Abstract
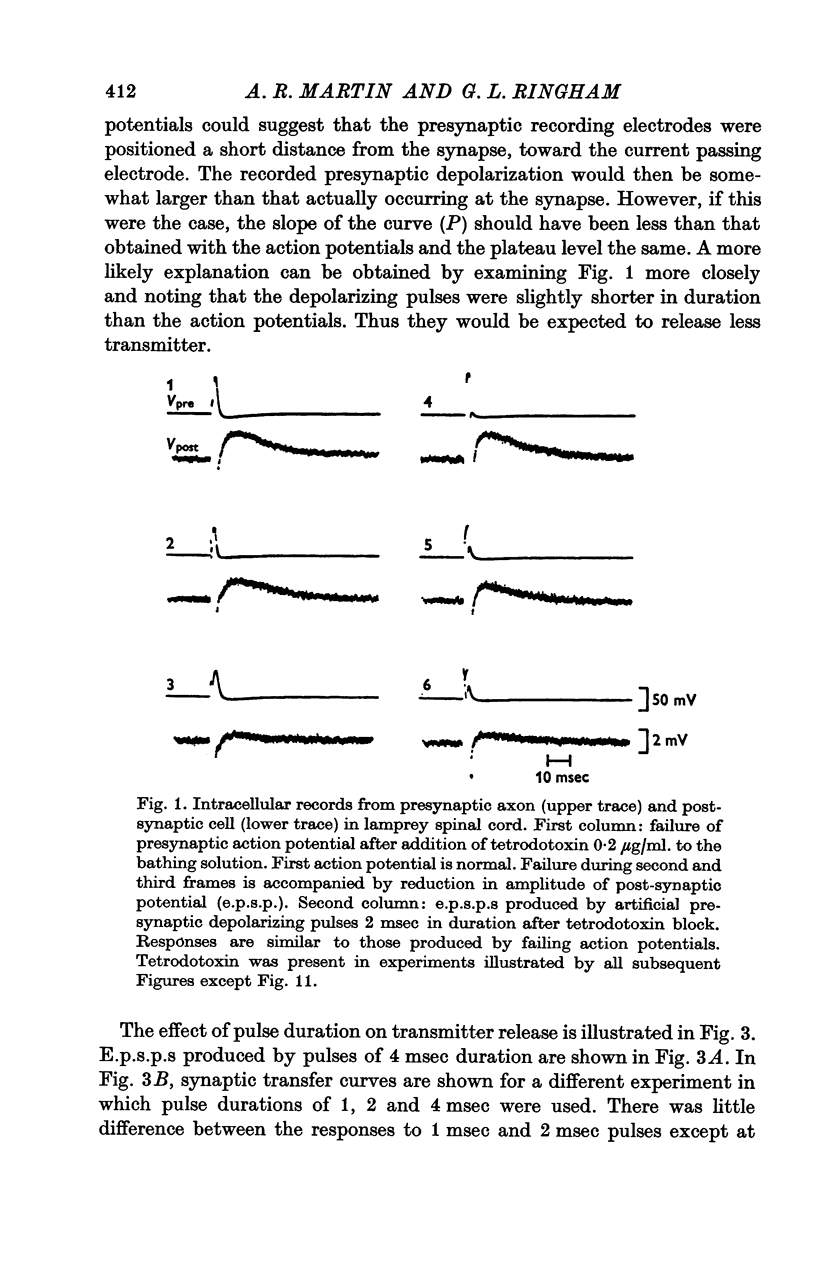
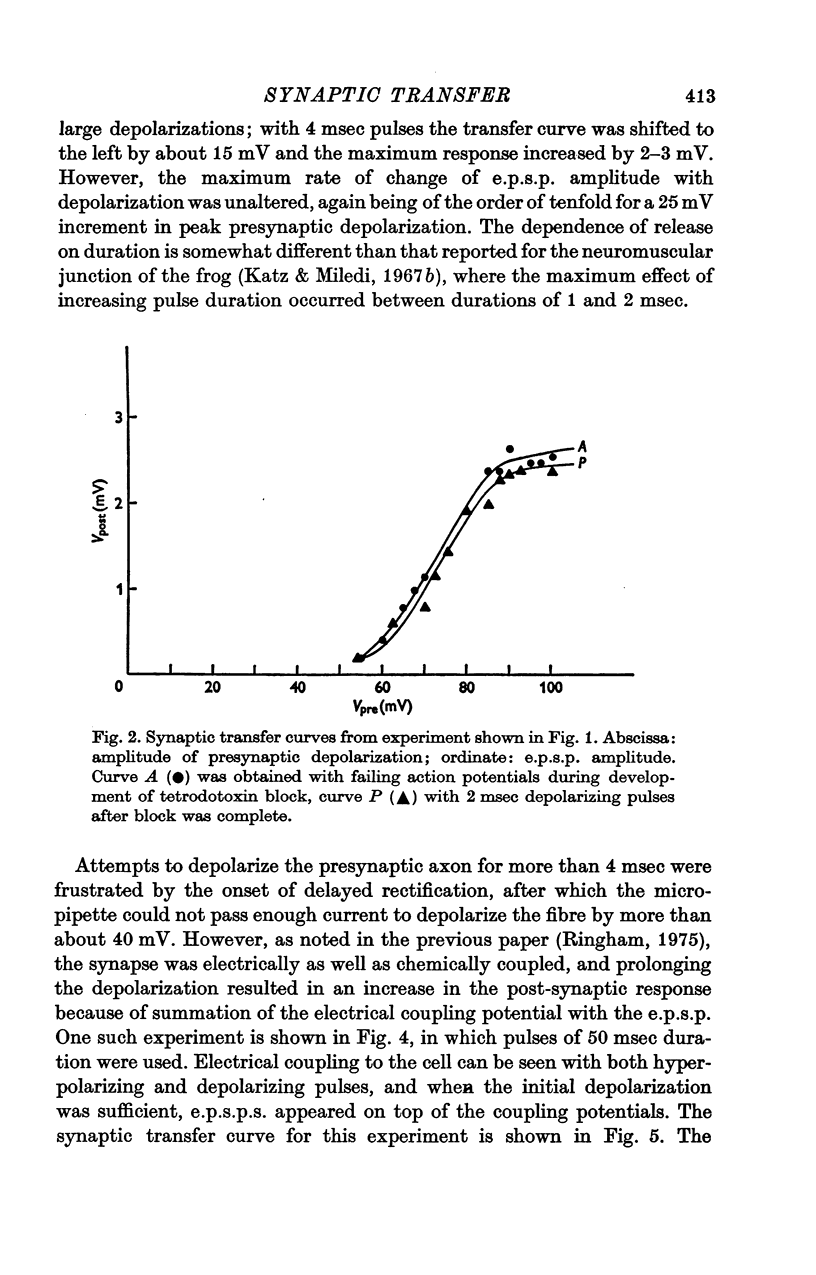
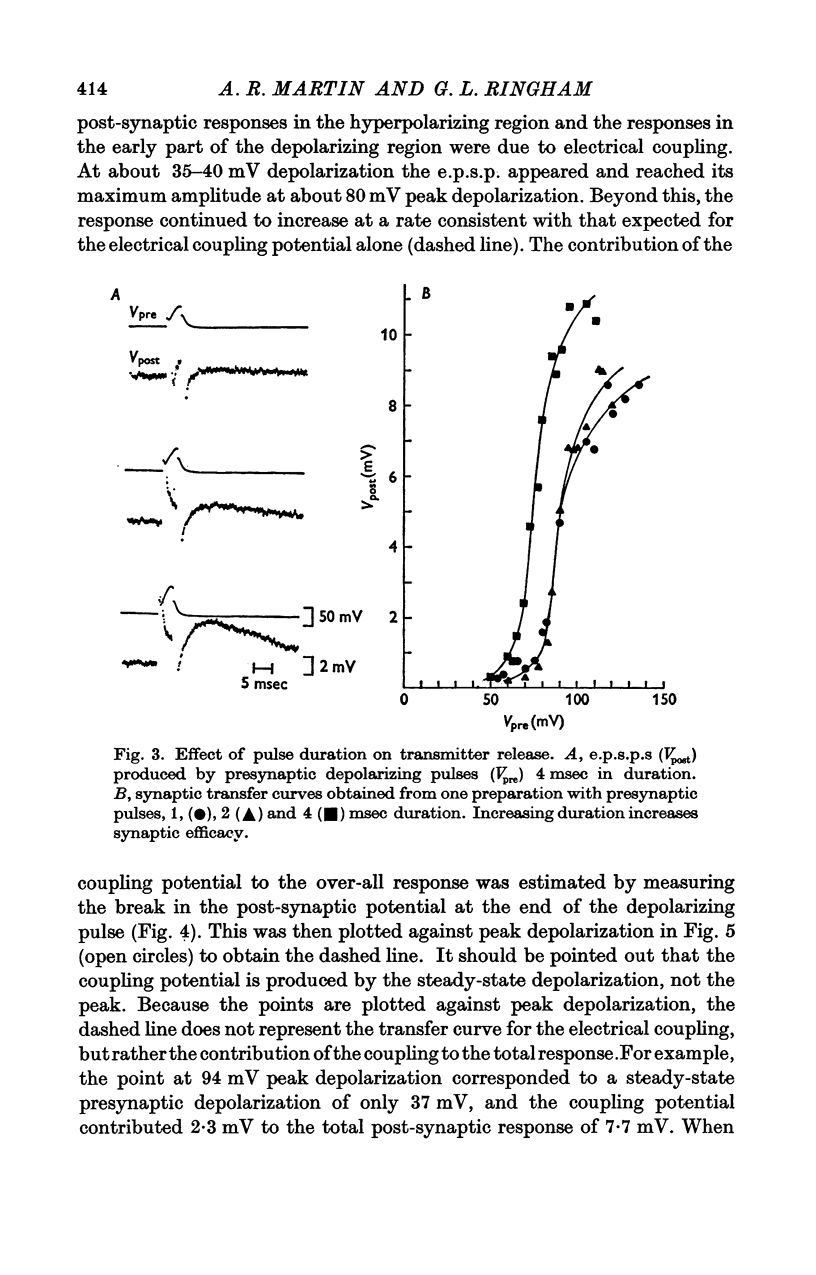
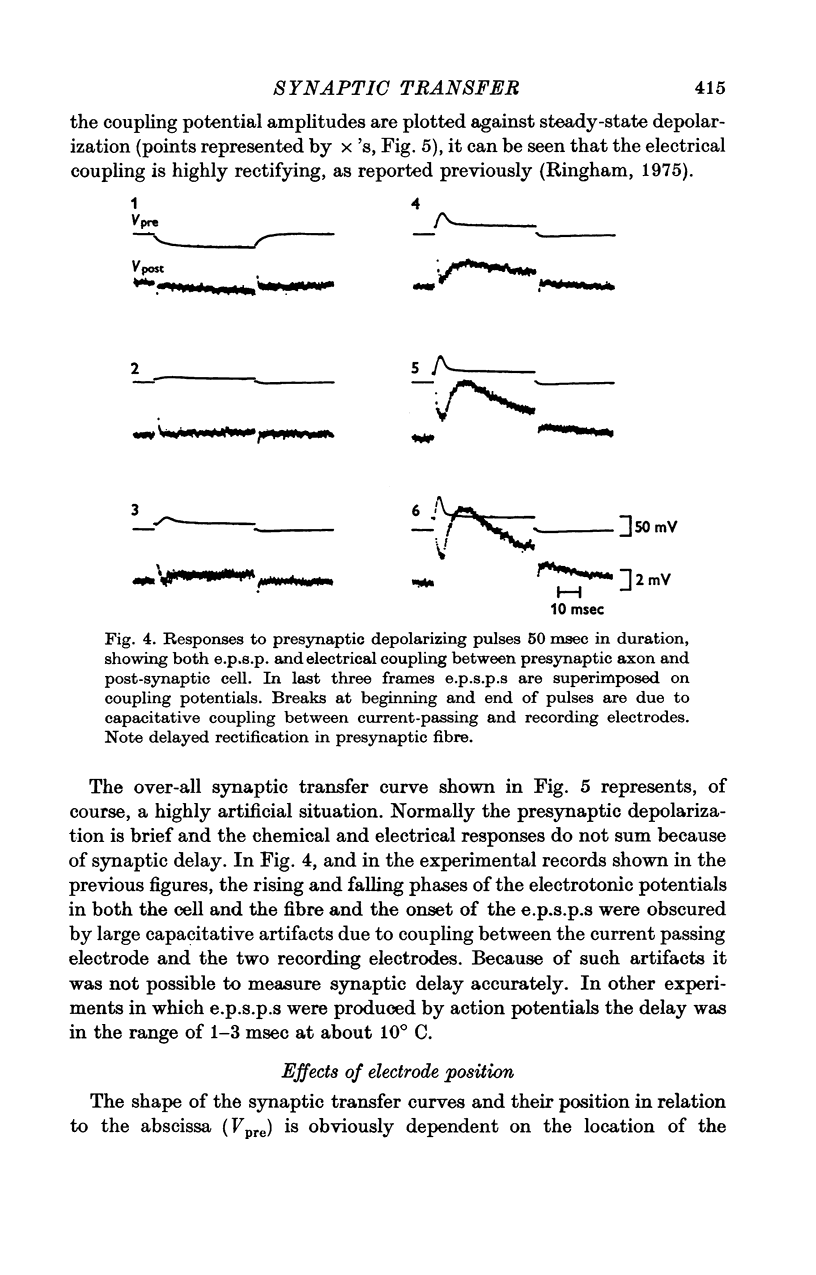
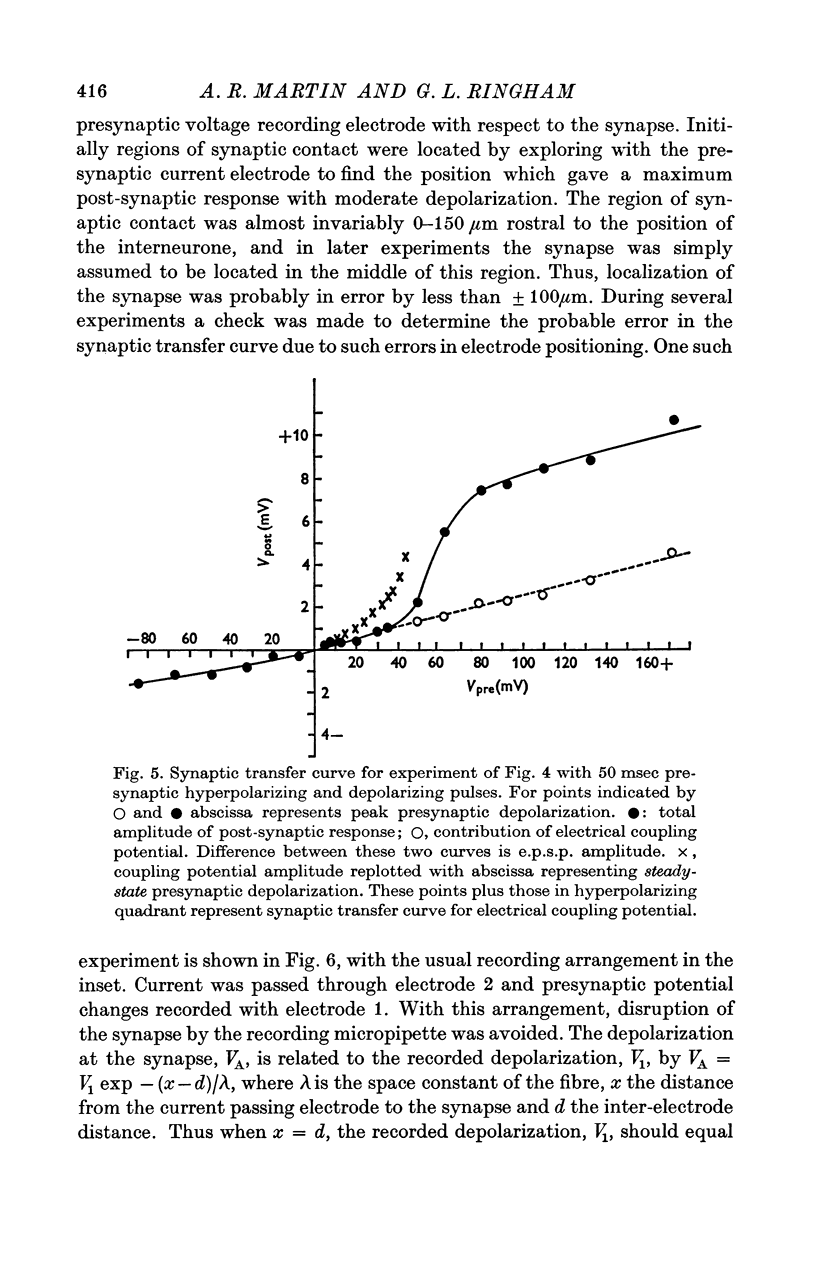
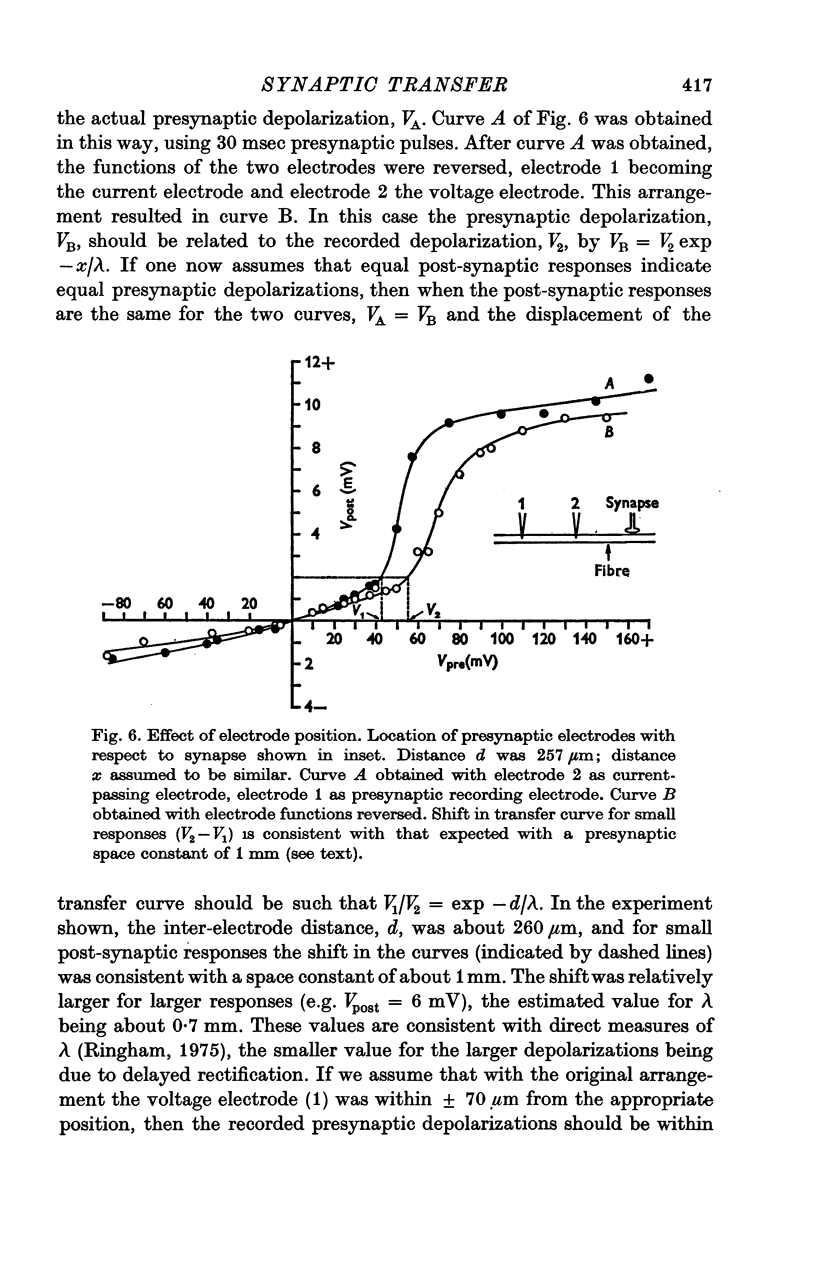
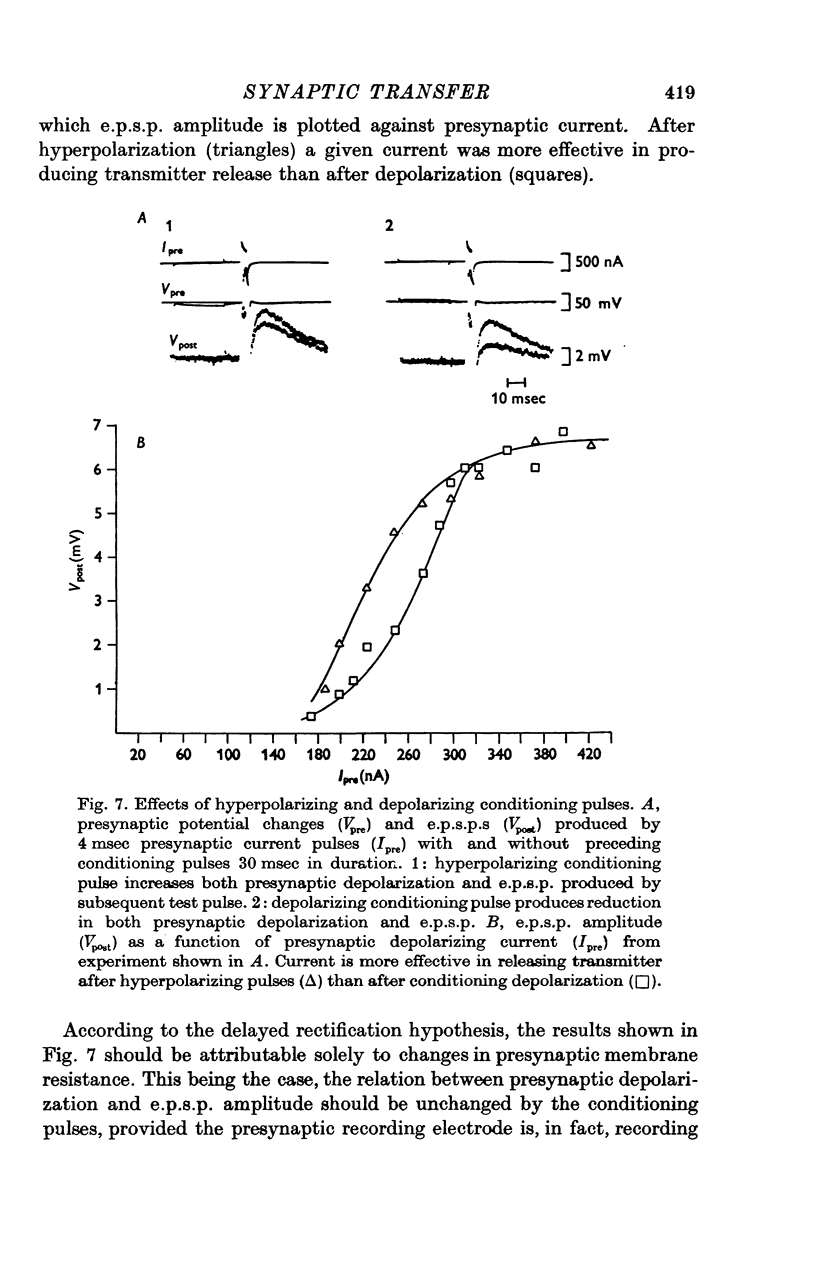
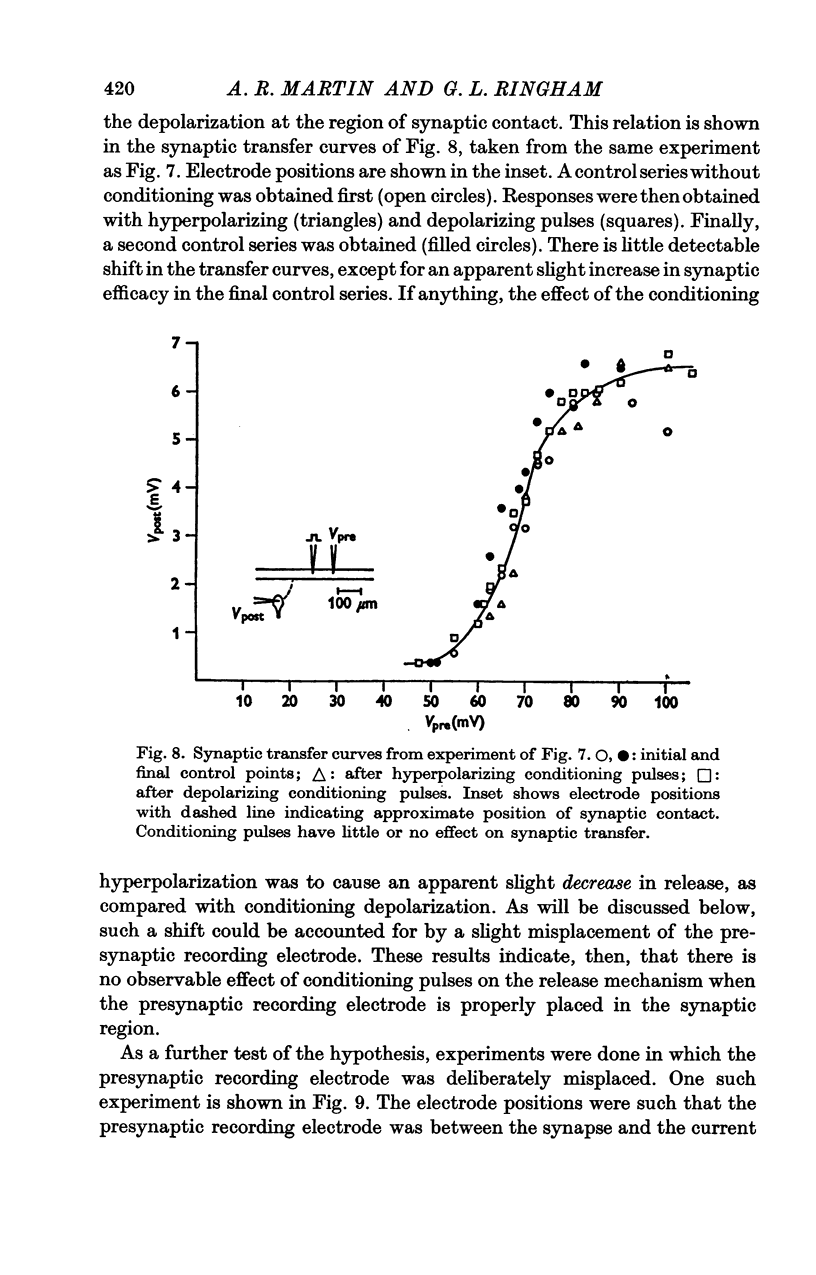
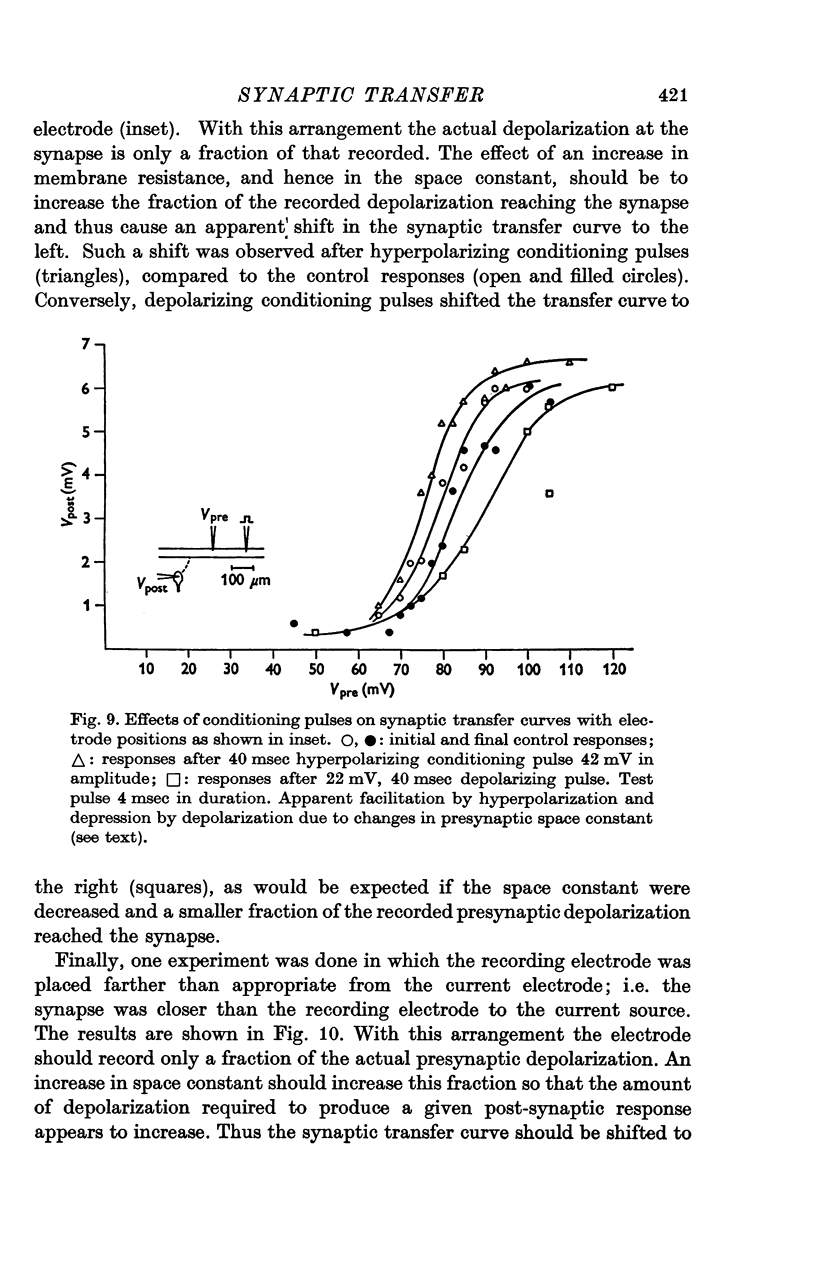
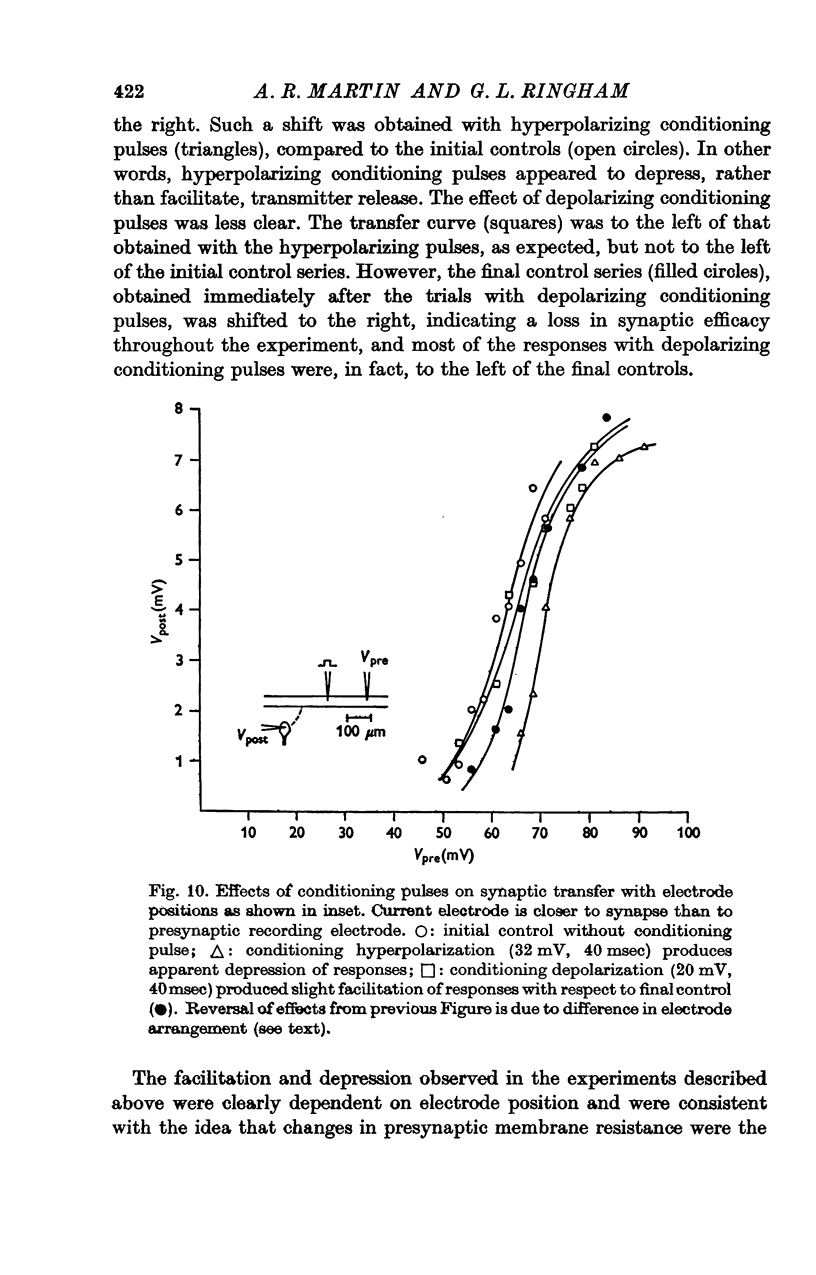
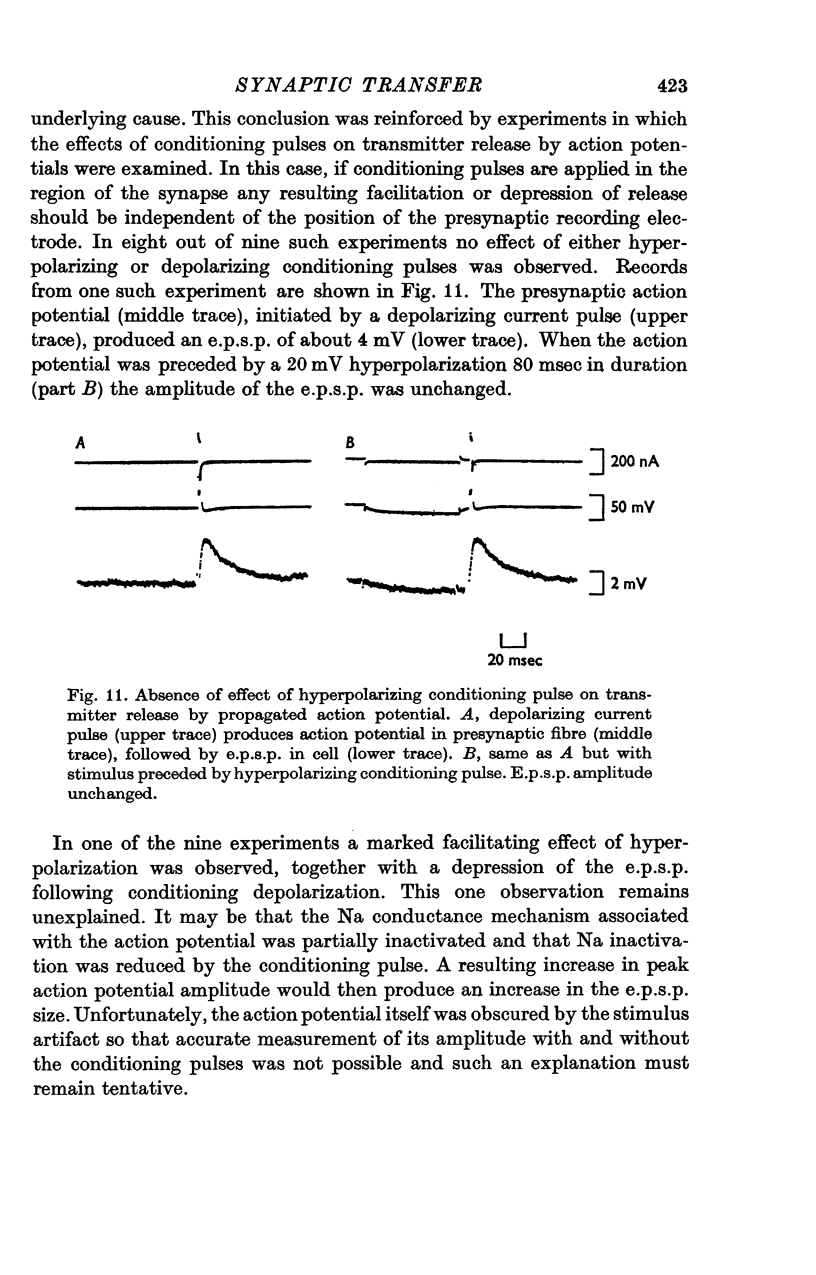
1. The relation between presynaptic depolarization and transmitter release was examined at a synapse between a Müller axon and a lateral interneurone in the