Abstract
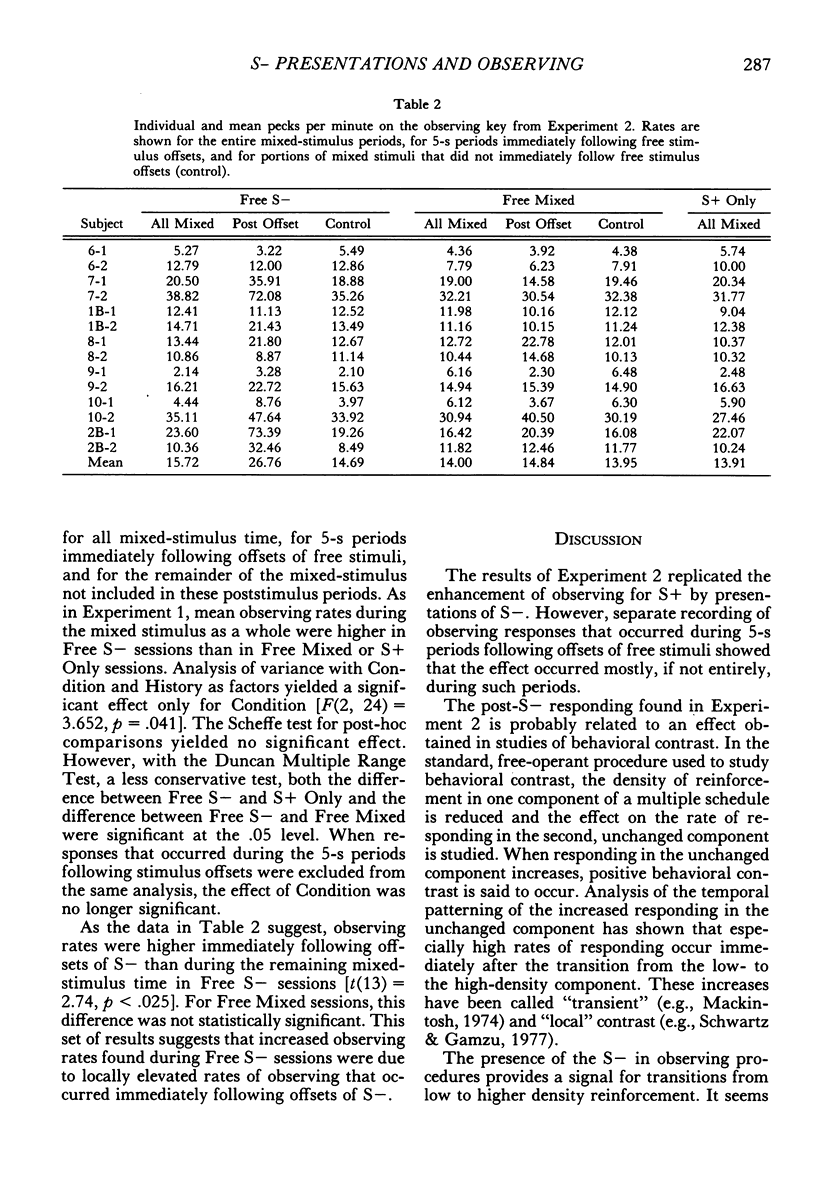
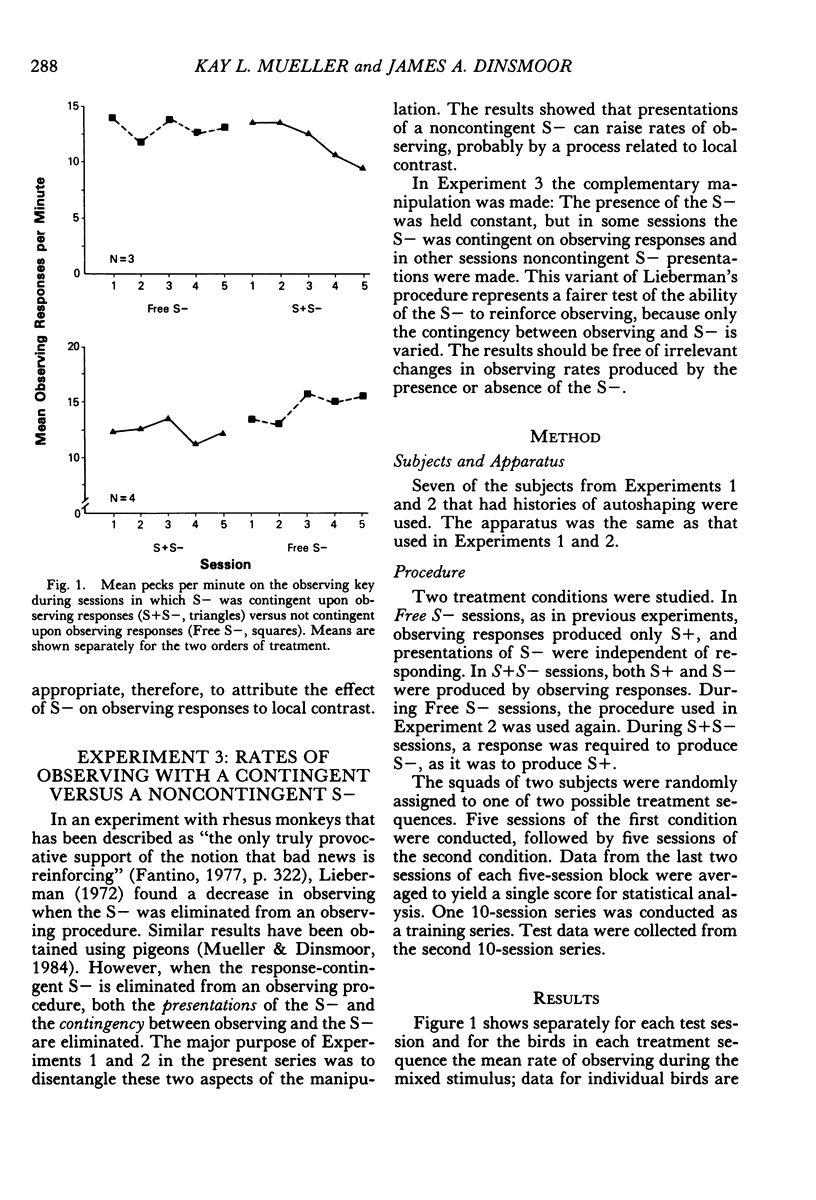
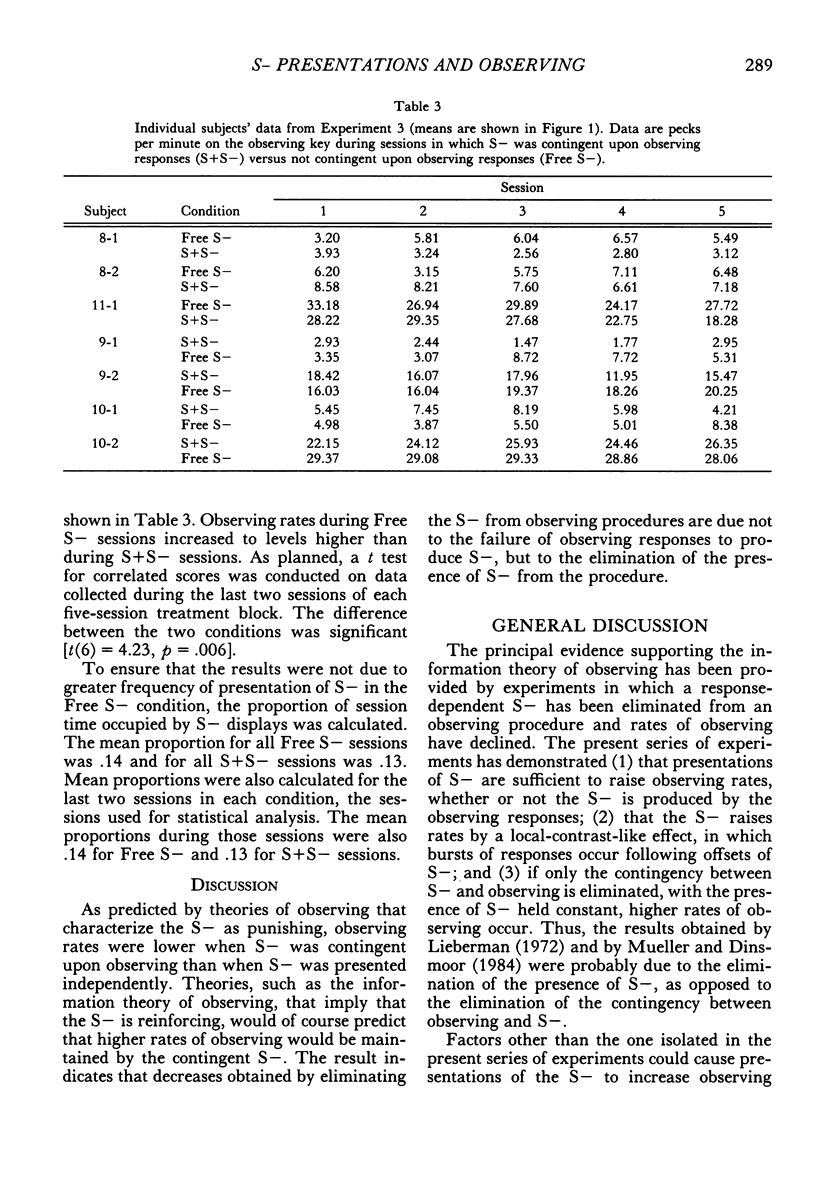
Theories of observing differ in predicting whether or not a signal for absence of reinforcement (S−) is capable of reinforcing observing responses. Experiments in which S− was first removed from and then restored to the procedure have yielded mixed results. The present experiments suggest that failure to control for the direct effect of presenting S− may have been responsible. Pigeons and operant procedures were used. Experiment 1 showed that presentations of S−, even when not contingent on observing, can raise the rate of an observing response that was reinforced only by presentations of a signal (S+) that accompanied a schedule of food delivery. Experiment 2 showed that this effect resulted from bursts of responding that followed offsets of S−. Experiment 3 showed that, when the presence of S− was held constant, lower rates occurred when S− was dependent on, rather than independent of, observing. These results support theories that characterize S− as incapable of reinforcing observing responses.
Keywords: observing, negative discriminative stimulus (S−), S− presentations, contingency of S−, information hypothesis, conditioned reinforcement, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auge R. J. Context, observing behavior, and conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Nov;22(3):525–533. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auge R. J. Effects of stimulus duration on observing behavior maintained by differential reinforcement magnitude. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Nov;20(3):429–438. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONEAU C. A., AXELROD S. Work decrement and reminiscence in pigeon operant responding. J Exp Psychol. 