Abstract
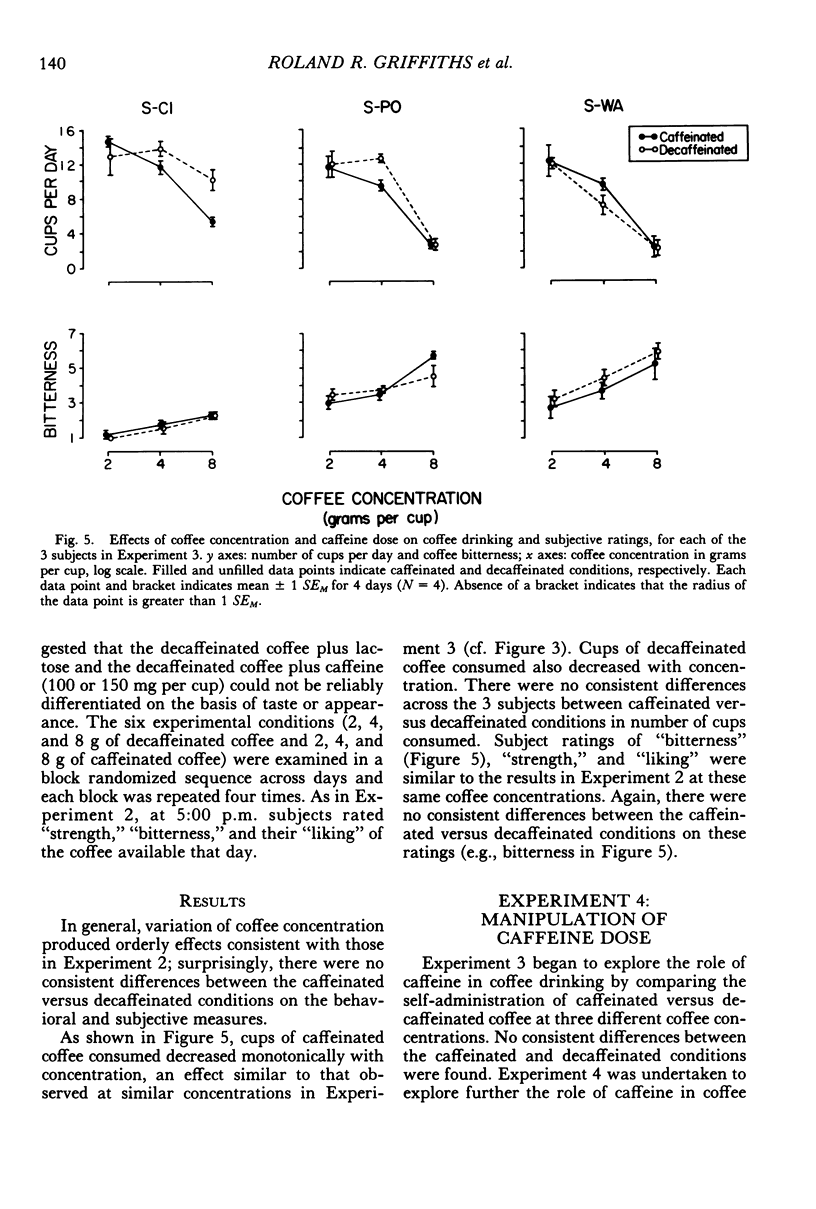
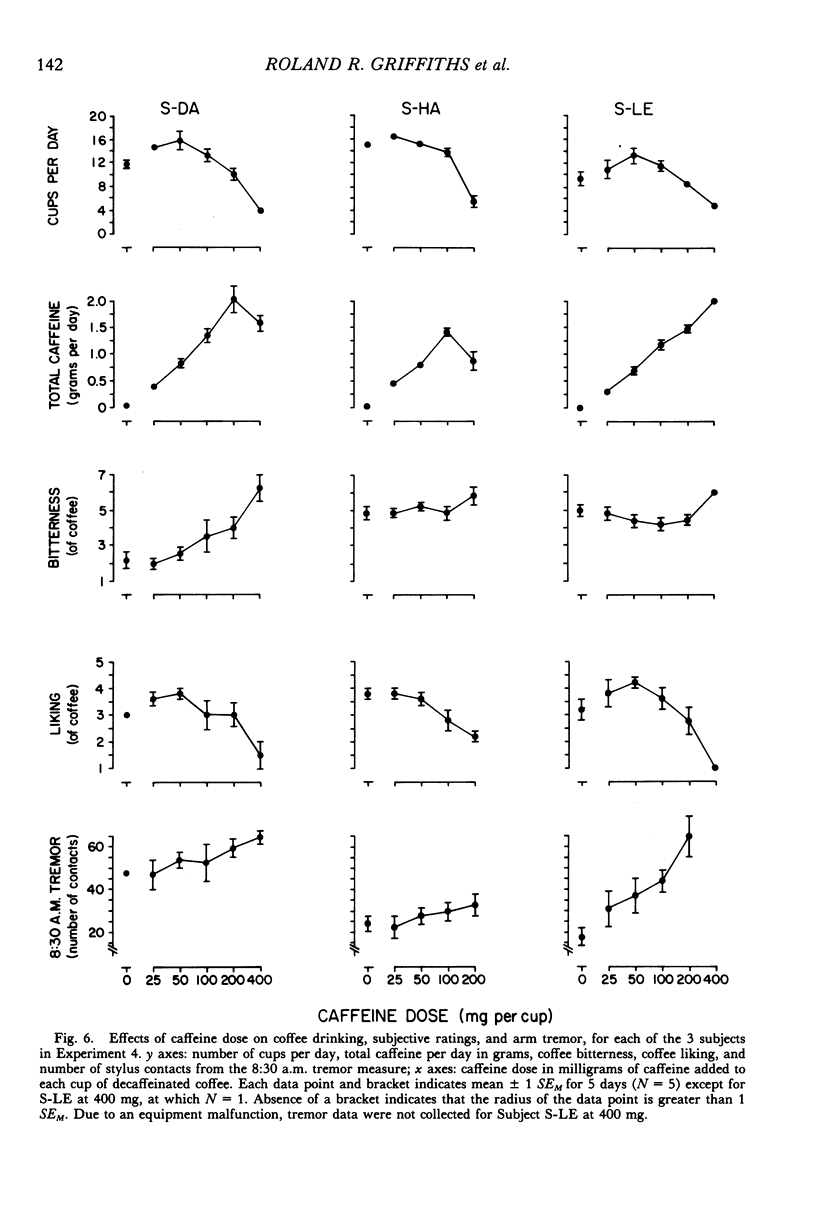
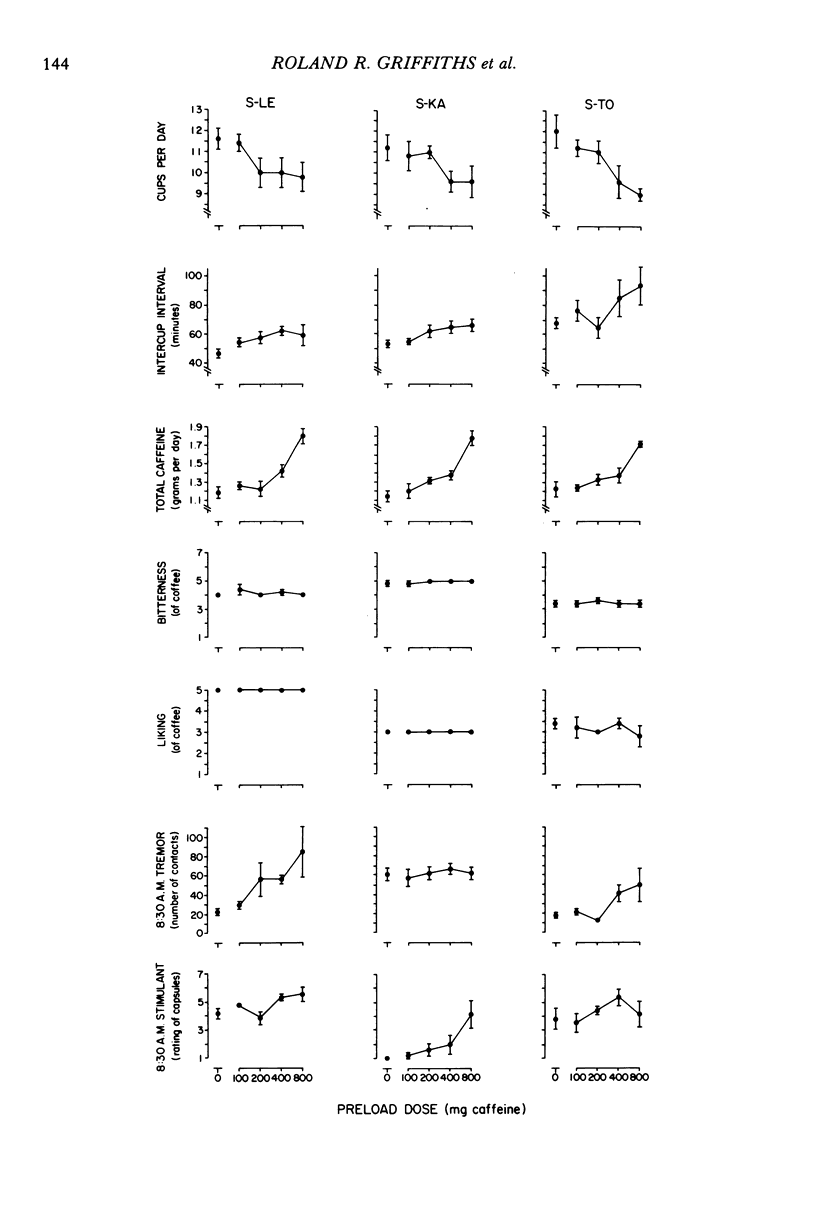
In a residential research ward coffee drinking was studied in 9 volunteer human subjects with histories of heavy coffee drinking. A series of five experiments was undertaken to characterize adlibitum coffee consumption and to investigate the effects of manipulating coffee concentration, caffeine dose per cup, and caffeine preloads prior to coffee drinking. Manipulations were double-blind and scheduled in randomized sequences across days. When cups of coffee were freely available, coffee drinking tended to be rather regularly spaced during the day with intercup intervals becoming progressively longer throughout the day; experimental manipulations showed that this lengthening of intercup intervals was not due to accumulating caffeine levels. Number of cups of coffee consumed was an inverted U-shaped function of both coffee concentration and caffeine dose per cup; however, coffee-concentration and dose-per-cup manipulations did not produce similar effects on other measures of coffee drinking (intercup interval, time to drink a cup, within-day distribution of cups). Caffeine preload produced dose-related decreases in number of cups consumed. As a whole, these experiments provide some limited evidence for both the suppressive and the reinforcing effects of caffeine on coffee consumption. Examination of total daily coffee and caffeine intake across experiments, however, provides no evidence for precise regulation (i.e., titration) of coffee or caffeine intake.