior: Interactions with nonverbal responding. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Nov;38(3):233–248. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe C. F., Beasty A., Bentall R. P. The role of verbal behavior in human learning: infant performance on fixed-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1983 Jan;39(1):157–164. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1983.39-157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poppen R. Human fixed-interval performance with concurrently programmed schedules: A parametric analysis. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Mar;37(2):251–266. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.37-251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


