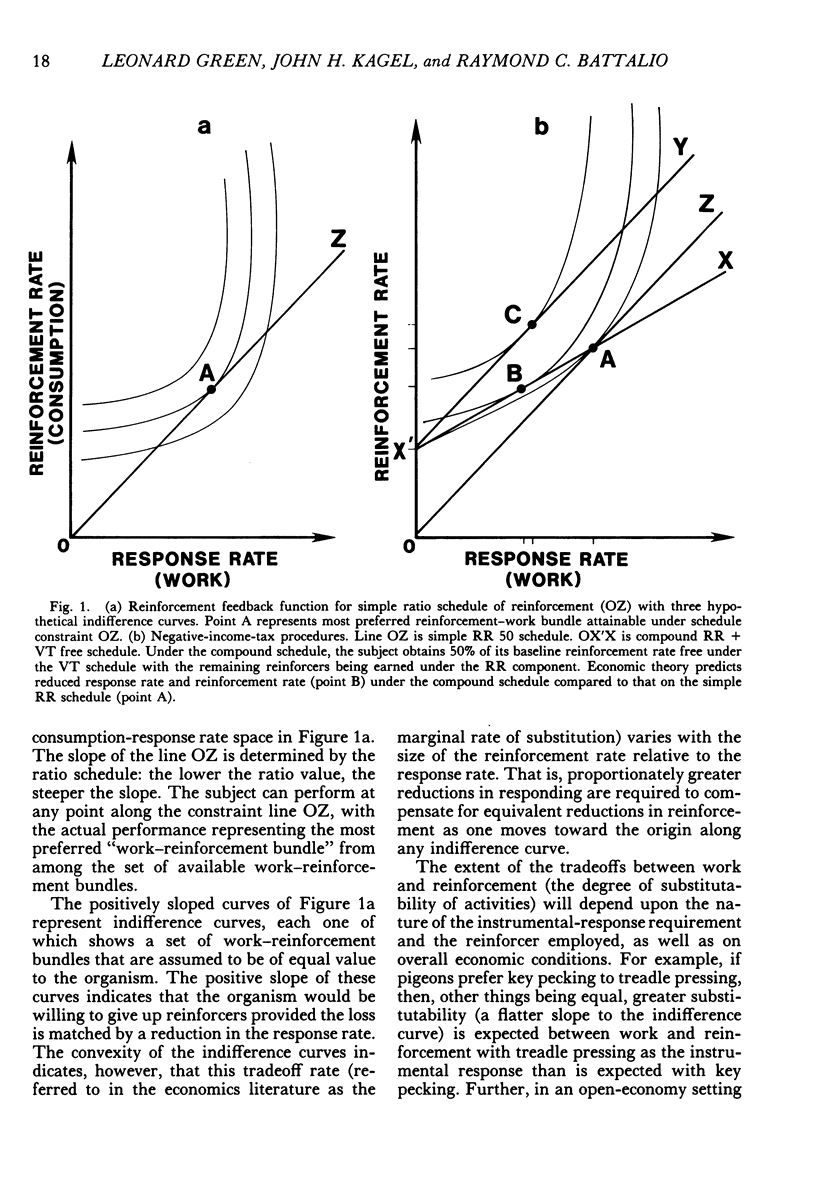
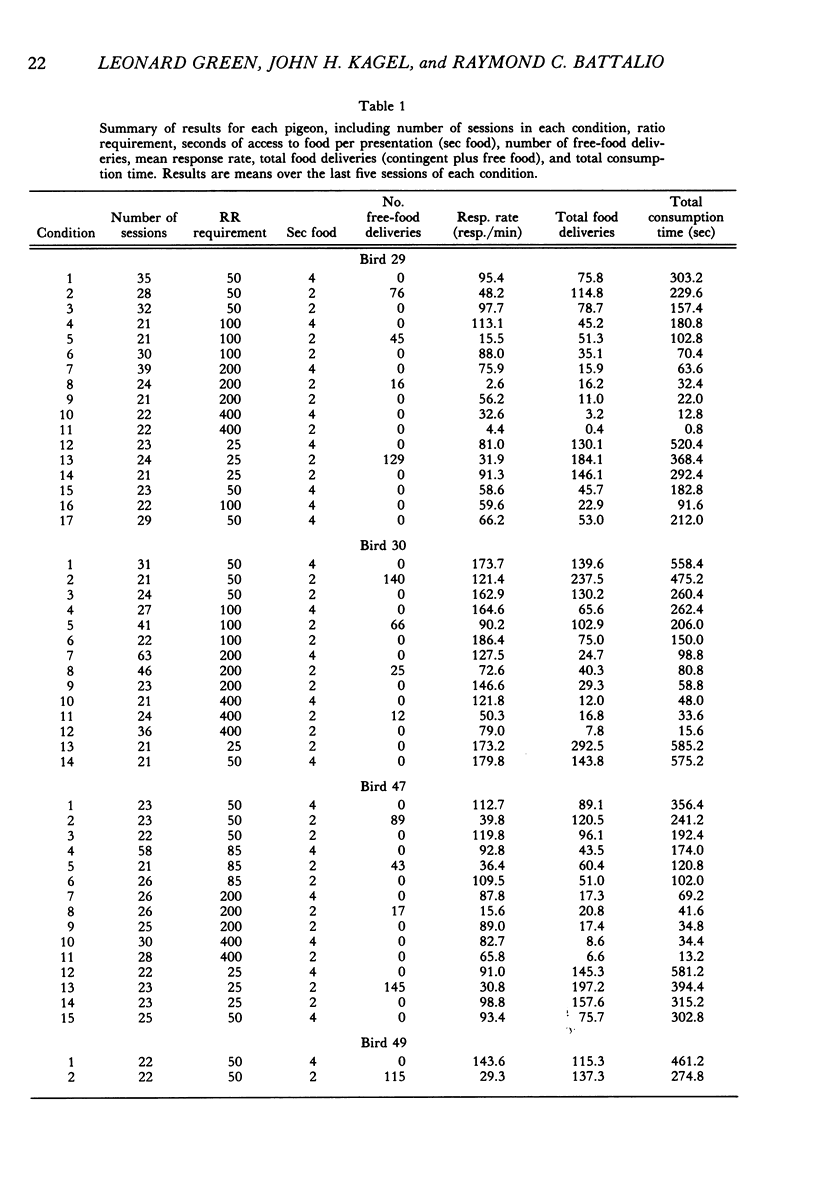
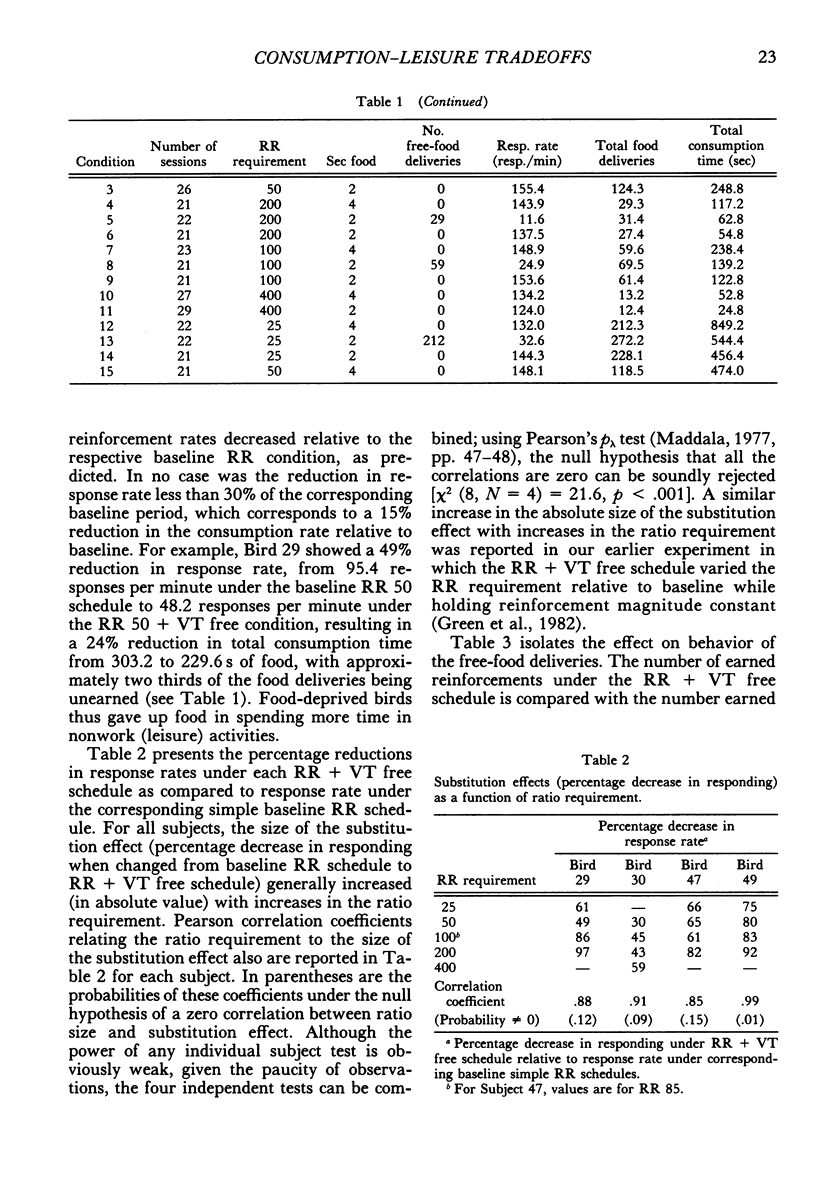
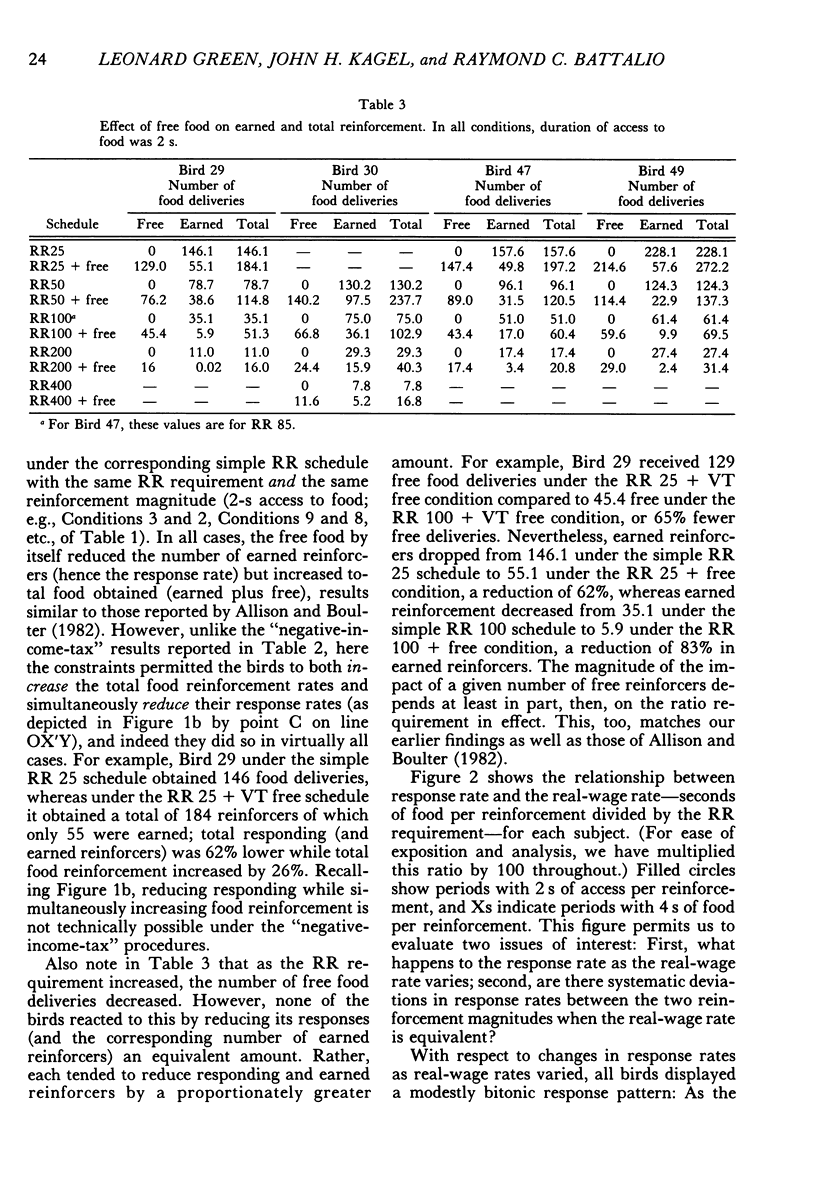
Abstract
Pigeons' rates of responding and food reinforcement under simple random-ratio schedules were compared with those obtained under comparable ratio schedules in which free food deliveries were added, but the duration of each food delivery was halved. These ratio-with-free-food schedules were constructed so that, were the pigeon to maintain the same rate of responding as it had under the simple ratio schedule, total food obtained (earned plus free) would remain unchanged. However, any reduction in responding would reduce total food consumption below that under the simple ratio schedule. These “compensated wage decreases” led to decreases in responding and decreases in food consumption, as predicted by an economic model of labor supply. Moreover, the reductions in responding increased as the ratio value increased (i.e., as wage rates decreased). Pigeons, therefore, substituted leisure for consumption. The relationship between these procedures and negative-income-tax programs is noted.
Keywords: economics, labor supply, substitution effects, ratio schedules, amount of reinforcement, key peck, pigeons
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess I. S., Wearden J. H. Superimposition of response-independent reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1986 Jan;45(1):75–82. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1986.45-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLESHLER M., HOFFMAN H. S. A progression for generating variable-interval schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:529–530. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond L. J. The effect of contingency upon the appetitive conditioning of free-operant behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Nov;34(3):297–304. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hursh S. R. Economic concepts for the analysis of behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1980 Sep;34(2):219–238. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1980.34-219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lattal K. A. Response-reinforcer dependence and independence in multiple and mixed schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1973 Sep;20(2):265–271. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1973.20-265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. A temporal limit on the effect of future food on current performance in an analogue of foraging and welfare. J Exp Anal Behav. 1984 Mar;41(2):117–124. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1984.41-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