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bigelow G., Griffiths R., Liebson I. Experimental models for the modification of human drug self-administration: Methodological developments in the study of ethanol self-administration by alcoholics. Fed Proc. 1975 Aug;34(9):1785–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boublik J. H., Quinn M. J., Clements J. A., Herington A. C., Wynne K. N., Funder J. W. Coffee contains potent opiate receptor binding activity. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):246–248. doi: 10.1038/301246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunker M. L., McWilliams M. Caffeine content of common beverages. J Am Diet Assoc. 1979 Jan;74(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chait L. D., Griffiths R. R. Effects of caffeine on cigarette smoking and subjective response. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Nov;34(5):612–622. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Booth G. H., Jr Gastric acid secretion and lower-esophageal-sphincter pressure in response to coffee and caffeine. N Engl J Med. 1975 Oct 30;293(18):897–899. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197510302931803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dews P. B. Caffeine. Annu Rev Nutr. 1982;2:323–341. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.02.070182.001543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernster V. L. Epidemiologic studies of caffeine and human health. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1984;158:377–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxx R. M., Rubinoff A. Behavioral treatment of caffeinism: reducing excessive coffee drinking. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Fall;12(3):335–344. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN A. WAKEFULNESS CAUSED BY CAFFEINE. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1964 May 25;248:269–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00348597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. M., Marshman J. A., Schwieder M., Berg R. Caffeine content of beverages as consumed. Can Med Assoc J. 1976 Feb 7;114(3):205–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. M. Caffeine--its identity, dietary sources, intake and biological effects. Nutr Rev. 1978 Apr;36(4):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.1978.tb03717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Bigelow G. E., Liebson I. Human sedative self-administration: effects of interingestion interval and dose. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Bigelow G. E., Liebson I., Kaliszak J. E. Drug preference in humans: double-blind choice comparison of pentobarbital, diazepam and placebo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Dec;215(3):649–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. R., Henningfield J. E., Bigelow G. E. Human cigarette smoking: manipulation of number of puffs per bout, interbout interval and nicotine dose. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Feb;220(2):256–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. J., Bartoshuk L. M., Cain W. S., Stevens J. C. PTC taste blindness and the taste of caffeine. Nature. 1975 Feb 6;253(5491):442–443. doi: 10.1038/253442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski L. T. Effect of caffeine on coffee drinking. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):354–355. doi: 10.1038/264354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster C. R., Fischman M. W., Johanson C. E. Internal stimulus control and subjective effects of drugs. NIDA Res Monogr. 1981 Jul;37:116–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS B., LATIES V. G. Enhancement of human performance by caffeine and the amphetamines. Pharmacol Rev. 1962 Mar;14:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