spinal cord of the lamprey. Two micro-electrodes, one for passing current and the other for recording the resulting voltage change, were placed in the presynaptic axon; a single electrode for recording the post-synaptic potential produced by release of transmitter was placed in the post-synaptic cell. 2. When action potentials were blocked with tetrodotoxin, brief depolarizing pulses in the presynaptic fibre were as effective as the action potential had been in producing transmitter release. 3. The release process had an apparent threshold depolarization of 40-50 mV and saturated at presynaptic depolarizations of the order of 100 mV. Increasing the duration of the presynaptic pulse increased the maximum level of release. 4. Displacing the presynaptic voltage recording electrode from the position of synaptic contact toward the current passing electrode increased the apparent depolarization required to produce a given level of transmitter release. This shift in the input-output relation was consistent in magnitude with the voltage attenuation between the presynaptic recording electrode and the synapse expected from the space constant of the fibre. 5. The effect of conditioning hyperpolarization and depolarization of the presynaptic fibre on subsequent transmitter release by brief depolarizing pulses was examined. No effect was observed when the presynaptic recording electrode was in the region of synaptic contact. When the presynaptic electrode was not so positioned, conditioning effects were observed which depended on electode position and could be attributed to changes in the space constant of the presynaptic fibre. No conditioning effects were observed on transmitter release by the action potential.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach A. A., Bennett M. V. Chemically mediated transmission at a giant fiber synapse in the central nervous system of a vertebrate. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Feb;53(2):183–210. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloedel J. R., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmission across the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(2):52P–53P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloedel J., Gage P. W., Llinás R., Quastel D. M. Transmitter release at the squid giant synapse in the presence of tetrodotoxin. Nature. 1966 Oct 1;212(5057):49–50. doi: 10.1038/212049a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUKAWA T., SASAOKA T., HOSOYA Y. Effects of tetrodotoxin on the neuromuscular junction. Jpn J Physiol. 1959 Jun 25;9(2):143–152. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.9.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMA K. Some observations on the fine structure of the giant synapse in the stellate ganglion of the squid, Doryteuphis bleekeri. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1962;56:437–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00335624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Further study of the role of calcium in synaptic transmission. J Physiol. 1970 May;207(3):789–801. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin and neuromuscular transmission. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):8–22. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. Tetrodotoxin-resistant electric activity in presynaptic terminals. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):459–487. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of prolonged depolarization on synaptic transfer in the stellate ganglion of the squid. J Physiol. 1971 Jul;216(2):503–512. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The release of acetylcholine from nerve endings by graded electric pulses. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Jan 31;167(1006):23–38. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K. Further study of the relationship between pre- and postsynaptic potentials in the squid giant synapse. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Aug;52(2):326–345. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringham G. L. Localization and electrical characteristics of a giant synapse in the spinal cord of the lamprey. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):395–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



