Abstract
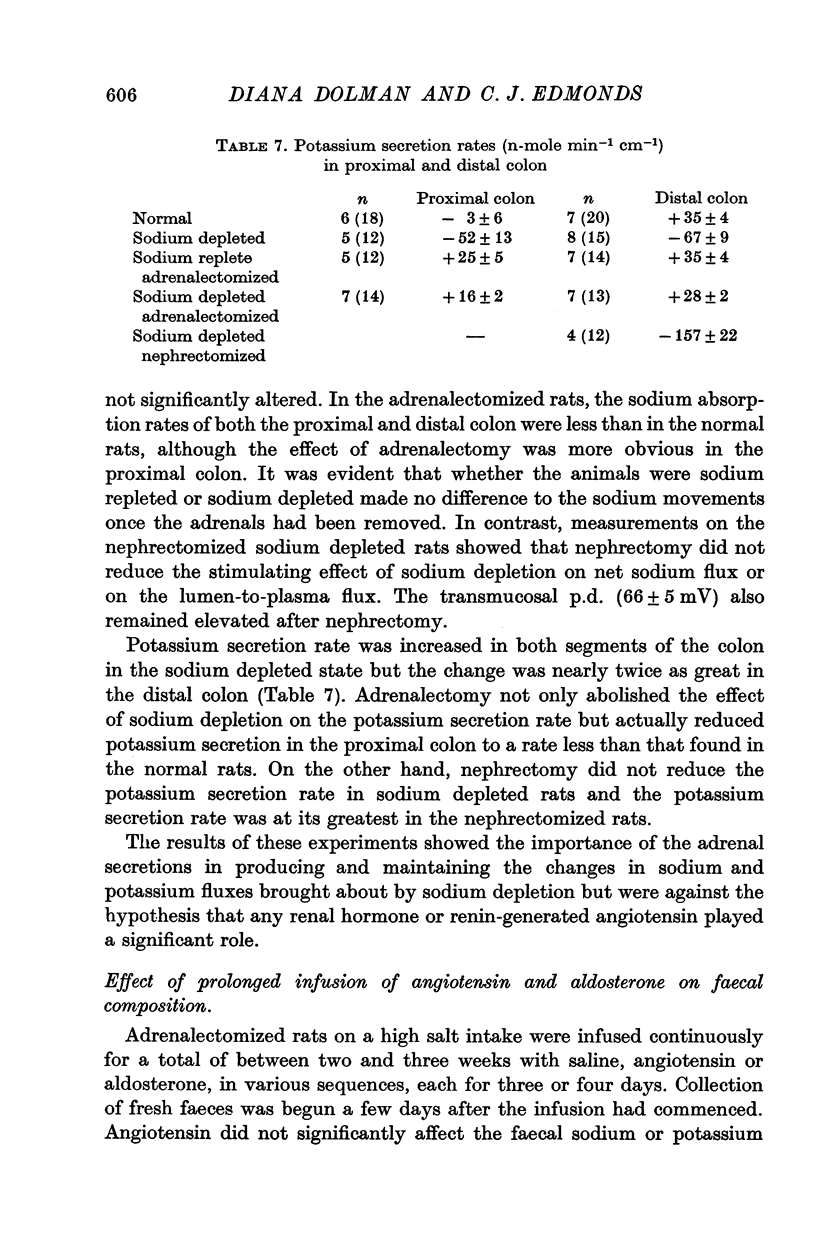
1. The roles of aldosterone and angiotensin in the direct control of epithelial sodium transport in vivo have been investigated by measurement of electrical p.d. changes and of the fluxes of sodium, potassium and chloride in rat colon, an organ actively involved in electrolyte homoeostasis. Exogenous angiotensin and aldosterone were given by both short- and long-term infusions and endogenous secretion of the hormones was varied by dietary sodium variation and by nephrectomy and/or adrenalectomy. 2. In vitro angiotensin has been shown to influence colonic salt and water absorption but in the present in vivo experiments administered angiotensin had no significant action on p.d. or on the ionic fluxes of the proximal or distal colon. The increase in p.d. produced by infusing aldosterone was unaffected by giving angiotensin concurrently. The effect of sodium depletion in stimulating sodium absorption and potassium secretion was completely abolished by adrenalectomy but was unaffected by nephrectomy. 3. During prolonged infusion of angiotensin into adrenalectomized rats, a small fall in faecal fluid and sodium content was observed, but this change would have little significance in sodium homoeostasis. 4. Aldosterone and sodium depletion stimulated sodium absorption in both proximal and distal colon but significant increase in potassium secretion was demonstrable only in the distal colon. Bicarbonate secretion (by calculation) was unaffected. In the proximal colon, the increased sodium absorption appeared to be accompanied by increased chloride absorption while in the distal colon it was principally the sodium-potassium exchange that was increased. 5. Adrenalectomy reduced potassium secretion in both proximal and distal colon but sodium absorption was only significantly reduced in the proximal colon. 6. It was concluded that there is no evidence that angiotensin in the living animal has a role as an important salt retaining hormone by direct epithelial action. Aldosterone has a considerable effect which is independent of the presence of angiotensin, and which differs in proximal and distal colon in regard to the relative effects on chloride absorption and potassium secretion.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barraclough M. A., Jones N. F., Marsden C. D. Effect of angiotensin on renal function in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1967 May;212(5):1153–1157. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.5.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonjour J. P., Malvin R. L. Renal extraction of PAH, GFR, and UNaV in the rat during infusion of angiotensin. Am J Physiol. 1969 Mar;216(3):554–558. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.3.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd G. W., Peart W. S. The relationship between angiotensin and aldosterone. Adv Metab Disord. 1971;5:77–117. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027305-8.50023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Control of fluid absorption in the renal proximal tubule. J Clin Invest. 1968 Sep;47(9):2016–2024. doi: 10.1172/JCI105888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron R. C., Leme C. E., Wilson D. R., Ing T. S., Wrong O. M. The effect of adrenal steroids on stool composition, as revealed by in vivo dialysis of faeces. Clin Sci. 1969 Aug;37(1):151–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker A. D., Munday K. A. The effect of the renin-angiotensin system on mucosal water and sodium transfer in everted sacs of rat jejunum. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):323–333. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. T., Munday K. A., Parsons B. J. Studies on the mechanism of action of angiotensin on fluid transport by the mucosa of rat distal colon. J Endocrinol. 1972 Sep;54(3):483–492. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0540483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies N. T., Munday K. A., Parsons B. J. The effect of angiotensin on rat intestinal fluid transfer. J Endocrinol. 1970 Sep;48(1):39–46. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0480039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Absorption of sodium and water by human rectum measured by a dialysis method. Gut. 1971 May;12(5):356–362. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.5.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Marriott J. C. The effect of aldosterone and adrenalectomy on the electrical potential difference of rat colon and on the transport of sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate. J Endocrinol. 1967 Dec;39(4):517–531. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. The gradient of electrical potential difference and of sodium and potassium of the gut contents along the caecum and colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):571–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J., Thompson B. D. Further development of a method for prolonged infusion of unrestrained rats. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):10P–12P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Transport of sodium and secretion of potassium and bicarbonate by the colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):589–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEALY J. K., BARCENA C., O'CONNELL J. M., SCHREINER G. E. RENAL AND PRESSOR ACTION OF ANGIOTENSIN IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jun;208:1093–1099. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Healy J. K., Douglas J. B., Arnold J. E. The effect of angiotensin on isolated rabbit renal tubules. Clin Sci. 1969 Dec;37(3):583–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornych A., Meyer P., Milliez P. Angiotensin, vasopressin, and cyclic AMP: effects on sodium and water fluxes in rat colon. Am J Physiol. 1973 May;224(5):1223–1229. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.5.1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horster M., Nagel W., Schnermann J., Thurau K. Zur Frage einer direkten Angiotensinwirkung auf die Natriumresorption im proximalen Tubulus und in der Henleschen Schleife der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;292(2):118–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGFORD H. G. TUBULAR ACTION OF ANGIOTENSIN. Can Med Assoc J. 1964 Jan 25;90:332–333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis W. J., Doyle A. E. The effects of varying doses of angiotensin on renal function and blood pressure in man and dogs. Clin Sci. 1965 Dec;29(3):489–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumbers E. R. Proceedings: Renin and angiotensin II of extrarenal origin in the plasma of female rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Oct;234(2):94P–95P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNE M. D., MUEHRCKE R. C., AIRD I. Primary aldosteronism. Q J Med. 1957 Jul;26(103):317–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee R. D., Locke W. Effect of angiotensin amide on sodium isotope flux and short-circuit current of isolated frog skin. Endocrinology. 1967 Dec;81(6):1301–1305. doi: 10.1210/endo-81-6-1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munday K. A., Parsons B. J., Poat J. A. The effect of angiotensin on cation transport by rat kidney cortex slices. J Physiol. 1971 May;215(1):269–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEART W. S. THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Jun;17:143–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards P. Clinical investigation of the effects of adrenal corticosteroid excess on the colon. Lancet. 1969 Mar 1;1(7592):437–442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91480-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. D., Edmonds C. J. Aldosterone, sodium depletion and hypothyroidism on the ATPase activity of rat colonic epithelium. J Endocrinol. 1974 Sep;62(3):489–496. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0620489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson B. D., Edmonds C. J. Comparison of effects of prolonged aldosterone administration on rat colon and renal electrolyte excretion. J Endocrinol. 1971 May;50(1):163–169. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0500163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