1962 Oct;64:352–354. doi: 10.1037/h0047944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badia P., Ryan K., Harsh J. Choosing schedules of signaled appetitive events over schedules of unsignaled ones. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Mar;35(2):187–195. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.35-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Browne M. P., Lawrence C. E. A test of the negative discriminative stimulus as a reinforcer of observing. J Exp Anal Behav. 1972 Jul;18(1):79–85. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1972.18-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Mueller K. L., Martin L. T., Bowe C. A. The acquisition of observing. J Exp Anal Behav. 1982 Nov;38(3):249–263. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1982.38-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmoor J. A., Mulvaney D. E., Jwaideh A. R. Conditioned reinforcement as a function of duration of stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1981 Jul;36(1):41–49. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1981.36-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLEHER R. T., GOLLUB L. R. A review of positive conditioned reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:543–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-s543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan J. C. Average uncertainty as a determinant of observing behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Sep;22(2):401–408. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.22-401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller K. L., Dinsmoor J. A. Testing the reinforcing properties of S-: a replication of Lieberman's procedure. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Jan;41(1):17–25. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvaney D. E., Dinsmoor J. A., Jwaideh A. R., Hughes L. H. Punishment of observing by the negative discriminative stimulus. J Exp Anal Behav. 1974 Jan;21(1):37–44. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1974.21-37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevin J. A., Shettleworth S. J. An analysis of contrast effects in multiple schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jul;9(4):305–315. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS C. C., Jr The stimulus conditions which follow learned responses. Psychol Rev. 1955 Sep;62(5):341–348. doi: 10.1037/h0040520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PROKASY W. F., Jr The acquisition of observing responses in the absence of differential external reinforcement. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1956 Apr;49(2):131–134. doi: 10.1037/h0046740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning, the peak shift, and behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):727–741. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYCKOFF L. B., Jr The role of observing responses in discrimination learning. Psychol Rev. 1952 Nov;59(6):431–442. doi: 10.1037/h0053932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. G. Factors influencing inhibitory stimulus control: differential reinforcement of other behavior during discrimination training. J Exp Anal Behav. 1970 Jul;14(1):87–91. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1970.14-87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisman R. G. Some determinants of inhibitory stimulus control. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 May;12(3):443–450. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. A. Contrast, component duration, and the following schedule of reinforcement. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process. 1979 Oct;5(4):379–396. doi: 10.1037//0097-7403.5.4.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


