Abstract
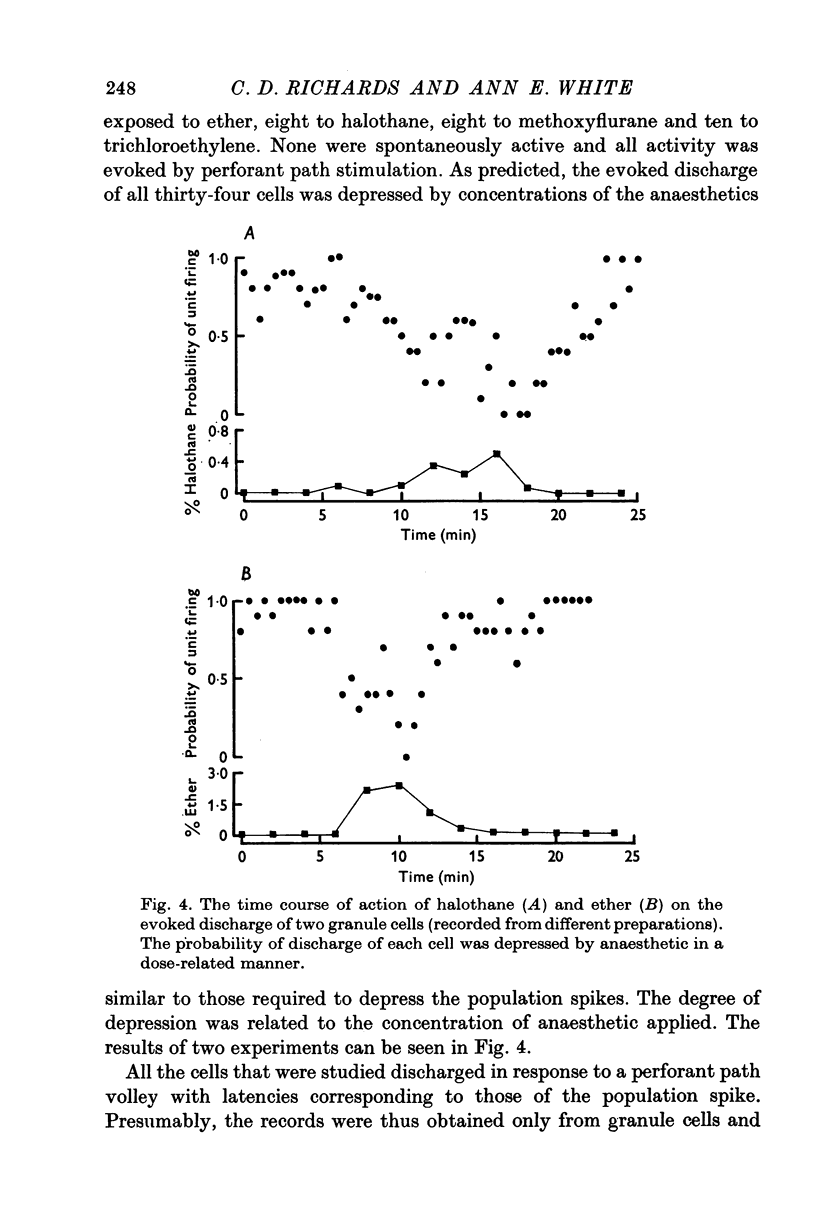
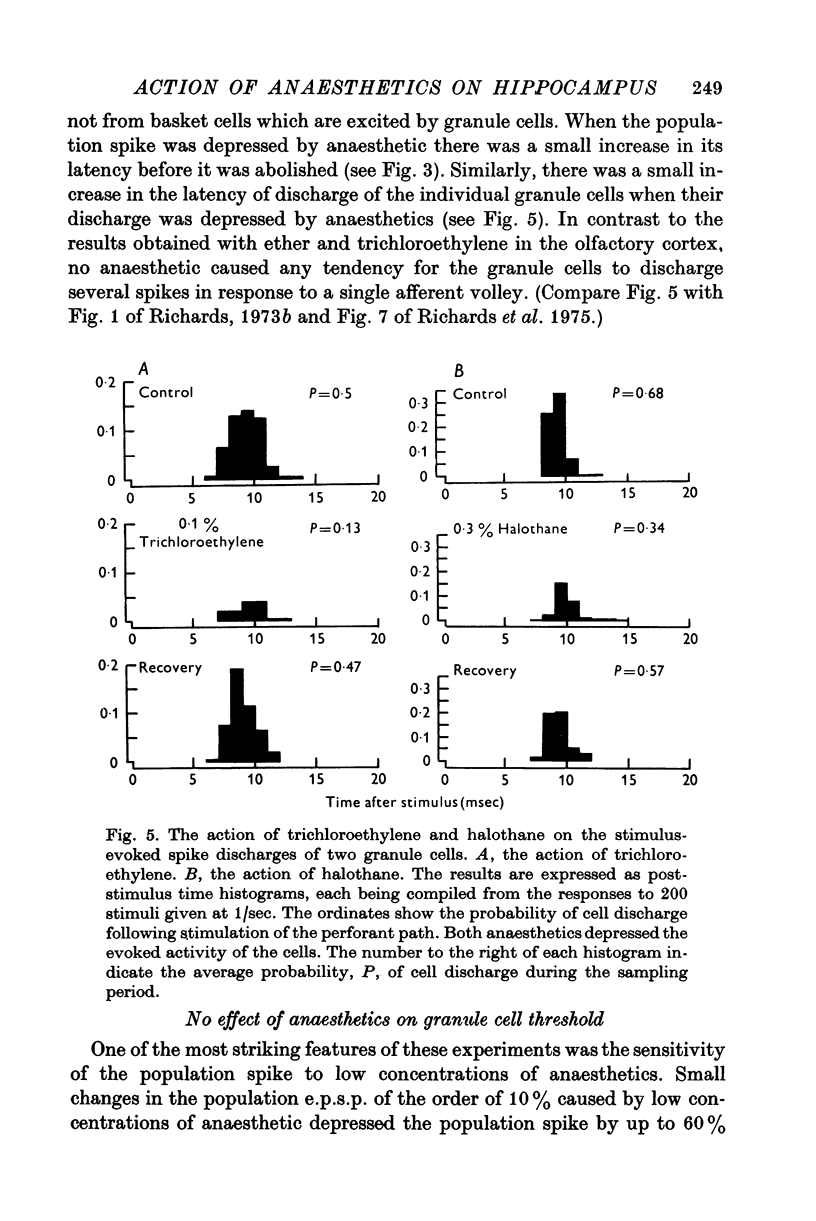
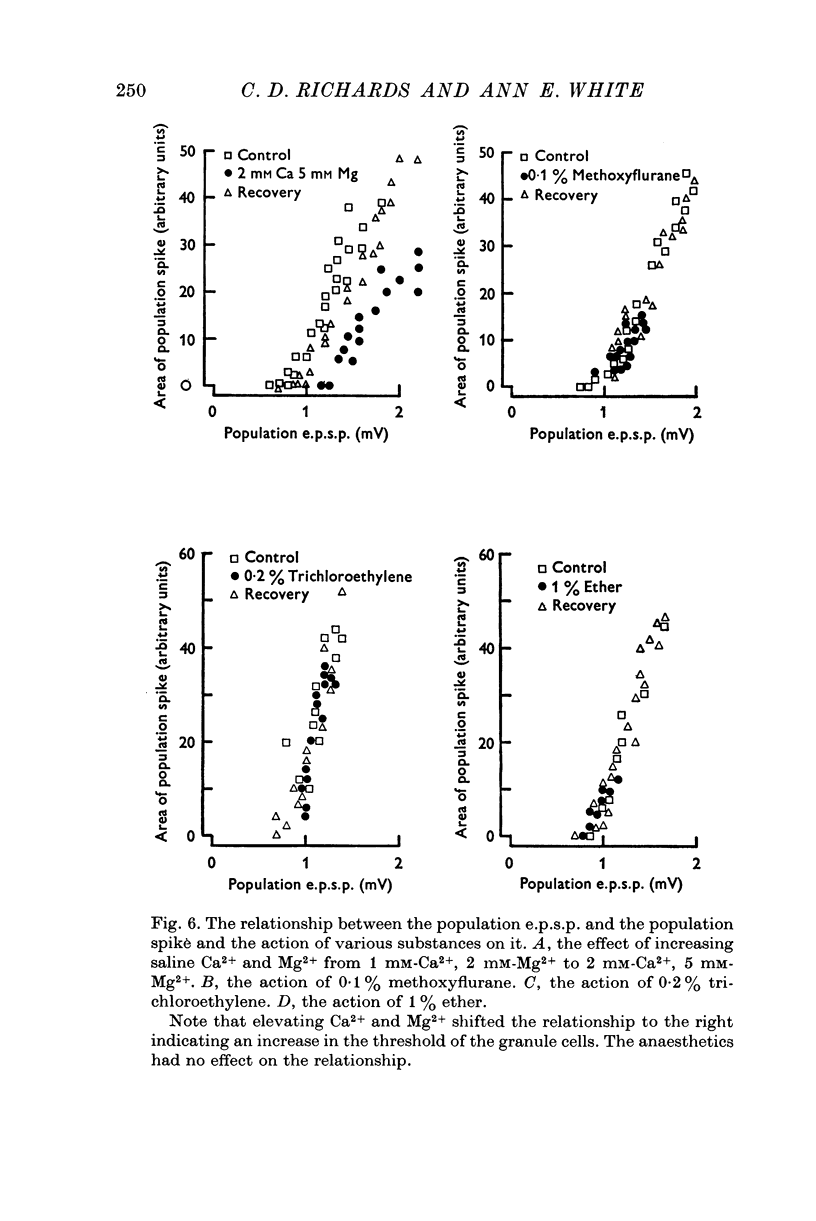
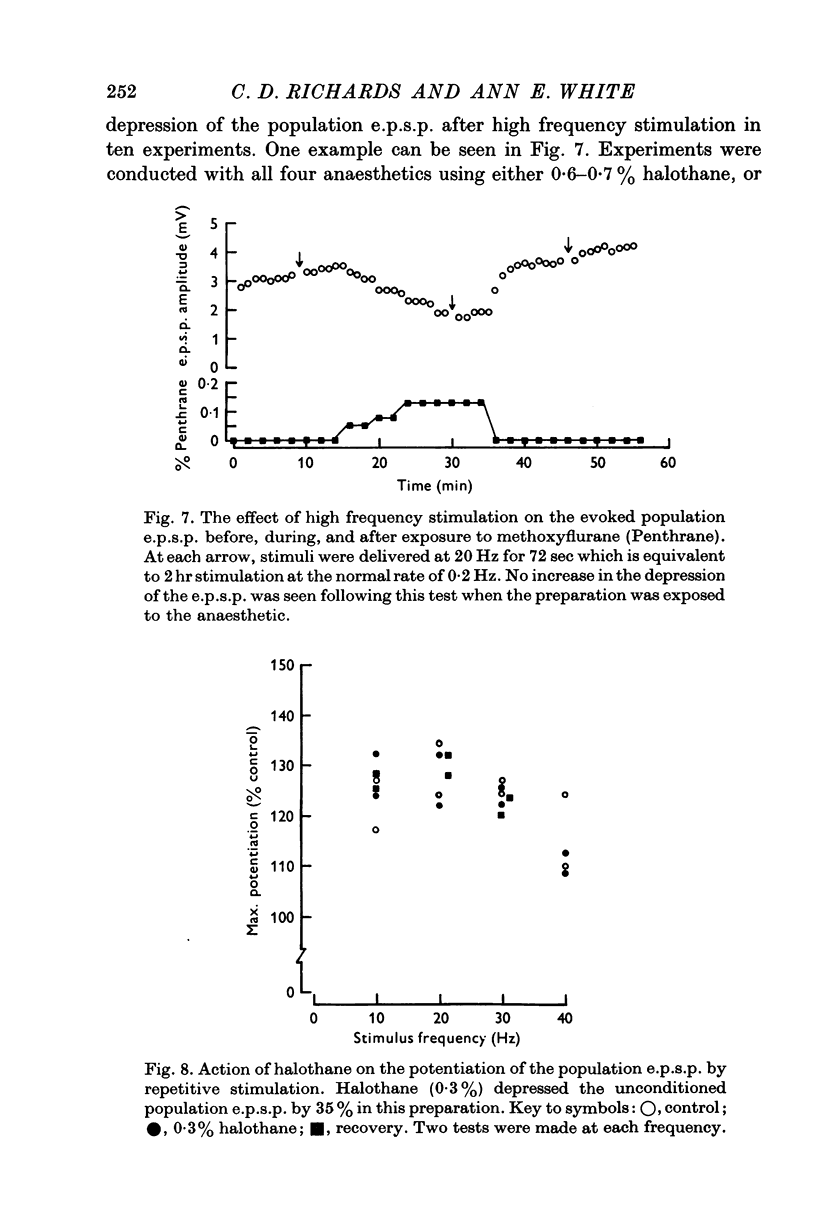
1. The action of four volatile anaesthetics on the evoked synaptic potentials of in vitro preparations of the hippocampus were examined. 2. All four anaesthetics (ether, halothane, methoxyflurane and trichloroethylene) depressed the synaptic transmission between the perforant path and the granule cells at concentrations lower than those required to maintain anaesthesia in intact animals. 3. The population excitatory post-synaptic potential (e.p.s.p.) and massed discharge of the cortical cells (population spike) were depressed at concentrations of the anaesthetics lower than those required to depress the compound action potential of the perforant path nerve fibres. None of the anaesthetics studied increased the threshold depolarization required for granule cell discharge. Furthermore, frequency potentiation of the evoked cortical e.p.s.p.s was not impaired by any of the anaesthetics studied. 4. It is concluded that all four anaesthetics depress synaptic transmission in the dentate gyrus either by reducing the amount of transmitter released from each nerve terminal in response to an afferent volley, or by decreasing the sensitivity of the post-synaptic membrane to released transmitted or by both effects together.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARTUSIO J. F., Jr Di-ethyl ether analgesia: a detailed description of the first stage of ether anesthesia in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Jul;111(3):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen P., Bliss T. V., Skrede K. K. Unit analysis of hippocampal polulation spikes. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13(2):208–221. doi: 10.1007/BF00234086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Gardner-Medwin A. R. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the unanaestetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):357–374. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliss T. V., Lomo T. Long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in the dentate area of the anaesthetized rabbit following stimulation of the perforant path. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(2):331–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON J. I., PARKHOUSE J. Blood trichloroethylene concentrations during anaesthesia under controlled conditions. Br J Anaesth. 1962 Mar;34:141–148. doi: 10.1093/bja/34.3.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELMQVIST D., QUASTEL D. M. PRESYNAPTIC ACTION OF HEMICHOLINIUM AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:463–482. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eger E. I., 2nd, Brandstater B., Saidman L. J., Regan M. J., Severinghaus J. W., Munson E. S. Equipotent alveolar concentrations of methoxyflurane, halothane, diethyl ether, fluroxene, cyclopropane, xenon and nitrous oxide in the dog. Anesthesiology. 1965 Nov-Dec;26(6):771–777. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196511000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARRABEE M. G., POSTERNAK J. M. Selective action of anesthetics on synapses and axons in mammalian sympathetic ganglia. J Neurophysiol. 1952 Mar;15(2):91–114. doi: 10.1152/jn.1952.15.2.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOYNING Y., OSHIMA T., YOKOTA T. SITE OF ACTION OF THIAMYLAL SODIUM ON THE MONOSYNAPTIC SPINAL REFLEX PATHWAY IN CATS. J Neurophysiol. 1964 May;27:408–428. doi: 10.1152/jn.1964.27.3.408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R. A further study of the statistical composition on the end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1955 Oct 28;130(1):114–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNER B., PENFIELD W. The effect of hippocampal lesions on recent memory. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1955;(80TH):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nafstad P. H. An electron microscope study on the termination of the perforant path fibres in the hippocampus and the fascia dentata. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;76(4):532–542. doi: 10.1007/BF00339754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A. The effects of anaesthetics on synaptic excitation and inhibition in the olfactory bulb. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):803–814. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olds J. Learning and the hippocampus. Rev Can Biol. 1972;31(Suppl):215–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penfield W., Mathieson G. Memory. Autopsy findings and comments on the role of hippocampus in experiential recall. Arch Neurol. 1974 Sep;31(3):145–154. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490390027001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBSON J. G., BURNS B. D., WELT P. J. The effect of inhaling dilute nitrous oxide upon recent memory and time estimation. Can Anaesth Soc J. 1960 Oct;7:399–410. doi: 10.1007/BF03021298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D. Does trichloroethylene have a different mode of action from other general anaesthetics? J Physiol. 1973 Aug;233(1):25P–27P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D. On the mechanism of barbiturate anaesthesia. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):749–767. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D. On the mechanism of halothane anaesthesia. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):439–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Russell W. J., Smaje J. C. The action of ether and methoxyflurane on synaptic transmission in isolated preparations of the mammalian cortex. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):121–142. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., Sercombe R. Calcium, magnesium and the electrical activity of guinea-pig olfactory coex in vitro. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):571–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards C. D., White A. E. Proceedings: Halothane and the depression of synaptic transmission through the perforant path synapses of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation. J Physiol. 1974 Sep;241(2):96P–98P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMJEN G. G. Effects of ether and thiopental on spinal presynaptic terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Jun;140:396–402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMJEN G. G., GILL M. The mechanism of the blockade of synaptic transmission in the mammalian spinal cord by diethyl ether and by thiopental. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Apr;140:19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somjen G. Effects of anesthetics on spinal cord of mammals. Anesthesiology. 1967 Jan-Feb;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196701000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiman A., Seeman P. The impulse-blocking concentrations of anesthetics, alcohols, anticonvulsants, barbiturates, and narcotics on phrenic and sciatic nerves. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;52(3):535–550. doi: 10.1139/y74-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall P. D. The mechanisms of general anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1967 Jan-Feb;28(1):46–53. doi: 10.1097/00000542-196701000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weakly J. N. Effect of barbiturates on 'quantal' synaptic transmission in spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):63–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto C., Kawai N. Generation of the seizure discharge in thin sections from the guinea pig brain in chloride-free medium in vitro. Jpn J Physiol. 1968 Oct 15;18(5):620–631. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.18.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


