Abstract
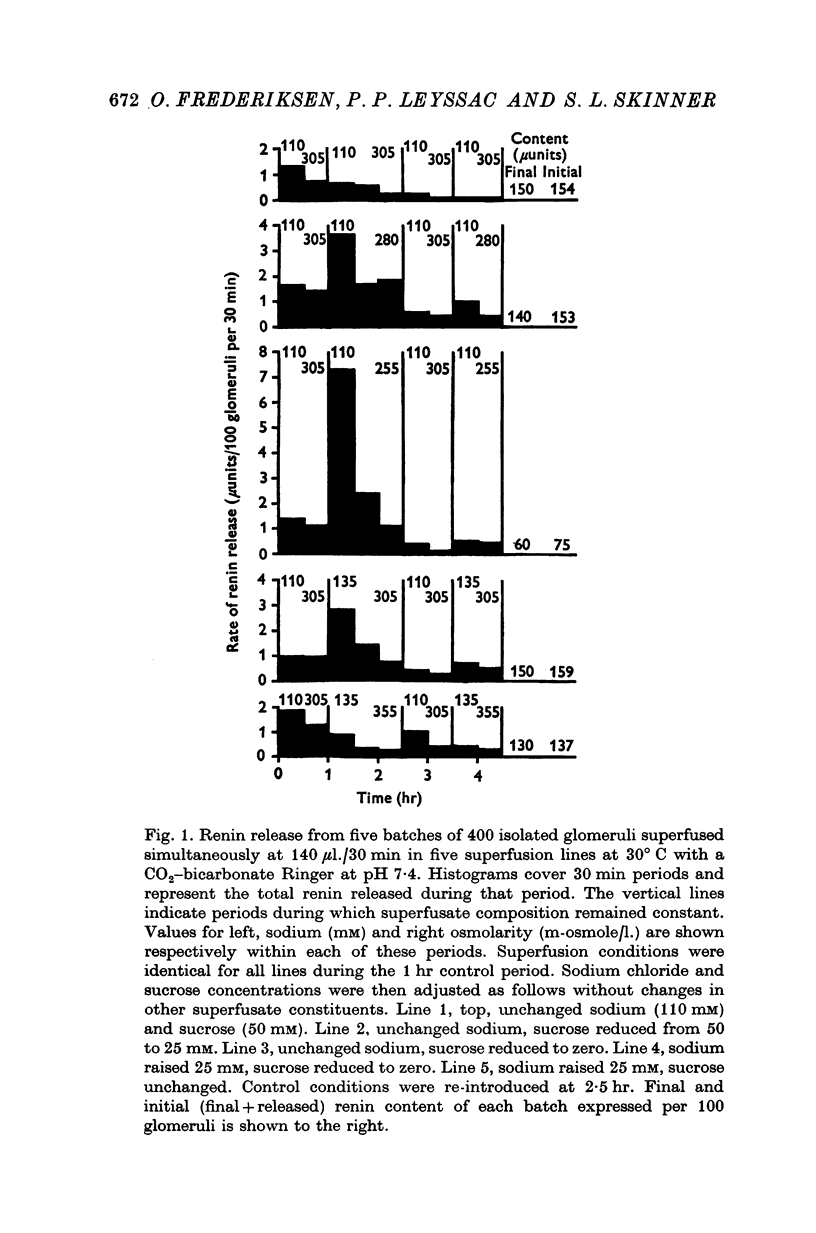
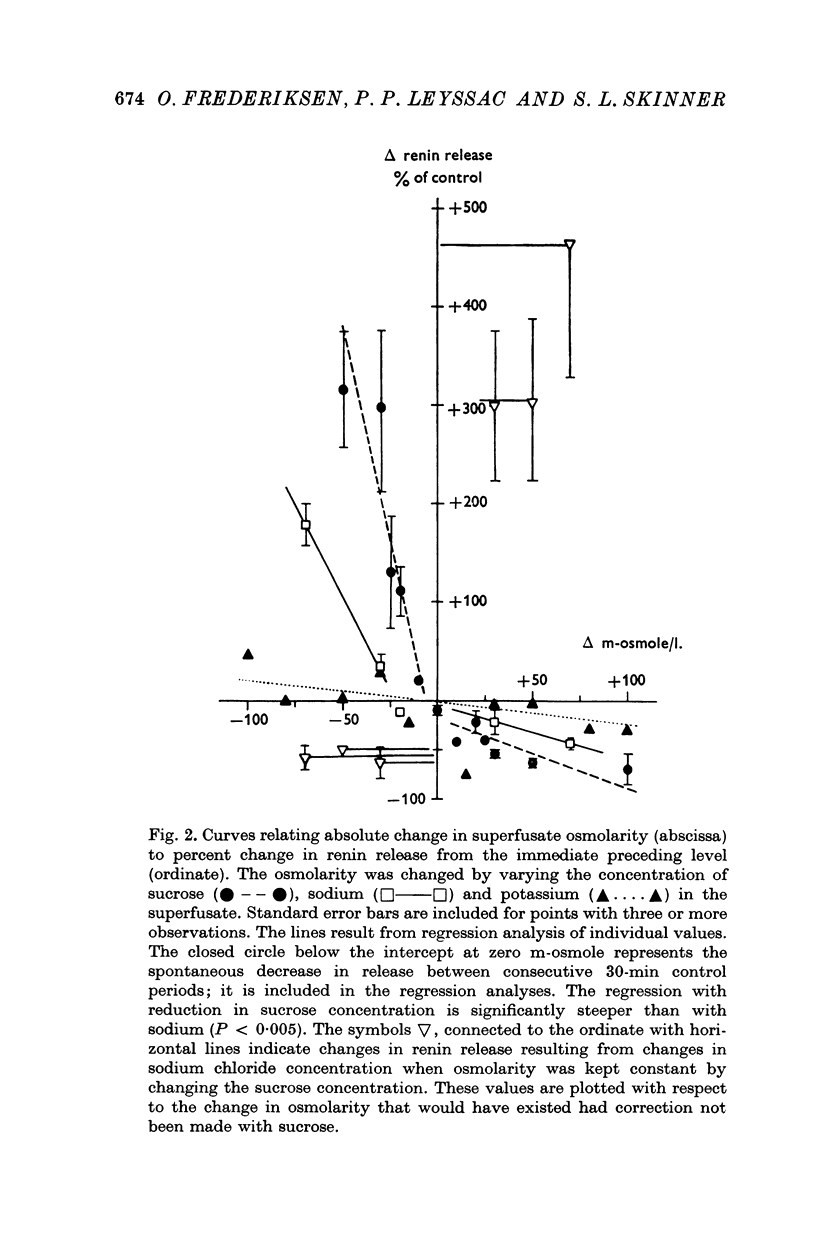
The rate of renin release from viable juxtaglomerular cells was studied during prolonged superfusion of isolated rat renal glomeruli with Ringer solutions of differing osmolarities. 2. Reduction in osmolarity from 305 to 285 m-osmole/l. by lowering sucrose concentration caused renin release rate to double. A rise in osmolarity of 30 m-osmole/l. by raising sucrose concentration halved release rate. 3. The response to osmolarity was graded. During the first 30 min following a 20 m-osmole/l. decrease in osmolarity, 1-57 +/- 0-22% (S.E. of mean) of cellular renin content was released; three times this amount was released with a decrease of 50 m-osmole/l. The effect persisted at lower release rates for 60-90 min. 4. The juxtaglomerular cells were four to five times more sensitive to changes in osmolarity through sucrose than sodium chloride concentration. Changes in potassium chloride concentration (7-57 mM) had little effect. 5. Sodium chloride had no direct ionic effect on renin release outside its osmotic properties. 6. The findings support a previous proposal that the rate of renin release in vitro relates directly to the volume of the juxtaglomerular cell. The hypothesis is developed that a similar mechanism may underlie renin secretion in vivo.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoi W., Wade M. B., Rosner D. R., Weinberger M. H. Renin release by rat kidney slices in vitro: effects of cations and catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1974 Sep;227(3):630–634. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.227.3.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair-West J. R., Brook A. H., Simpson P. A. Renin responses to water restriction and rehydration. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blendstrup K., Leyssac P. P., Poulsen K., Skinner S. L. Characteristics of renin release from isolated superfused glomeruli in vitro. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):653–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK W. F., PICKERING G. W. The location of renin in the rabbit kidney. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:526–536. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellasega M., Grantham J. J. Regulation of renal tubule cell volume in hypotonic media. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jun;224(6):1288–1294. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.6.1288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Pawsey C. G. The relative effects of serum sodium concentration and the state of body fluid balance on renin secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1971 Jan;32(1):117–119. doi: 10.1210/jcem-32-1-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash F. D., Rostorfer H. H., Bailie M. D., Wathen R. L., Schneider E. G. Renin release: relation to renal sodium load and dissociation from hemodynamic changes. Circ Res. 1968 Apr;22(4):473–487. doi: 10.1161/01.res.22.4.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome H. H., Bartter F. C. Plasma renin activity in relation to serum sodium concentration and body fluid balance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Dec;28(12):1704–1711. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-12-1704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKINNER S. L., MCCUBBIN J. W., PAGE I. H. CONTROL OF RENIN SECRETION. Circ Res. 1964 Jul;15:64–76. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokabe H., Nishimura H., Kawabe K., Tenmoku S., Arai T. Plasma renin activity in varying hydrated states in the bullfrog. Am J Physiol. 1972 Jan;222(1):142–146. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDER A. J., MILLER R. CONTROL OF RENIN SECRETION IN THE ANESTHETIZED DOG. Am J Physiol. 1964 Sep;207:537–546. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander A. J. Control of renin release. Physiol Rev. 1967 Jul;47(3):359–382. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


