Abstract
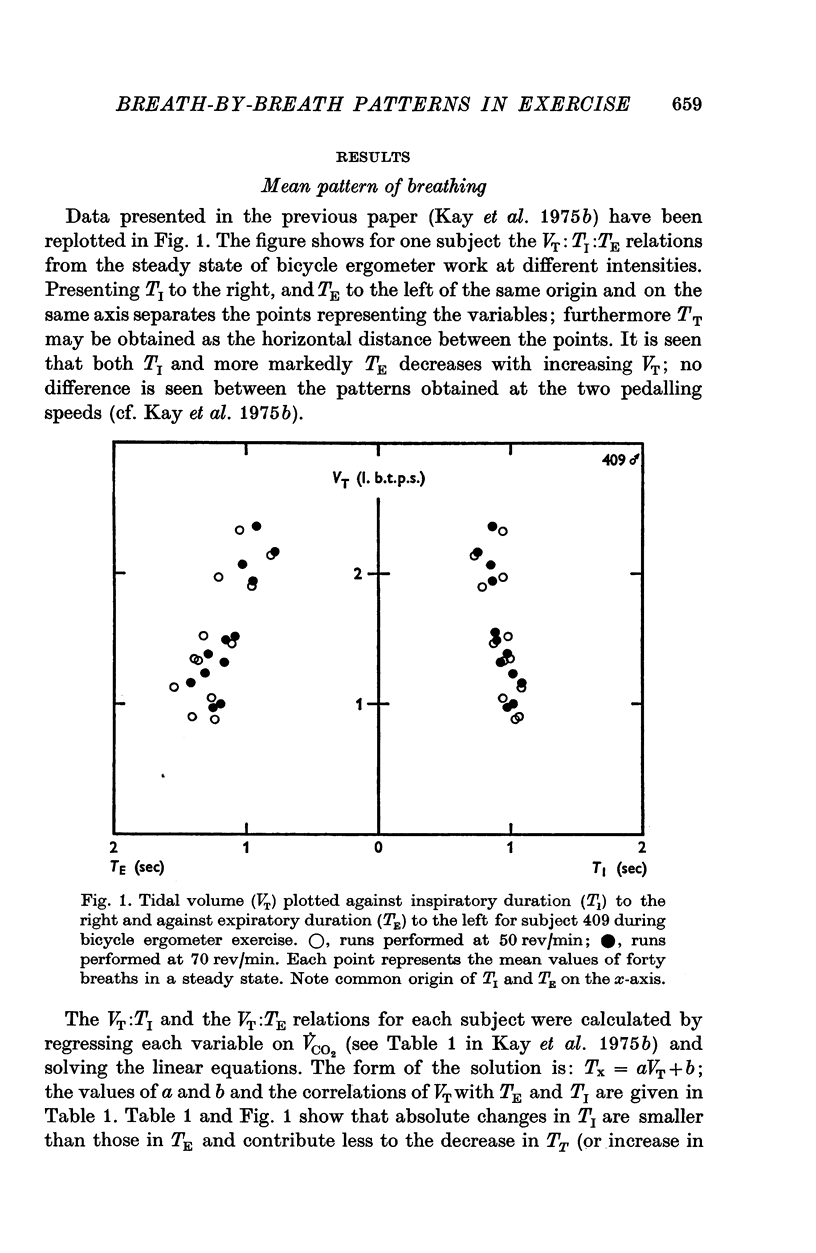
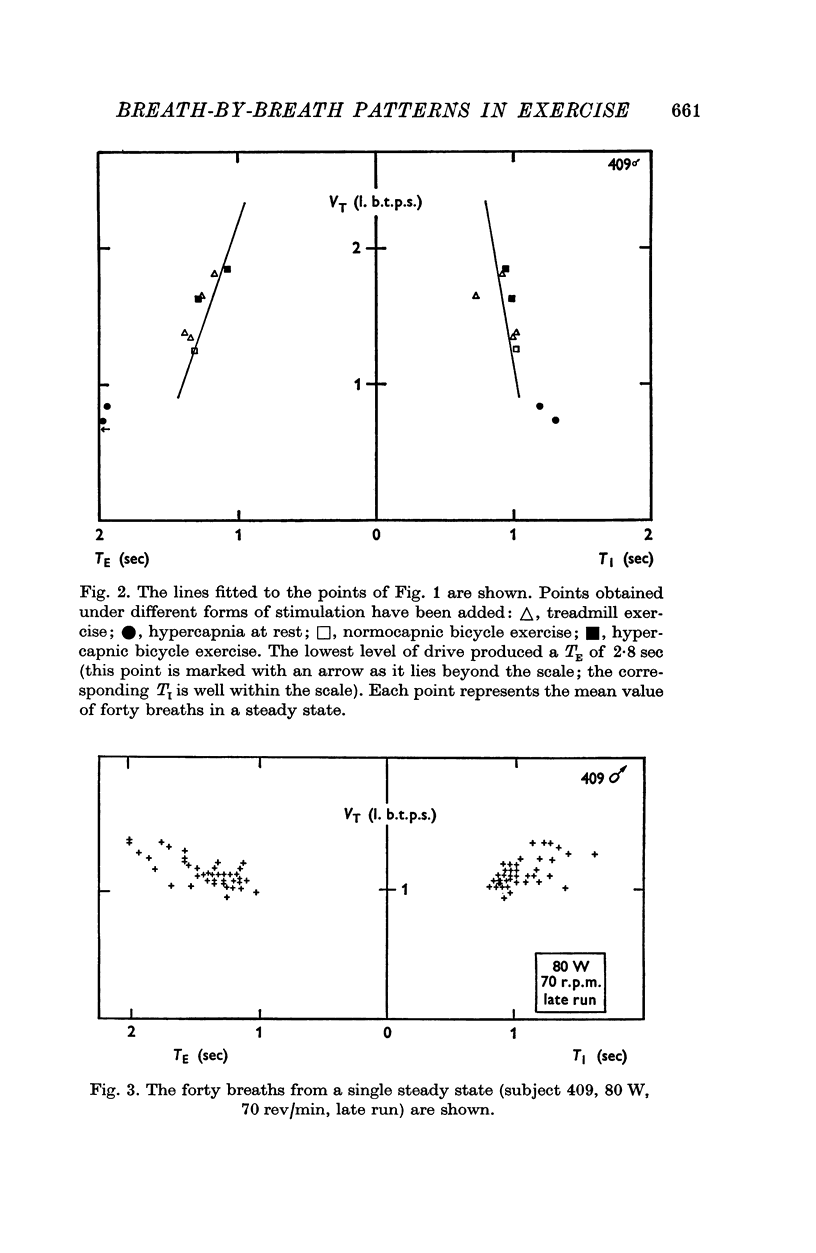
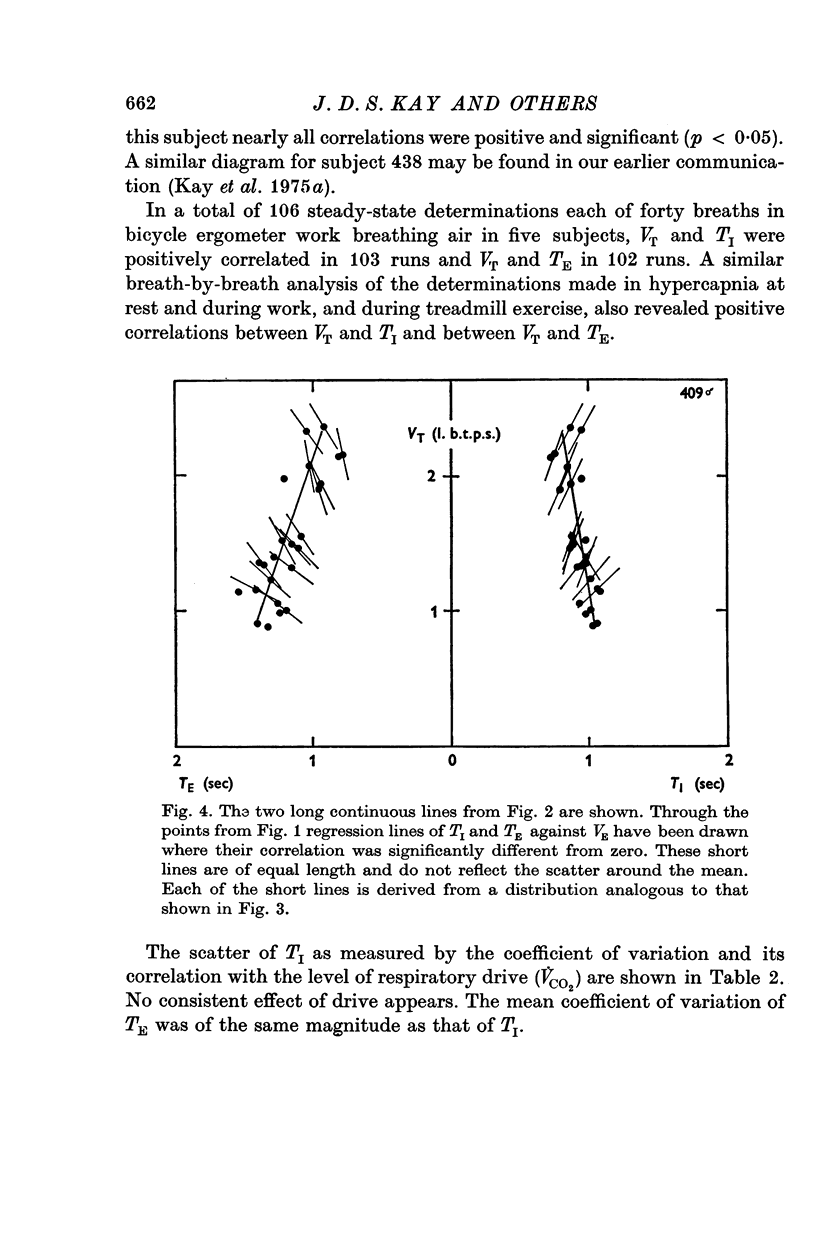
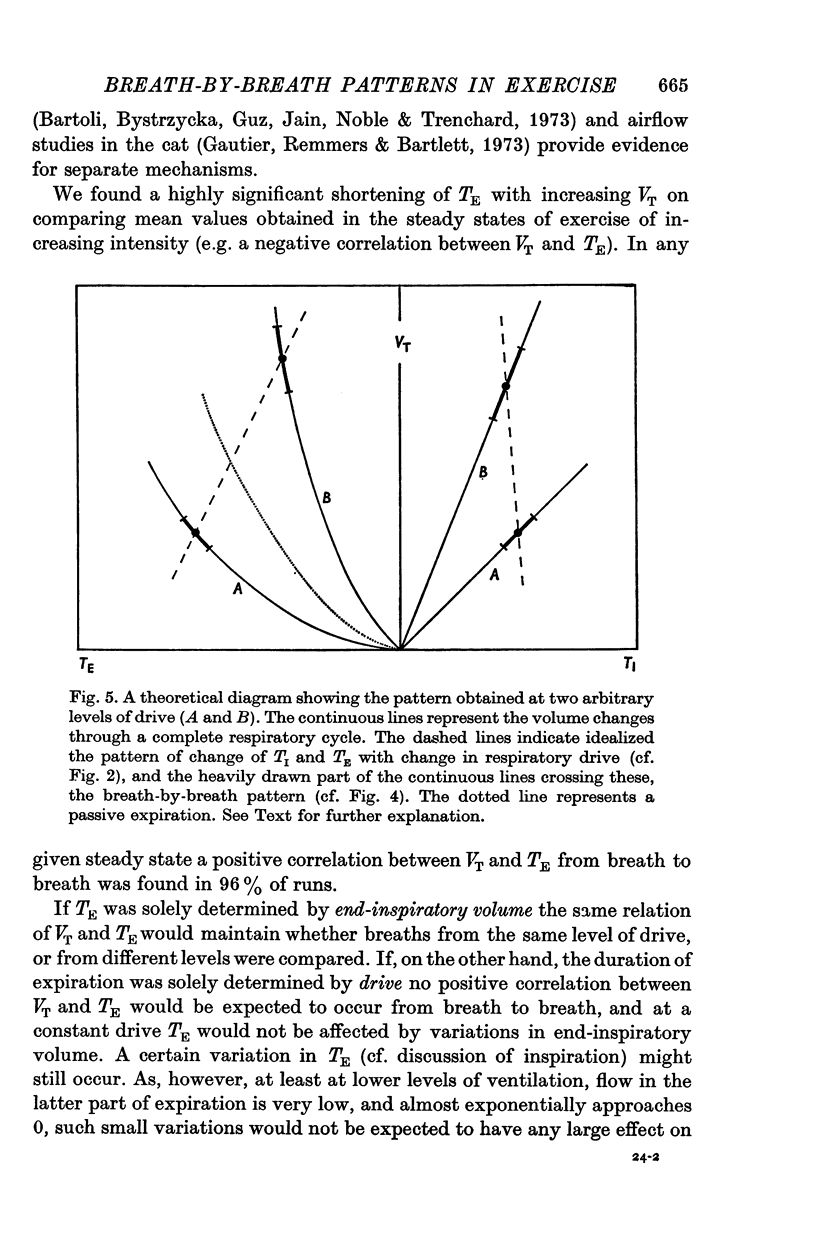
1. The breathing pattern, that is the relation between tidal volume (VT) and the inspiratory (TI) and expiratory (TE) durations, has been studied for individual breaths (forty in each steady state). 2. Five healthy subjects were studied in steady-state exercise on a bicycle ergometer breathing air; three of them were also studied in hypercapnia, at rest and during exercise, and two of them also during exercise on a treadmill. 3. Tidal volume and respiratory frequency both increased with work load. The increase in frequency was largely due to a progressive decrease in TE; TI also decreased. 4. At any constant level of respiratory drive (constant work load or chemical load) VT was positively correlated with both TI and TE in more than 95% of cases. 5. A simple model of the respiratory cycle which fits both the observed mean and breath-by-breath patterns and which involves no new assumptions is presented.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRODY A. W. Mechanical compliance and resistance of the lung-thorax calculated from the flow recorded during passive expiration. Am J Physiol. 1954 Aug;178(2):189–196. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett D., Jr, Remmers J. E., Gautier H. Laryngeal regulation of respiratory airflow. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):194–204. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartoli A., Bystrzycka E., Guz A., Jain S. K., Noble M. I., Trenchard D. Studies of the pulmonary vagal control of central respiratory rhythm in the absence of breathing movements. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):449–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G. W., von Euler C., Marttila I., Roos B. Steady state effects of CO-2 and temperature on the relationship between lung volume and inspiratory duration (Hering-Breuer threshold curve). Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Nov;92(3):351–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark F. J., von Euler C. On the regulation of depth and rate of breathing. J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(2):267–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejours P., Puccinelli R., Armand J., Dicharry M. Breath-to-breath variations of pulmonary gas exchange in resting man. Respir Physiol. 1966;1(3):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(66)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN J. H., HOWELL J. B. The correlation of intercostal muscle activity with respiratory air flow in concious human subjects. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:471–476. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier H., Remmers J. E., Bartlett D., Jr Control of the duration of expiration. Respir Physiol. 1973 Jul;18(2):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(73)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey E. N., Lloyd B. B., Cunningham D. J., Jukes M. G., Bolton D. P. Effects of various respiratory stimuli on the depth and frequency of breathing in man. Respir Physiol. 1966;1(2):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(66)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlastala M. P., Wranne B., Lenfant C. J. Cyclical variations in FRC and other respiratory variables in resting man. J Appl Physiol. 1973 May;34(5):670–676. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1973.34.5.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennett S., Russell T., Warnock K. A. Proceedings: The duration of inspiration during changing states of ventilation in man. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):54P–55P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. D., Petersen E. S., Vejby-Christensen H. Breathing in man during steady-state exercise on the bicycle at two pedalling frequencies, and during treadmill walking. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):645–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman G. R., Watson A. W. Effect of added dead-space on pulmonary ventilation during sub-maximal, steady-state exercise. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Oct;58(4):305–313. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1973.sp002224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox C. K. Characteristics of inflation and deflation reflexes during expiration of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Mar;36(2):284–295. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETIT J. M., MILIC-EMILI G., DELHEZ L. Role of the diaphragm in breathing in conscious normal man: an electromyographic study. J Appl Physiol. 1960 Nov;15:1101–1106. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1960.15.6.1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIBAN I. P. An analysis of some short-term patterns of breathing in man at rest. J Physiol. 1963 May;166:425–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Euler C., Wexler I., Herrero F. Control mechanisms determining rate and depth of respiratory movements. Respir Physiol. 1970 Jul;10(1):93–108. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(70)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



